Introduction to PCS Exam
The Punjab Public Service Commission (PPSC) has been established under Article 315 of the Constitution of India, with the basic purpose of recruiting officials in various departments of the Government as per the requisitions sent by the Government in this regard from time to time.
The Punjab State Civil Services Combined Competitive Examination (PSCSCCE) is being conducted by the PPSC for recruitment of officers in the Punjab Civil Service (Executive Branch), Deputy Superintendent of Police, Tehsildar, Food Supply and Consumer Affairs Officer, Block Development & Panchayat Officers, Labour-Cum-Conciliation Officer, Employment Generation and Training Officer and Deputy Superintendent of Jails (Grade-II)/ District Probation Officer (Jails). On successful culmination of Punjab State Civil Services Combined Competitive Examination (PSCSCCE), the merit wise names of qualified candidates will be sent by the commission, to the Government for making appointment to these services. All these services are governed by the Service Rules of the respective service and the Government after counseling and allocation of the candidates to the respective departments may consider the names sent by the PPSC for appointment against these posts as per respective Service Rules.
Educational Qualifications For PCS Exam
- The candidate should possess a bachelor degree in any discipline from a recognised university or institution for PCS Exam; Provided that the candidate may be permitted to take preliminary examination while studying for the qualifying degree. However, the candidate shall be required to produce proof of qualifying the degree course for being eligible to take the Main Competitive Examination (As per Punjab State Civil Services (Appointment by Combined Competitive Examination) Rules, 2009)
- No candidate shall be eligible for appearing in the Preliminary Competitive Examination, unless he/she has passed the Matriculation Examination with Punjabi as one of the compulsory or elective subjects or any other equivalent examination in Punjabi language, which may be specified by the Government from time to time on or before the last date of submission of Application Forms.
- For the purpose of eligibility forPunjab State Civil Services Combined Competitive Examination (PSCSCCE) , the expression "recognised university" or "institution" shall have the same meaning, as assigned to it in the Punjab Civil Services (General and Common Conditions of Service) Rules, 1994.
Age Limit For PCS Exam
- For PCS Exam, As mandated by Punjab State Civil Services (Appointment by Combined Competitive Examination) Rules, 2009 read with Punjab Civil Services (Executive Branch) Rules 1976, and Govt. instructions issued from time to time, the candidate should have attained the minimum age of 21 years and should not have attained the age of 37 years on the first day of January of the year in which the last day falls for submission of application to the Commission. In other words, the candidate should have attained the age of 21 years but should not be older than 37 years on 1st January 2018. Provided that in the case of the post of Deputy Superintendent Police and Deputy Superintendent Jails)/ District Probation Officer (Grade-II) in Punjab Prisons State Service, a candidate should have attained the minimum age of 21 years and should not have attained the age of maximum 28 years on the first day of the year, as referred to above.
- The upper age limit for PCS Exam a Punjab Government or any Board, Corporation, Commission or Authority under it, Other State Government or the Government of India, employees may be relaxed up to 45 years. However no age relaxation is permissible for Punjab Police Services.
- The Upper age limit for PCS Exam may be relaxed up to 33 years for Scheduled Castes and Backward Classes of Punjab only in case of Punjab Police Service and Punjab Prisons Services .
- The Upper age limit for PCS Exam may be relaxed up to 42 years for Scheduled Castes and Backward Classes of Punjab only in case of other services except Punjab Police Service and Punjab Prisons Services.
- For PCS Exam, Ex-servicemen of Punjab Domicile shall be allowed to deduct the period of his service in the Armed Forces of Union from his actual age and if the resultant age does not exceed the maximum age limit prescribed for direct appointment to such a vacancy in the Service Rules concerned by more than three years, he shall be deemed to satisfy the condition regarding age limit.
- Upper age limit for PCS Exam may be relaxed up to 42 years for Widows, Divorced women and certain other Categories of women. However no age relaxation is permissible for women in case of Punjab Police Services and Punjab Prisons Services.
- Upper age limit for PCS Exam may be relaxed up to 47 years for Physically Handicapped of Punjab only. However no age relaxation is permissible in case of Punjab Police Services and Punjab Prisons Services .
Scheme of PSCSCCE-2018
- The selection process for filling posts in various departments based on the Punjab State Civil Services Combined Competitive Examination (PSCSCCE) will commence with inviting applications from the candidates, who fulfill the qualifying criteria. The candidates who apply in response to the advertisement for these posts will be registered by filling Online Application Form, a link of which is available on the website of the Commission http://ppsc.gov.in
- No candidate who applies for this PCS Exam through any other means but through Online Application Form shall be eligible to take this Examination. Candidates who register and fill in Online Application Form, would be issued Admit Cards prior to the conduct of Preliminary Competitive Examination as described in the instructions for filling up Online Application Form.
- For PCS Exam, there is no scrutiny carried out of the applications with reference to eligibility/authenticity etc. So issue of Admit Cards does not confer any right to the candidate about his eligibility. The candidature of the candidate shall be considered provisional till the time of verification of documents of the candidate before the interview or at the time of interview, when the candidate shall produce his/her original certificates for verification by the Commission.
- For PCS Exam, If any document/certificate/statement of the candidate is found false or forged or make him/her ineligible before the interview or at the time of the interview or any time thereafter, his/her candidature may be rejected and further action will be taken as per law.
- Essential steps involved in the selection process of PCS Examare:
i) Preliminary Competitive Examination; and
ii) Main Competitive Examination (written and Interview).
Procedure and scheme for the Preliminary Examination:
The preliminary competitive examination will consist of two papers of 200 marks each and shall comprise of objective type (multiple choice) questions. The detail is as follows:-
| |
Subject |
No of
Questions |
Marks for each
Question |
Total
Marks |
| Paper –I |
General Studies |
100 |
2 |
200 |
| Paper – II |
Civil Services Aptitude Test
(CSAT) |
80 |
2.5 |
200 |
Note:
- Both the papers of preliminary competitive examination will be of objective type multiple choice questions.
- Duration of each paper for preliminary examination will be two hours. However, visually impaired candidates will be given additional 20 minutes.
- There will be no negative marking in the written preliminary examination test, however there may be negative marking for any objections to the Answer Key found false/frivolous/not supported by authentic evidence..
- The question paper of preliminary competitive examination shall be bilingual and shall be printed in English (Roman script) and Punjabi (Gurumukhi script) except for questions where candidates’ proficiency in language is to be tested.
- The standard of questions of preliminary competitive examination would be to test the knowledge as is expected of a person who has attained education at least up to graduation level.
- Preliminary Examination is only a screening test for selecting candidates who would be eligible to take the Main Examination and the marks obtained in this Examination shall not be counted towards the merit of the candidates arrived at after the Main Examination.
- Candidates equal to 13 times of the vacancies advertised in each category would qualify from amongst those appearing in the Preliminary Examination for the Main Examination, provided that, such number of candidates are available and, are otherwise eligible for admission to the Main Examination.
Procedure and scheme for the Main Examination:
| |
Paper |
Maximum Marks |
| 1 |
Punjabi (in Gurumukhi Script) Compulsory (of 10+2
Standard) |
100 |
| 2 |
English Compulsory (of 10+2 standard) |
100 |
| 3 |
Essay (Three Essays of 50 marks each) |
150 |
| 4 |
General Studies Paper-I (History, Geography and
Society) |
250 |
| 5 |
General Studies Paper-II (Indian Constitution &
Polity, Governance and International Relations) |
250 |
| 6 |
General Studies Paper-III (Economy, Statistics and
Security issues) |
250 |
| 7 |
General Studies Paper-IV (Science & Technology,
Environment, Problem Solving and Decision
Making) |
250 |
| |
Interview |
150 |
| |
Grand Total |
1500 |
Note:-
- All papers shall be descriptive in nature and duration of each paper in main competitive examination will be three hours. Visually impaired candidates will, however, be allowed an extra time of 30 minutes in each paper.
- The main competitive examination shall include seven compulsory papers.
- Candidates will have the option to attempt all the papers in main competitive examination , except the language papers in Punjabi or English medium.
- Candidates exercising the option to answer Papers in Punjabi language in main competitive examination may, if they so desire, give English version within brackets of only the description of the technical terms, if any, in addition to the version in Punjabi language.
- The question papers other than language papers in main competitive examination will be set in English. However, when any candidate opts for attempting any paper(s) in Punjabi medium, the question papers shall be printed in Punjabi accordingly.
- Details of syllabi of main competitive examination is mentioned at the last section of this page.
- Interview of PCS Exam shall be conducted for only those candidates who qualify on the basis of their performance in the main competitive examination and who fulfil the criteria of eligibility.
- In PCS Exam, no candidate shall be eligible to appear in the interview unless he/she obtains 45% marks in the aggregate of all the papers (read 40 % for the candidates belonging to Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes) including at least 25% marks in each paper provided that if in main competitive examination, a sufficient number of candidates do not obtain 45% marks in the aggregate (read 40 % for the candidates belonging to Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes), the Commission may at their discretion lower this percentage to not below 40% (read 35 % for the candidates belonging to Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes), however, the minimum percentage for each paper shall remain unchanged.
- In PCS Exam, no candidate shall be considered to have qualified the competitive examination unless he obtains at least 45% marks in the aggregate in the main examination including interview marks (read 40 % for the candidates belonging to Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes), except in the case of main competitive examination for which this percentage has been lowered to not less than 40% (read 35 % for the candidates belonging to Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes) by the Commission in which case the qualifying percentage shall be as determined by the Commission
- From amongst the candidates who have appeared for the Main written examination, candidates not more than three times the number of vacancies advertised in each category shall be called for the interview, provided that, such number of candidates are available and, are otherwise eligible for the Interview.
- Names of qualified candidates for Main written examination shall be arranged in order of merit according to the aggregate marks obtained in the main written examination and the interview.
- Note: In the event that the aggregate marks obtained in the Written and Interview parts of the Main Examination taken together of two or more candidates are equal, the candidate securing higher marks in the written part of the Main Examination shall be ranked higher. Should the marks in the written part of the Main Examination of such candidates are also equal, the candidate securing higher marks in the aggregate of the General Studies papers in the written part of the Main Examination shall rank higher. Should those also be equal, the candidate older in age shall rank higher. (AGGREGATE OF GENERAL STUDIES PAPER MEANS AGGREGATE OF GENERAL STUDY PAPER-I, PAPER-II, PAPER-III AND PAPER-IV)
How to apply for PSCSCCE-2018
The candidate after making himself/herself well acquainted with the General Information and Guidelines for filling Online Application Form may apply for PSCSCCE-2018 using Online Application Form link.
Application fee
| Name of Category |
Online Application
charges |
Examination Fee |
Total |
Scheduled Castes/ Scheduled Tribes of all
States and Backward Classes of Punjab |
Rs. 500/- |
Rs. 625/- |
1125/- |
| Ex-Servicemen of Punjab |
Rs. 500/- |
No Fee to be paid |
500/- |
All Others Categories (including Lineal
Descendent of Ex-servicemen, Punjab) |
Rs. 500/- |
Rs. 2500/- |
3000/- |
| Physically Handicapped, Punjab |
Rs. 500/- |
Rs. 1250/- |
1750/- |
Nationality For PCS Exam
A candidate shall be a:
- Citizen of India; or
- Citizen of Nepal; or
- Subject of Bhutan; or
- Tibetan refugee who came over to India before the Ist January. 1962, with the intention of permanently settling in India; or
- A person of Indian origin who has migrated from Pakistan, Burma, Sri Lanka and East African countries of Kenya, Uganda and United Republic of Tanzania (formerly Tanganyika and Zanzibar) Zambia, Malawi, Zaire, Ethiopia and Vietnam with the intention of permanently settling in India;
- Provided that a candidate other than the candidates possessing Indian nationality shall be a person in whose favour a certificate of eligibility has been issued by the Competent Authority as notified Punjab Civil Services (General and Common Conditions of Service) Rules, 1994.
Special Instructions for the post of Deputy Superintendent of Police and Deputy Superintendent of Jails (Grade-II)/ District Probation Officer (Jails) in PCS Exam
The candidates who opt for the Punjab Police Service and who qualify the Main Competitive Examination shall have to qualify the physical test as per rule 7 (1) of the Punjab Police Service Rules-1959 read with Notification No. 1/146/94-1H3 (Part-II)/ 1743 dated 09/7/2009, Each candidate is required to fulfil the following physical standards:
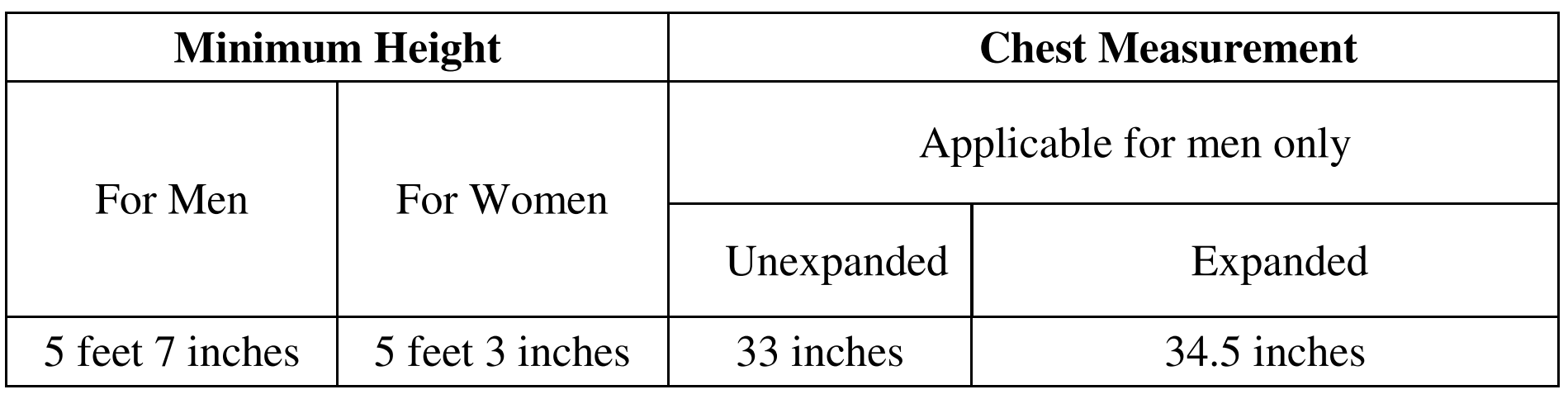
Besides the above requirement, the candidates have to qualify the Physical Test for the post of Deputy Superintendent Police and Deputy Superintendent of Jails (Grade-II)/ District Probation Officer (Jails), the candidates have to mandatorily qualify the physical test mentioned at Serial no. 1 in the table below. In addition the candidates have to qualify any two physical test events of the three physical test events mentioned at serial no. 2, 3 and 4:-
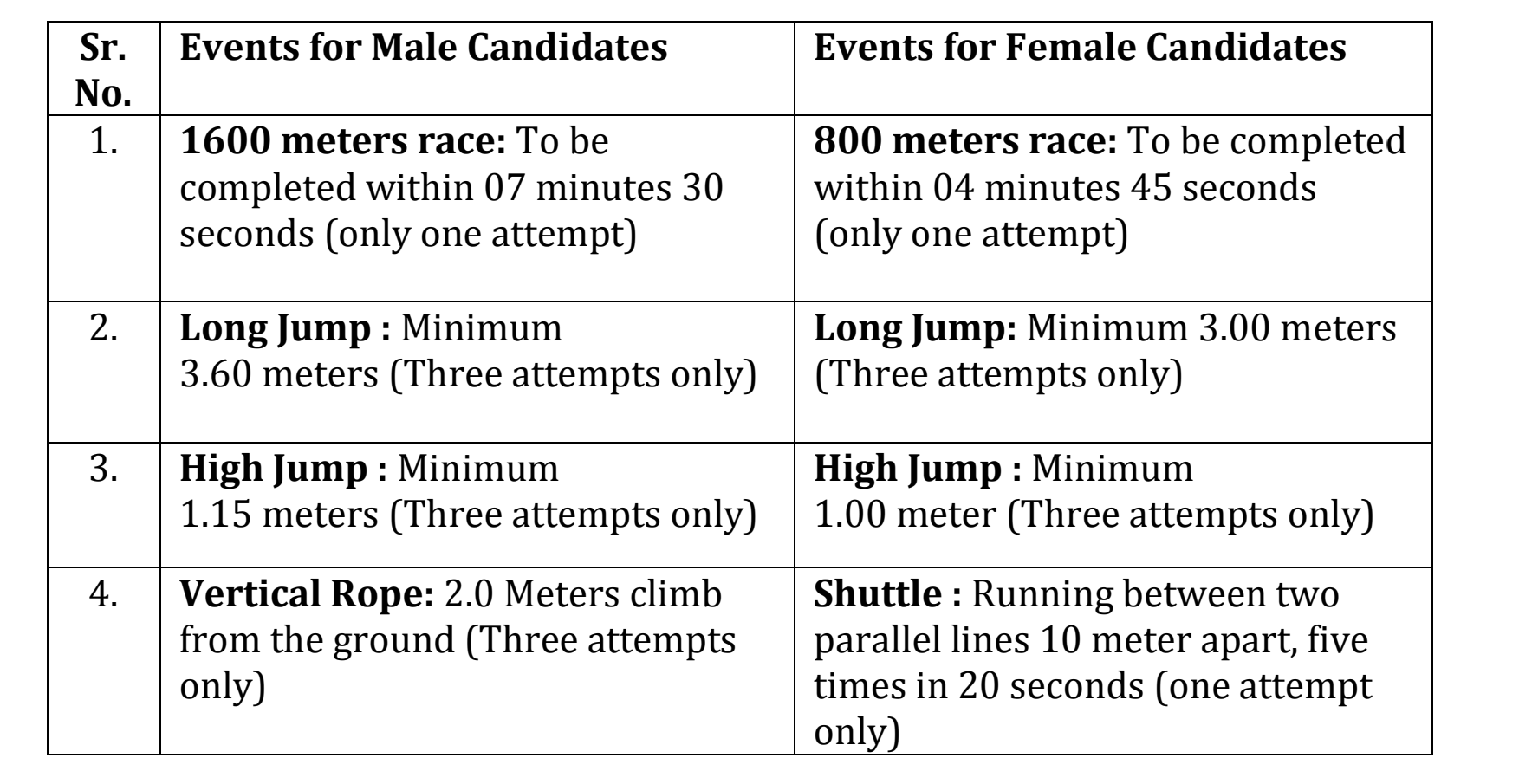
Number of Attempts for this and similar Examinations
- Unless covered by any of the exceptions, which may from time to time be notified by the Government in this behalf, every candidate appearing for the examination after the commencement of Punjab State Civil Services (Appointment by Combined Competitive Examination) Rules, 2009, shall be permitted to avail upto four attempts at the examination.
- For the purpose of this rule, an appearance of a candidate in the Preliminary Examination, shall be deemed to be an attempt at the examination.
- Ex-servicemen category candidates are also permitted four attempts at the Examination.
Conditions which may render a candidate ineligibleFor PCS Exam
The following conditions, among others, shall render the candidates ineligible for the Preliminary Competitive Examination:
- Insufficient examination fee;
- Examination fee deposited by means other than Bank Challan in any branch of the State Bank of India.
- Wrong/incomplete information given in the application form;
- Candidates debarred by the PPSC/other Public Service Commissions;
- Non-fulfillment of any of the eligibility conditions, including those of age and educational qualifications.
SYLLABUS OF PUNJAB STATE CIVIL SERVICES COMBINED COMPETITIVE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION
Paper –I (General Studies)
1. Everyday Science:
- States of matter, structure of atom, versatile nature of carbon. Acids, bases, salts, corrosion in metals, action of soaps.
- Life on Earth – evolution, marine & terrestrial life. Human body and life processes, nutrition, disease - its causes & prevention, infectious diseases, lifestyle diseases.
- Public health initiatives, mother and child health, immunisation & vaccination, HIVAIDS, TB, polio etc.
- Force-laws of motion & gravitation, Archimedes principle. Energy – kinetic & potential.
- Light – reflection & refraction – concepts and applications. Sound – propagation & reflection- concepts and applications. Electric current – concepts and applications.
- Computers and telecommunication – concepts and applications.
2. Environmental studies:
- Composition and structure of the atmosphere. Solar system – heat balance & temperature.
- Atmospheric circulation & weather system, water cycle.
- Climate change – fossil fuels, greenhouse gases, renewable energy, clean development mechanism, carbon credits.
- Water – oceans, rivers, glaciers, lakes, groundwater etc. Biodiversity & conservation.
- Soil – types, crops, food chain etc. Pollution and toxicity etc.
3. Political theory & international order:
- Basic concept of freedom, equality, social justice, rights & duties, citizenship, nationalism, secularism etc.
- United Nations and its organs/agencies, other international organisations like the World Bank, IMF, WTO, EU, G20, BRICS etc. and their role in the World peace, trade & development.
4. Indian polity:
- Basic features, provisions, schedules of the Indian Constitution, key amendments.
- Panchayati Raj. Elections – People’s Representation Act, electoral reforms. Rise of regionalism and coalition politics.
- Armed challenges to the Indian state since independence.
5. History of India:
- The Indus valley civilisation.
- The Aryan and the Vedic age. Jainism and Buddhism.
- The Maurya Gupta periods.
- Advent of Islam and Sultanate period (political, social & cultural). The Bhakti Movement.
- The Mughals (political, social & cultural till Aurangzeb).
- The coming of the European Powers and the advent of the British rule.
- The Mutiny of 1857.
- The British rule and the Indian National Movement (1857-1947)
- World History:
- The Renaissance and the Industrial Revolution in Europe. The American Revolution 1776.
- The French Revolution 1789.
- The Russian Revolution 1917.
- World Wars I & II.
6. Indian Economy:
- Indian economic development (1950-1991) – key economic policies, public sector dominance, bank nationalisation etc.
- Five year plans – key goals and main achievements.
- Liberalisation, privatisation and globalisation era since 1991 – key policies, decisions and results.
- Performance of Indian economy since 1991 – Growth, fiscal & revenue deficits, trade, commerce & balance of payments, inflation, growth of service sector.
- Key challenges and responses – agriculture and food security, industrialisation, poverty alleviation & employment, rural & urban infrastructure, social sector – health, education etc.
7. Geography:
- Population – distribution, density, growth and comparison. Migration – types, causes and consequences.
- Human development. Human settlements. Land resources and agriculture.
- Water resources.
- Mineral and energy resources. Manufacturing industries.
- Planning and sustainable development in India. Transport and communication.
- International trade.
- Geographical perspective on selected issues and problems.
8. Current events of national and international importance.
9. Punjab
a) Geography:
Geographical and agro-climatic regions, rivers, water resources, sharing of waters, demographics, human development indices
b) People, Society and Culture:
Major personalities in history of Punjab, religious movements, major religions & spiritual personalities, Punjabi literature, folklore, performing arts, fine arts and crafts
c) History:
Sufis, saints and gurus, Lodhis and Mughals, Sikh rulers, the British period, nationalist movement in Punjab, Punjab in independent India.
d) Economy:
Agriculture, animal husbandry, industrial & service sectors, major occupations, development & economic growth, public finance (including central-state fiscal issues), public sector institutions, cooperatives etc.
Paper –II (Civil Services Aptitude Test)
- Reading comprehension; Punjabi and English language comprehension, antonyms and synonyms, grammar and sentence formation.
- Interpersonal skills including communication skills
- Logical reasoning, analytical and mental ability
- Basic numerical skills; numbers, magnitudes, percentages, numerical relation appreciation
- Data analysis; Graphic presentations, charts, tables, spreadsheets.
Note: The topics listed in the syllabus are only indicative for the general guidance of the candidates and cannot be deemed as exhaustive list.
SYLLABUS OF PUNJAB STATE CIVIL SERVICES COMBINED COMPETITIVE MAIN EXAMINATION
ENGLISH
(100 Marks)
SECTION-A
1. Comprehension (Unseen Passage)— 10 Marks
(An unseen passage followed by Questions to be answered.)
2. Precis writing— 10 Marks
(Passage to be summarized to 1/3rd)
3. Letter writing—(200 words) 10marks
4. Essay writing (Any general topic 300 words) 10 Marks
5. Translation 10 Marks
SECTION-B
6. Grammar 50 Marks
ESSAY
(150 Marks)
Candidates will be required to write three short essays in English or Punjabi on specified topics. The choice of subjects will be given. They will be expected to keep closely to the subject of the essay to arrange their ideas in an orderly fashion, and to write concisely. Credit will be given for content value, effective and exact expression.

GENERAL STUDIES-I
HISTORY, GEOGRAPHY AND SOCIETY
Section- 1: HISTORY
1.1 History of the world : Events from 18th century; industrial revolution, world wars, redrawal of national boundaries, colonization, decolonization, political philosophies like Communism, Capitalism, Socialism etc. -their forms and effect on society.
1.2 Indian culture- Salient aspects of Art Forms, Literature and Architecture from ancient to modern times.
1.3 Modern Indian history from the middle of the eighteenth century until the present- significant events, personalities and issues.
1.4 Socio-religious reform movements with special reference to Punjab.
1.5 The Freedom Struggle - its various stages and important contributors /contributions from different parts of the country with special reference to Punjab.
1.6 Post-independence consolidation and reorganization within the country.
1.7 History of Punjab:
1.7. 1 Ranjit Singh’s rise to power, civil and military administration and relations with the British
1.7. 2 Annexation of Punjab with special reference to the causes and consequences of the Anglo-Sikh wars.
Section-2: GEOGRAPHY
2.1 Physical Geography: Salient features of world’s physical geography. Distribution of key natural resources across the world (including South Asia and the Indian subcontinent); factors responsible for the location of primary,
secondary, and tertiary sector industries in various parts of the world (including India)
2.2 Important Geophysical phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic activity, cyclone etc., geographical features and their locationchanges in critical geographical features (including water-bodies and icecaps)
and in flora and fauna and the effects of such changes.
2.3 Geography of Punjab:
2.3. 1 Physiographic details of Punjab; Geomorphic features of Punjab, Punjab’s strategic location with reference to International Border;
2.3. 2 Crops of Punjab; Modern concepts of Farming; Problems faced by agriculturists/ Issues in Agriculture: Depletion of ground water, etc;
Section-3: SOCIETY
3.1 Salient features of Indian Society, Diversity of India.
3.2 Role of women and women’s organization, population and associated issues, poverty and developmental issues, urbanization, their problems and their remedies
3.3 Effects of globalization on Indian society
3.4 Social empowerment, communalism, regionalism & secularism
3.5 Ethics and Society: Essence, determinants and consequences of Ethics in human actions; dimensions of ethics; ethics in private and public relationships.
3. 6 Human Values – Role of family, society and educational institutions in inculcating values; lessons from the lives and teachings of great leaders and reformers- Gautam Buddha, Mahavira, Kabir, Guru Nanak; Swami Vivekananda, Jyotibha Phule, Ishwar Chandra Vidya Sagar and Mahatma Gandhi.
3.7 Vulnerable sections of the population - Welfare schemes by the Centre and State of Punjab and their performance; Mechanisms, laws, institutions and Bodies constituted for their protection and betterment.
3.8 Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector- Health, Education, Human Resources; Issues relating to Poverty and Malnutrition.
GENERAL STUDIES-II
INDIAN CONSTITUTION& POLITY, GOVERNANCE AND INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
Section-1: INDIAN CONSTITUTION & POLITY
1.1 Indian Constitution- historical underpinnings, evolution, features, amendments, significant provisions and basic structure.
1.2 Functions and responsibilities of Union and the States, issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure, devolution of powers and finances up to local levels and challenges therein.
1.3 Separation of powers between various organs; Dispute redressal mechanisms and institutions.
1.4 Comparison of the Indian constitutional scheme with that of other countries
1.5 Parliament and State Legislatures - structure, functioning, conduct of business, powers & privileges and issues arising out of these.
1.6 Structure, organization and functioning of the Executive and the Judiciary; Ministries and Departments of the Government; pressure groups and formal/informal associations and their role in the Polity.
1.7 Salient features of the Representation of People’s Act.
1.8 Appointment to various Constitutional posts; Powers, functions and responsibilities of various Constitutional Bodies
1.9 District Administration - Evolution of District Administration; Panchayati Raj Institutions and Urban Local Bodies.
Section-2 GOVERNANCE:
2.1 Statutory, regulatory and various quasi-judicial bodies
2.2 Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation; Development processes and the development organizations- the role of NGOs, SHGs,
donors, charities, institutional and other stakeholders
2.3 Important aspects of governance, transparency and accountability, egovernance- applications, models, successes, limitations and potential; citizens charters, transparency & accountability and institutional and other
measures; Role of civil services in a democracy; Changing trends in Governance
2.4 Values and Ethics in Governance- Ethical concerns and dilemmas in government and private institutions; laws, rules, regulations and conscience as sources of ethical guidance; accountability and ethical governance;
strengthening of ethical and moral values in governance; ethical issues in international relations and funding.
2.5 Probity in Governance: Concept of Governance; Philosophical basis of governance and probity; corporate governance; Information sharing and transparency in government, Right to Information, Codes of Ethics, Codes
of Conduct, Citizen’s Charters, Work culture, Quality of service delivery, Utilization of public funds, challenges of corruption.
Section-3: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
3.1 India and its neighborhood- relations;
3.2 Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests;
3.3 Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests, Indian Diaspora
3.4 Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure and mandate.
Note: The candidates are expected to be aware about the current developments related to the topics mentioned above.
GENERAL STUDIES-III
ECONOMY, STATISTICS AND SECURITY ISSUES
Section-1: Indian Economy
1.1 Issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment; sustainable development; Inclusive growth and issues arising from it; Government Budgeting;
1.2 Major crops, cropping patterns in various parts of the country, different types of irrigation and irrigation systems; storage, transport and marketing of agricultural produce- issues and related constraints; e-technology in the
aid of farmers; Issues related to direct and indirect farm subsidies and minimum support prices; Technology missions; economics of animal rearing.
1.3 Public Distribution System- objectives, functioning, limitations, revamping; issues of buffer stocks and food security;
1.4 Food processing and related industries in India- scope and significance, location, upstream and downstream requirements, supply chain management
1.5 Land reforms in India; Effects of liberalization on the economy, changes in industrial policy and their effects on industrial growth.
1.6 Infrastructure- Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc; Investment models
1.7 Human Resource Development:
1.7.1 Importance of Human capital in economic development
1.7.2 Nature, types and problems of unemployment in India, Trends of Employment in India, Skill development and demographic dividend
1.8 Punjab Economy: Planning- various aspects of developmental planning; Industry; Infrastructure.
Section-2: Statistical analysis, graphs and diagrams
This part will test the candidate’s ability to draw conclusions from information presented in statistical, graphical or diagrammatical form and to interpret the same.
Section-3: Issues related to Security
3.1 Linkages between development and spread of extremism;
3.2 Role of external, State and non-State actors in creating challenges to internal security; Challenges to internal security through communication networks; role of media and social networking sites in internal security
challenges,
3.3 Basics of cyber security; money-laundering and its prevention;
3.4 Security challenges and their management in border areas; linkages of organized crime with terrorism.
3.5 Various Security forces and agencies and their mandate
Note: The candidates are expected to be aware about the current developments related to the topics mentioned above.
GENERAL STUDIES-IV
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY, ENVIRONMENT, PROBLEM SOLVING & DECISION MAKING
Section-1 : Science and Technology
1.1 Science and Technology
1.1.1 Developments and applications of science and technology and their effects in everyday life
1.1.2 Achievements of Indians in science & technology; indigenization of technology and developing new technology.
1.1.3 Recent developments in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, robotics, nanotechnology, etc.
1.1.4 Issues relating to intellectual property rights.
1.2 Modern Trends in Life Sciences
1.2.1 Progress of Agricultural Science and its impact– Introduction to Biotechnology and its applications; Veterinary and Animal Scienceslatest developments.
1.2.2 Introduction to and applications of Genetic Engineering & Stem Cell Research
1.2.3 Human Diseases and Microbial infections; Common infections and preventive measures; preventive measures during out breaks; Immunity and vaccination
Section-2: Environment
2.1 Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, Issues related to Climate change; environmental impact assessment
2.2 Water management- Issues in India; Present scenario, Methods and importance of water conservation
2.3 Definition, nature, types and classification of disasters
2.4 Natural Hazards: Floods, earthquakes, tsunamis, landslides, etc., Risk reduction and mitigation measures
Section-3: Situations in Civil Service -Problem Solving and Decision Making
3.1 Tackling situations of Natural disasters/ Major Accidents/ Law and order, Controlling riots, Handling public protests and dharnas, Land Acquisition and Rehabilitation, Designing Projects, Implementation of National Flagship Schemes/ Programmes, Public Private Partnership in effective service delivery, Managing and financing Municipal services e.g. Solid waste management, Conservation of natural resources- water, forests, etc, Pollution control,
Reviving a loss making PSU, Planning and target achievement, Gender sensitization and women empowerment, Empowerment of vulnerable sections of the society, Improving Education and Enhancing Skill development, Urban settlement-Slums and Housing issues, Managing Issues related to Urban/ Rural drinking water supply and sanitation, etc.
Note: A duly structured situation will be presented to the candidates and they will be asked to analyze and suggest their own solution to the problem arising out of situation.