Directions Q. (1 - 7): In the given passage, there are blanks, each of which has been numbered. Against each, five words are suggested, one of which fits the blank appropriately.
We all have a ___ (1) ___ in the infrastructure surrounding us-the roads, buildings, power lines and telephone networks that we __ (2) _____ on daily. How well they are built and operated is __ (3) ____ to economic growth and is a key arbiter of an economy's competitiveness- and yet, virtually every economy faces an array of infrastructure challenges. Just a few examples illustrate some of the pressing issues. South Africa's power distribution network has an estimated maintenance backlog of $4 billion- equivalent to half of the country's total investment in electronic power generation and distribution in 2011. The U.S. Department of Transportation estimates that 15% of the country's roads are in an unacceptable condition and says that road congestion costs the US an estimated $100 billion per year. Just to keep _____ (4) _____ with anticipated global GDP growth, the world needs to spend $57 trillion, or on average $3.2 trillion a year, on infrastructure over the next 18 years. That is more than the entire worldwide stock of infrastructure on the ground today-and nearly 60% more than the world has invested over the past 18 years. Tackling maintenance backlogs, future-proofing infrastructure to cope with climate change and ___ (5) _____development goals such as access to clean water and all-weather roads to transport goods to markets would cost a great deal. The bill for all of that looks prohibitive at a time when many governments are highly indebted and capital is tight. A focus on both, the huge need for additional investment and potential difficulties in financing it, ___ (6) ____ the debate Pessimism rules, but it needn't be that way. There are ways of cutting the bill down to size and dealing with the challenge. The answer ___ (7) ____ in improving the way we plan, build and operate infrastructure- in other words, we need to boost its productivity.
Question:
Blank 1 as per Passage
Stake
Interest
Compromise
Decision
Subsidy
Directions Q. (1 - 7): In the given passage, there are blanks, each of which has been numbered. Against each, five words are suggested, one of which fits the blank appropriately.
We all have a ___ (1) ___ in the infrastructure surrounding us-the roads, buildings, power lines and telephone networks that we __ (2) _____ on daily. How well they are built and operated is __ (3) ____ to economic growth and is a key arbiter of an economy's competitiveness- and yet, virtually every economy faces an array of infrastructure challenges. Just a few examples illustrate some of the pressing issues. South Africa's power distribution network has an estimated maintenance backlog of $4 billion- equivalent to half of the country's total investment in electronic power generation and distribution in 2011. The U.S. Department of Transportation estimates that 15% of the country's roads are in an unacceptable condition and says that road congestion costs the US an estimated $100 billion per year. Just to keep _____ (4) _____ with anticipated global GDP growth, the world needs to spend $57 trillion, or on average $3.2 trillion a year, on infrastructure over the next 18 years. That is more than the entire worldwide stock of infrastructure on the ground today-and nearly 60% more than the world has invested over the past 18 years. Tackling maintenance backlogs, future-proofing infrastructure to cope with climate change and ___ (5) _____development goals such as access to clean water and all-weather roads to transport goods to markets would cost a great deal. The bill for all of that looks prohibitive at a time when many governments are highly indebted and capital is tight. A focus on both, the huge need for additional investment and potential difficulties in financing it, ___ (6) ____ the debate Pessimism rules, but it needn't be that way. There are ways of cutting the bill down to size and dealing with the challenge. The answer ___ (7) ____ in improving the way we plan, build and operate infrastructure- in other words, we need to boost its productivity.
Question:
Blank 2 as per Passage
Use
Rely
Confide
Commute
Charge
Directions Q. (1 - 7): In the given passage, there are blanks, each of which has been numbered. Against each, five words are suggested, one of which fits the blank appropriately.
We all have a ___ (1) ___ in the infrastructure surrounding us-the roads, buildings, power lines and telephone networks that we __ (2) _____ on daily. How well they are built and operated is __ (3) ____ to economic growth and is a key arbiter of an economy's competitiveness- and yet, virtually every economy faces an array of infrastructure challenges. Just a few examples illustrate some of the pressing issues. South Africa's power distribution network has an estimated maintenance backlog of $4 billion- equivalent to half of the country's total investment in electronic power generation and distribution in 2011. The U.S. Department of Transportation estimates that 15% of the country's roads are in an unacceptable condition and says that road congestion costs the US an estimated $100 billion per year. Just to keep _____ (4) _____ with anticipated global GDP growth, the world needs to spend $57 trillion, or on average $3.2 trillion a year, on infrastructure over the next 18 years. That is more than the entire worldwide stock of infrastructure on the ground today-and nearly 60% more than the world has invested over the past 18 years. Tackling maintenance backlogs, future-proofing infrastructure to cope with climate change and ___ (5) _____development goals such as access to clean water and all-weather roads to transport goods to markets would cost a great deal. The bill for all of that looks prohibitive at a time when many governments are highly indebted and capital is tight. A focus on both, the huge need for additional investment and potential difficulties in financing it, ___ (6) ____ the debate Pessimism rules, but it needn't be that way. There are ways of cutting the bill down to size and dealing with the challenge. The answer ___ (7) ____ in improving the way we plan, build and operate infrastructure- in other words, we need to boost its productivity.
Question:
Blank 3 as per Passage
Close
Deciding
Trivial
Crucial
Insistent
Directions Q. (1 - 7): In the given passage, there are blanks, each of which has been numbered. Against each, five words are suggested, one of which fits the blank appropriately.
We all have a ___ (1) ___ in the infrastructure surrounding us-the roads, buildings, power lines and telephone networks that we __ (2) _____ on daily. How well they are built and operated is __ (3) ____ to economic growth and is a key arbiter of an economy's competitiveness- and yet, virtually every economy faces an array of infrastructure challenges. Just a few examples illustrate some of the pressing issues. South Africa's power distribution network has an estimated maintenance backlog of $4 billion- equivalent to half of the country's total investment in electronic power generation and distribution in 2011. The U.S. Department of Transportation estimates that 15% of the country's roads are in an unacceptable condition and says that road congestion costs the US an estimated $100 billion per year. Just to keep _____ (4) _____ with anticipated global GDP growth, the world needs to spend $57 trillion, or on average $3.2 trillion a year, on infrastructure over the next 18 years. That is more than the entire worldwide stock of infrastructure on the ground today-and nearly 60% more than the world has invested over the past 18 years. Tackling maintenance backlogs, future-proofing infrastructure to cope with climate change and ___ (5) _____development goals such as access to clean water and all-weather roads to transport goods to markets would cost a great deal. The bill for all of that looks prohibitive at a time when many governments are highly indebted and capital is tight. A focus on both, the huge need for additional investment and potential difficulties in financing it, ___ (6) ____ the debate Pessimism rules, but it needn't be that way. There are ways of cutting the bill down to size and dealing with the challenge. The answer ___ (7) ____ in improving the way we plan, build and operate infrastructure- in other words, we need to boost its productivity.
Question:
Blank 4 as per Passage
Gait
Stride
Walk
Tread
pace
Directions Q. (1 - 7): In the given passage, there are blanks, each of which has been numbered. Against each, five words are suggested, one of which fits the blank appropriately.
We all have a ___ (1) ___ in the infrastructure surrounding us-the roads, buildings, power lines and telephone networks that we __ (2) _____ on daily. How well they are built and operated is __ (3) ____ to economic growth and is a key arbiter of an economy's competitiveness- and yet, virtually every economy faces an array of infrastructure challenges. Just a few examples illustrate some of the pressing issues. South Africa's power distribution network has an estimated maintenance backlog of $4 billion- equivalent to half of the country's total investment in electronic power generation and distribution in 2011. The U.S. Department of Transportation estimates that 15% of the country's roads are in an unacceptable condition and says that road congestion costs the US an estimated $100 billion per year. Just to keep _____ (4) _____ with anticipated global GDP growth, the world needs to spend $57 trillion, or on average $3.2 trillion a year, on infrastructure over the next 18 years. That is more than the entire worldwide stock of infrastructure on the ground today-and nearly 60% more than the world has invested over the past 18 years. Tackling maintenance backlogs, future-proofing infrastructure to cope with climate change and ___ (5) _____development goals such as access to clean water and all-weather roads to transport goods to markets would cost a great deal. The bill for all of that looks prohibitive at a time when many governments are highly indebted and capital is tight. A focus on both, the huge need for additional investment and potential difficulties in financing it, ___ (6) ____ the debate Pessimism rules, but it needn't be that way. There are ways of cutting the bill down to size and dealing with the challenge. The answer ___ (7) ____ in improving the way we plan, build and operate infrastructure- in other words, we need to boost its productivity.
Question:
Blank 5 as per Passage
Competing
Meeting
Succeeding
Engaging
Agreeing
Directions Q. (1 - 7): In the given passage, there are blanks, each of which has been numbered. Against each, five words are suggested, one of which fits the blank appropriately.
We all have a ___ (1) ___ in the infrastructure surrounding us-the roads, buildings, power lines and telephone networks that we __ (2) _____ on daily. How well they are built and operated is __ (3) ____ to economic growth and is a key arbiter of an economy's competitiveness- and yet, virtually every economy faces an array of infrastructure challenges. Just a few examples illustrate some of the pressing issues. South Africa's power distribution network has an estimated maintenance backlog of $4 billion- equivalent to half of the country's total investment in electronic power generation and distribution in 2011. The U.S. Department of Transportation estimates that 15% of the country's roads are in an unacceptable condition and says that road congestion costs the US an estimated $100 billion per year. Just to keep _____ (4) _____ with anticipated global GDP growth, the world needs to spend $57 trillion, or on average $3.2 trillion a year, on infrastructure over the next 18 years. That is more than the entire worldwide stock of infrastructure on the ground today-and nearly 60% more than the world has invested over the past 18 years. Tackling maintenance backlogs, future-proofing infrastructure to cope with climate change and ___ (5) _____development goals such as access to clean water and all-weather roads to transport goods to markets would cost a great deal. The bill for all of that looks prohibitive at a time when many governments are highly indebted and capital is tight. A focus on both, the huge need for additional investment and potential difficulties in financing it, ___ (6) ____ the debate Pessimism rules, but it needn't be that way. There are ways of cutting the bill down to size and dealing with the challenge. The answer ___ (7) ____ in improving the way we plan, build and operate infrastructure- in other words, we need to boost its productivity.
Question:
Blank 6 as per Passage
Convey
Subject
Dominates
Command
Prompt
Directions Q. (1 - 7): In the given passage, there are blanks, each of which has been numbered. Against each, five words are suggested, one of which fits the blank appropriately.
We all have a ___ (1) ___ in the infrastructure surrounding us-the roads, buildings, power lines and telephone networks that we __ (2) _____ on daily. How well they are built and operated is __ (3) ____ to economic growth and is a key arbiter of an economy's competitiveness- and yet, virtually every economy faces an array of infrastructure challenges. Just a few examples illustrate some of the pressing issues. South Africa's power distribution network has an estimated maintenance backlog of $4 billion- equivalent to half of the country's total investment in electronic power generation and distribution in 2011. The U.S. Department of Transportation estimates that 15% of the country's roads are in an unacceptable condition and says that road congestion costs the US an estimated $100 billion per year. Just to keep _____ (4) _____ with anticipated global GDP growth, the world needs to spend $57 trillion, or on average $3.2 trillion a year, on infrastructure over the next 18 years. That is more than the entire worldwide stock of infrastructure on the ground today-and nearly 60% more than the world has invested over the past 18 years. Tackling maintenance backlogs, future-proofing infrastructure to cope with climate change and ___ (5) _____development goals such as access to clean water and all-weather roads to transport goods to markets would cost a great deal. The bill for all of that looks prohibitive at a time when many governments are highly indebted and capital is tight. A focus on both, the huge need for additional investment and potential difficulties in financing it, ___ (6) ____ the debate Pessimism rules, but it needn't be that way. There are ways of cutting the bill down to size and dealing with the challenge. The answer ___ (7) ____ in improving the way we plan, build and operate infrastructure- in other words, we need to boost its productivity.
Question:
Blank 7 as per Passage
Reclines
Lay
Expects
Lies
Belongs
Directions : Select the phrase/connector from the given three options which can be used to form a single sentence from the two sentences given below, implying the same meaning expressed in the statement sentences.
Question:
There are enough dirges being sung for public sector banks, but strangely the performance of their stocks does not reflect this. Five out of the seven public sector banks made losses and the profit – makers showed a worse bad loans ratio.
A. On account of the fact that five out of seven public sector banks made losses
B. The performance of public sector banks does not reflect
C. Although dirges are being sung for public sector banks
Both A and B
Only B
Only C
Only A
None of these
Directions : Each question given below has two blanks, each blank indicates that something has been omitted. Choose the word that best fits in the meaning of the sentence as a whole.
Question:
Most auto-rickshaw drivers in the city __________ to ply for short distances since doing so does not ________ them much.
agree, profit
Refuse, earn
disagree, revenue
accept, affects
ask, comfort
Directions : Each question given below has two blanks, each blank indicates that something has been omitted. Choose the word that best fits in the meaning of the sentence as a whole.
Question:
During power cuts, one can never get _________ to the customer service executive to ________ a complaint regarding the same.
across, lodge
through, write
over, dictate
along, create
off, file
Directions : Select the phrase/connector from the given three options which can be used to form a single sentence from the two sentences given below, implying the same meaning expressed in the statement sentences.
Question:
The entrepreneurship ethos in India has come a long way and has made rapid strides in recent years. It now ranks in the top five start-up communities in the world.
A. India ranks fifth among the start-up communities in the world
B. he country has made rapid strides in recent years because
C. Moreover, the entrepreneurship ethos in India has come a long way
Both A and B
Only B
Only C
Only A
None of these
Directions : Select the phrase/connector from the given three options which can be used to form a single sentence from the two sentences given below, implying the same meaning expressed in the statement sentences.
Question:
Higher prices of cereals, rice, fruits and pulses led to an increase in food inflation. Non – food inflation was driven mainly by fibres and oilseeds.
A. While higher prices of cereals
B. Despite the higher price of rice, fruits and pulses
C. Non- food inflation was always driven by
Both A and B
Only B
Both B and C
Only A
None of these
Directions : Each question given below has two blanks, each blank indicates that something has been omitted. Choose the word that best fits in the meaning of the sentence as a whole.
Question:
In the olden days, shopkeepers used to dupe the ________ customers by attacking removable magnetic weights _______ their weighing instruments.
cheating, for
strict, with
docile, across
innocent, under
lovely, from
Directions : Each question given below has two blanks, each blank indicates that something has been omitted. Choose the word that best fits in the meaning of the sentence as a whole.
Question:
In order to avoid _______ due to car parking, appropriate signage and painted boundary strips at parking locations have been ________ in the building premises.
problem, install
traffic, felicitated
congestion, provided
accidents, fix
sleeping, used
Directions : Each question given below has two blanks, each blank indicates that something has been omitted. Choose the word that best fits in the meaning of the sentence as a whole.
Question:
Though surprising, it is __________ that Rupesh has not got the job by _______ of his parents' political connections.
veritable, inspiration
veracious, influence
paradoxical, intent
true, virtue
alleged, power
Directions : Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions.
The term "shadow bank" was coined in 2007 to describe risky off-balance-sheet vehicles hatched by banks to sell loans repackaged as bonds. Today, the term is used more loosely to cover all financial intermediaries that perform the bank-like activity but are not regulated as one. These include mobile payment systems, pawnshops, peer-to-peer lending websites, hedge funds and bond-trading platforms set up by technology firms. Among the biggest are asset management companies. In 2013 investment funds make such loans raised a whopping $97 billion worldwide. The Financial Stability Board, an international watchdog estimates that globally, the informal lending sector serviced assets worth $80 trillion in 2014 up from $26 trillion more than a decade earlier. Shadow banks have flourished in part because the traditional ones, battered by losses incurred during the financial slump, are under pressure. Tighter capital requirements and fear of heavy penalties have kept them grounded. In China, where banks are discouraged from lending to certain industries and are mandated to offer frustratingly low-interest rates on deposits, non-banks fill the gap. About two-thirds of all lending in the country by shadow banks are in fact 'bank loans in disguise'. Critics worry that unlike banks, which lend against deposits from customers, nonbanks loan money using investor's cash and rotating lines of credit. This is especially risky when skittish investors who bet on short term gains withdraw their money at once. But non-bank financing need not always be a bad thing. It offers an additional source of credit to individuals and businesses in countries where formal banking is either expensive or absent. It also takes some burden off banks which have big 'maturity mismatches' (the difference between the amount of time a depositor's money is parked in the bank minus the time that it is loaned out). And belatedly, regulators, too, are waking up to the new financial order of shadow banking. Banks must now declare structured investment vehicles on their balance sheets. Authorities are imposing leverage limits on various forms of shadow banks in America and Europe. It is a small start to rein in an industry that accounts for a quarter of the global financial system.
Question:
Which of the following can be said about banking regulators?
These have been innovative in helping economies recover from the 2008 crisis. .
Their approach to the regulation of shadow banks is unnecessarily stringent.
These have washed their hands off and warned people against shadow banks.
These have been slow to respond to the growth of shadow banking.
None of the given statements can be said about banking regulators
Directions : Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions.
The term "shadow bank" was coined in 2007 to describe risky off-balance-sheet vehicles hatched by banks to sell loans repackaged as bonds. Today, the term is used more loosely to cover all financial intermediaries that perform the bank-like activity but are not regulated as one. These include mobile payment systems, pawnshops, peer-to-peer lending websites, hedge funds and bond-trading platforms set up by technology firms. Among the biggest are asset management companies. In 2013 investment funds make such loans raised a whopping $97 billion worldwide. The Financial Stability Board, an international watchdog estimates that globally, the informal lending sector serviced assets worth $80 trillion in 2014 up from $26 trillion more than a decade earlier. Shadow banks have flourished in part because the traditional ones, battered by losses incurred during the financial slump, are under pressure. Tighter capital requirements and fear of heavy penalties have kept them grounded. In China, where banks are discouraged from lending to certain industries and are mandated to offer frustratingly low-interest rates on deposits, non-banks fill the gap. About two-thirds of all lending in the country by shadow banks are in fact 'bank loans in disguise'. Critics worry that unlike banks, which lend against deposits from customers, nonbanks loan money using investor's cash and rotating lines of credit. This is especially risky when skittish investors who bet on short term gains withdraw their money at once. But non-bank financing need not always be a bad thing. It offers an additional source of credit to individuals and businesses in countries where formal banking is either expensive or absent. It also takes some burden off banks which have big 'maturity mismatches' (the difference between the amount of time a depositor's money is parked in the bank minus the time that it is loaned out). And belatedly, regulators, too, are waking up to the new financial order of shadow banking. Banks must now declare structured investment vehicles on their balance sheets. Authorities are imposing leverage limits on various forms of shadow banks in America and Europe. It is a small start to rein in an industry that accounts for a quarter of the global financial system.
Question:
Which of the following is the central theme of the passage?
The global economy is headed for a financial collapse given the state of China's economy.
Shadow banking, an indispensable part of the global financial system, is unnecessarily perceived as risky.
There is tremendous upheaval in the banking sector with only state-owned banks safe and sound.
Shadow banks which can be useful are a high-risk alternative to traditional banks and need regulation.
Traditional banks are the safest given the risk the financial system currently faces.
Directions : Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions.
The term "shadow bank" was coined in 2007 to describe risky off-balance-sheet vehicles hatched by banks to sell loans repackaged as bonds. Today, the term is used more loosely to cover all financial intermediaries that perform the bank-like activity but are not regulated as one. These include mobile payment systems, pawnshops, peer-to-peer lending websites, hedge funds and bond-trading platforms set up by technology firms. Among the biggest are asset management companies. In 2013 investment funds make such loans raised a whopping $97 billion worldwide. The Financial Stability Board, an international watchdog estimates that globally, the informal lending sector serviced assets worth $80 trillion in 2014 up from $26 trillion more than a decade earlier. Shadow banks have flourished in part because the traditional ones, battered by losses incurred during the financial slump, are under pressure. Tighter capital requirements and fear of heavy penalties have kept them grounded. In China, where banks are discouraged from lending to certain industries and are mandated to offer frustratingly low-interest rates on deposits, non-banks fill the gap. About two-thirds of all lending in the country by shadow banks are in fact 'bank loans in disguise'. Critics worry that unlike banks, which lend against deposits from customers, nonbanks loan money using investor's cash and rotating lines of credit. This is especially risky when skittish investors who bet on short term gains withdraw their money at once. But non-bank financing need not always be a bad thing. It offers an additional source of credit to individuals and businesses in countries where formal banking is either expensive or absent. It also takes some burden off banks which have big 'maturity mismatches' (the difference between the amount of time a depositor's money is parked in the bank minus the time that it is loaned out). And belatedly, regulators, too, are waking up to the new financial order of shadow banking. Banks must now declare structured investment vehicles on their balance sheets. Authorities are imposing leverage limits on various forms of shadow banks in America and Europe. It is a small start to rein in an industry that accounts for a quarter of the global financial system.
Question:
Which of the following aptly describes the tone of the passage?
Obsequious
Reckless
Poignant
Acrimonious
None of these
Directions : Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions.
The term "shadow bank" was coined in 2007 to describe risky off-balance-sheet vehicles hatched by banks to sell loans repackaged as bonds. Today, the term is used more loosely to cover all financial intermediaries that perform the bank-like activity but are not regulated as one. These include mobile payment systems, pawnshops, peer-to-peer lending websites, hedge funds and bond-trading platforms set up by technology firms. Among the biggest are asset management companies. In 2013 investment funds make such loans raised a whopping $97 billion worldwide. The Financial Stability Board, an international watchdog estimates that globally, the informal lending sector serviced assets worth $80 trillion in 2014 up from $26 trillion more than a decade earlier. Shadow banks have flourished in part because the traditional ones, battered by losses incurred during the financial slump, are under pressure. Tighter capital requirements and fear of heavy penalties have kept them grounded. In China, where banks are discouraged from lending to certain industries and are mandated to offer frustratingly low-interest rates on deposits, non-banks fill the gap. About two-thirds of all lending in the country by shadow banks are in fact 'bank loans in disguise'. Critics worry that unlike banks, which lend against deposits from customers, nonbanks loan money using investor's cash and rotating lines of credit. This is especially risky when skittish investors who bet on short term gains withdraw their money at once. But non-bank financing need not always be a bad thing. It offers an additional source of credit to individuals and businesses in countries where formal banking is either expensive or absent. It also takes some burden off banks which have big 'maturity mismatches' (the difference between the amount of time a depositor's money is parked in the bank minus the time that it is loaned out). And belatedly, regulators, too, are waking up to the new financial order of shadow banking. Banks must now declare structured investment vehicles on their balance sheets. Authorities are imposing leverage limits on various forms of shadow banks in America and Europe. It is a small start to rein in an industry that accounts for a quarter of the global financial system.
Question:
Which of the following can be used to replace the phrase ‘Among the biggest are asset management companies’?
Asset management companies are responsible for over half the credit in America.
The financial crisis hurt asset management companies in China the most.
Asset management companies occupy the largest share of shadow banking firms.
With high rates of interest asset management companies are showing the highest profits.
None of the given statements
Directions : Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions.
The term "shadow bank" was coined in 2007 to describe risky off-balance-sheet vehicles hatched by banks to sell loans repackaged as bonds. Today, the term is used more loosely to cover all financial intermediaries that perform the bank-like activity but are not regulated as one. These include mobile payment systems, pawnshops, peer-to-peer lending websites, hedge funds and bond-trading platforms set up by technology firms. Among the biggest are asset management companies. In 2013 investment funds make such loans raised a whopping $97 billion worldwide. The Financial Stability Board, an international watchdog estimates that globally, the informal lending sector serviced assets worth $80 trillion in 2014 up from $26 trillion more than a decade earlier. Shadow banks have flourished in part because the traditional ones, battered by losses incurred during the financial slump, are under pressure. Tighter capital requirements and fear of heavy penalties have kept them grounded. In China, where banks are discouraged from lending to certain industries and are mandated to offer frustratingly low-interest rates on deposits, non-banks fill the gap. About two-thirds of all lending in the country by shadow banks are in fact 'bank loans in disguise'. Critics worry that unlike banks, which lend against deposits from customers, nonbanks loan money using investor's cash and rotating lines of credit. This is especially risky when skittish investors who bet on short term gains withdraw their money at once. But non-bank financing need not always be a bad thing. It offers an additional source of credit to individuals and businesses in countries where formal banking is either expensive or absent. It also takes some burden off banks which have big 'maturity mismatches' (the difference between the amount of time a depositor's money is parked in the bank minus the time that it is loaned out). And belatedly, regulators, too, are waking up to the new financial order of shadow banking. Banks must now declare structured investment vehicles on their balance sheets. Authorities are imposing leverage limits on various forms of shadow banks in America and Europe. It is a small start to rein in an industry that accounts for a quarter of the global financial system.
Question:
Which of the following has/have impacted the growth of shadow banks?
A. Faulty audits of these institutions by the Financial Stability Board.
B. The state of traditional banks post the financial crisis.
C. Need for credit which traditional banks are unable to meet.
Only A and B
Only B and C
Only B
All A, B and C
Only A and C
Directions : Read each sentence to find out whether there is any grammatical or idiomatic error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. If there is ‘No error', mark the answer (5). (Ignore errors of punctuation, if any).
Question:
It is ironic that the management (1) / of the organisation refuses to adhere (2) / to the same standards of corporate governance (3) / that it requires of companies deals with it. (4) / No error (5)
It is ironic that the management
of the organisation refuses to adhere
to the same standards of corporate governance
that it requires of companies deals with it
No error
Directions : Read each sentence to find out whether there is any grammatical or idiomatic error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. If there is ‘No error', mark the answer (5). (Ignore errors of punctuation, if any).
Question:
With so lowly call rates, the new (1) / telecom service company is definitely going (2) / to give the current market leaders a (3) / run for their money and market share. (4) / No error (5)
With so lowly call rates, the new
telecom service company is definitely going
to give the current market leaders a
run for their money and market share
No error
Directions : Read each sentence to find out whether there is any grammatical or idiomatic error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. If there is ‘No error', mark the answer (5). (Ignore errors of punctuation, if any).
Question:
While retailers may well be on their (1) / way to experiment with the change in policy (2) / for the next few months, consumers may also take (3) / time to get used to late night shopping. (4) / No error (5)
While retailers may well be on their
way to experiment with the change in policy
for the next few months, consumers may also take
time to get used to late night shopping
No error
Directions : Read each sentence to find out whether there is any grammatical or idiomatic error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. If there is ‘No error', mark the answer (5). (Ignore errors of punctuation, if any).
Question:
The shrewd manager left Samarth (1) / with no choice however to resign from (2) / the post by transferring him to (3) / an entirely remote and hostile location. (4) / No error (5)
The shrewd manager left Samarth
with no choice however to resign from
the post by transferring him to
an entirely remote and hostile location
No error
Directions : Read each sentence to find out whether there is any grammatical or idiomatic error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. If there is ‘No error', mark the answer (5). (Ignore errors of punctuation, if any).
Question:
One way of dealing with such a (1) / situation is by issuing a legal notice (2) / to the accused, when the other is (3) / to settle the matter amicably. (4) / No error (5)
One way of dealing with such a
situation is by issuing a legal notice
to the accused, when the other is
to settle the matter amicably
No error
Directions : Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions.
These are difficult times for America's free-traders. There is anger at `globalism'. Even Americans who were in favour of the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP)-an ambitious new agreement between 12 Pacificrim-countries- have turned against it. This may be linked to the globalisation of supply chains. Production of traded goods has become `unbundled'. Firms once tended to design new gadgets and order the supplies needed to build them in a single factory or city. In the past' few decades, more efficient global shipping and improvements in communications allow firms to spread production across far-flung locations to design phone in America, source parts from several Asian economies and assemble it in China. The share of parts and components in trade rose from 22% to 28% between 1980 and 2000. In 2005, trade-in 'intermediate inputs' accounted for an estimated 56% of trade in goods and 73% in services across rich countries. This dispersion of production chains contributed to a dramatic acceleration in global trade growth. It also changed the way many workers view trade. As production has spread around the world, countries have specialised in different segments of the supply chain. While those, such as China, with lots of low-cost labour, focused on manufacturing and assembly, more advanced economies followed a different path. Cities like New York and San Francisco enjoyed an initial advantage in the most lucrative bits of the Modern supply chain: research and development, engineering and finance. As a result, growth in supply-chain trade has been a boon for the powerful and profitable firms with headquarters in those cities, and for the highly skilled, well compensated workers they employ. America's lot in this new world is, on the whole, a happy one. Many countries envy its fortunate position as a hub for innovative cities. Most studies of the potential effects of TPP conclude that the deal would raise American output by a small but meaningful amount: just under a percentage point of GDP, perhaps over the next 15 years. But the obstacles confronting new trade deals are formidable. More generous redistribution, perhaps through an expanded programme of tradeadjustment assistance, could help neutralise some opposition. But discomfort with TPP is mostly rooted in a mistrust of the elite. Voters who are sceptical of the value of TPP will be unlikely to change their stripes without some demonstration that pacts of its kind benefit the many rather than just the few.
Question:
Which of the following is true in context of the passage?
Global public opinion is against America's trade policies.
In America, wages of low skilled workers have risen tremendously over the last decade.
America's GDP growth has fallen in the past few years.
American firms are no longer a leader in technology.
None of these
Directions : Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions.
These are difficult times for America's free-traders. There is anger at `globalism'. Even Americans who were in favour of the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP)-an ambitious new agreement between 12 Pacificrim-countries- have turned against it. This may be linked to the globalisation of supply chains. Production of traded goods has become `unbundled'. Firms once tended to design new gadgets and order the supplies needed to build them in a single factory or city. In the past' few decades, more efficient global shipping and improvements in communications allow firms to spread production across far-flung locations to design phone in America, source parts from several Asian economies and assemble it in China. The share of parts and components in trade rose from 22% to 28% between 1980 and 2000. In 2005, trade-in 'intermediate inputs' accounted for an estimated 56% of trade in goods and 73% in services across rich countries. This dispersion of production chains contributed to a dramatic acceleration in global trade growth. It also changed the way many workers view trade. As production has spread around the world, countries have specialised in different segments of the supply chain. While those, such as China, with lots of low-cost labour, focused on manufacturing and assembly, more advanced economies followed a different path. Cities like New York and San Francisco enjoyed an initial advantage in the most lucrative bits of the Modern supply chain: research and development, engineering and finance. As a result, growth in supply-chain trade has been a boon for the powerful and profitable firms with headquarters in those cities, and for the highly skilled, well compensated workers they employ. America's lot in this new world is, on the whole, a happy one. Many countries envy its fortunate position as a hub for innovative cities. Most studies of the potential effects of TPP conclude that the deal would raise American output by a small but meaningful amount: just under a percentage point of GDP, perhaps over the next 15 years. But the obstacles confronting new trade deals are formidable. More generous redistribution, perhaps through an expanded programme of tradeadjustment assistance, could help neutralise some opposition. But discomfort with TPP is mostly rooted in a mistrust of the elite. Voters who are sceptical of the value of TPP will be unlikely to change their stripes without some demonstration that pacts of its kind benefit the many rather than just the few.
Question:
What do the statistics in the passage convey?
Developed countries are benefitting most from trade agreements.
The TPP has benefitted China and America the most.
China's dominance in manufacturing is waning.
Global trade has grown explosively.
Contrary to political projections, trade-in Asian has not risen dramatically.
Directions : Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions.
These are difficult times for America's free-traders. There is anger at `globalism'. Even Americans who were in favour of the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP)-an ambitious new agreement between 12 Pacificrim-countries- have turned against it. This may be linked to the globalisation of supply chains. Production of traded goods has become `unbundled'. Firms once tended to design new gadgets and order the supplies needed to build them in a single factory or city. In the past' few decades, more efficient global shipping and improvements in communications allow firms to spread production across far-flung locations to design phone in America, source parts from several Asian economies and assemble it in China. The share of parts and components in trade rose from 22% to 28% between 1980 and 2000. In 2005, trade-in 'intermediate inputs' accounted for an estimated 56% of trade in goods and 73% in services across rich countries. This dispersion of production chains contributed to a dramatic acceleration in global trade growth. It also changed the way many workers view trade. As production has spread around the world, countries have specialised in different segments of the supply chain. While those, such as China, with lots of low-cost labour, focused on manufacturing and assembly, more advanced economies followed a different path. Cities like New York and San Francisco enjoyed an initial advantage in the most lucrative bits of the Modern supply chain: research and development, engineering and finance. As a result, growth in supply-chain trade has been a boon for the powerful and profitable firms with headquarters in those cities, and for the highly skilled, well compensated workers they employ. America's lot in this new world is, on the whole, a happy one. Many countries envy its fortunate position as a hub for innovative cities. Most studies of the potential effects of TPP conclude that the deal would raise American output by a small but meaningful amount: just under a percentage point of GDP, perhaps over the next 15 years. But the obstacles confronting new trade deals are formidable. More generous redistribution, perhaps through an expanded programme of tradeadjustment assistance, could help neutralise some opposition. But discomfort with TPP is mostly rooted in a mistrust of the elite. Voters who are sceptical of the value of TPP will be unlikely to change their stripes without some demonstration that pacts of its kind benefit the many rather than just the few.
Question:
Which of the following best describes America's view of TPP?
Americans are unequivocally in favour of the TPP as it will benefit them the most.
The TPP is detrimental as it has fuelled long-term conflicts between rich and developing nations.
The TPP has elevated mass unemployment and is resented by all Americans.
The TPP has strengthened America's relationship with Asia and Europe.
Americans are wary of the TPP as its benefits are indeterminate.
Directions : Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions.
These are difficult times for America's free-traders. There is anger at `globalism'. Even Americans who were in favour of the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP)-an ambitious new agreement between 12 Pacificrim-countries- have turned against it. This may be linked to the globalisation of supply chains. Production of traded goods has become `unbundled'. Firms once tended to design new gadgets and order the supplies needed to build them in a single factory or city. In the past' few decades, more efficient global shipping and improvements in communications allow firms to spread production across far-flung locations to design phone in America, source parts from several Asian economies and assemble it in China. The share of parts and components in trade rose from 22% to 28% between 1980 and 2000. In 2005, trade-in 'intermediate inputs' accounted for an estimated 56% of trade in goods and 73% in services across rich countries. This dispersion of production chains contributed to a dramatic acceleration in global trade growth. It also changed the way many workers view trade. As production has spread around the world, countries have specialised in different segments of the supply chain. While those, such as China, with lots of low-cost labour, focused on manufacturing and assembly, more advanced economies followed a different path. Cities like New York and San Francisco enjoyed an initial advantage in the most lucrative bits of the Modern supply chain: research and development, engineering and finance. As a result, growth in supply-chain trade has been a boon for the powerful and profitable firms with headquarters in those cities, and for the highly skilled, well compensated workers they employ. America's lot in this new world is, on the whole, a happy one. Many countries envy its fortunate position as a hub for innovative cities. Most studies of the potential effects of TPP conclude that the deal would raise American output by a small but meaningful amount: just under a percentage point of GDP, perhaps over the next 15 years. But the obstacles confronting new trade deals are formidable. More generous redistribution, perhaps through an expanded programme of tradeadjustment assistance, could help neutralise some opposition. But discomfort with TPP is mostly rooted in a mistrust of the elite. Voters who are sceptical of the value of TPP will be unlikely to change their stripes without some demonstration that pacts of its kind benefit the many rather than just the few.
Question:
Which of the following is the author's view of free trade?
Uniform laws and regulations across developing countries have vastly benefitted free trade.
There have been tremendous shifts in free trade but its benefits need to be more equitably distributed.
Protecting national interest at the cost of free trade is the need of the hour.
It is a service to reduce the gap between the haves and the have-nots.
None of the options illustrates the author's view -of free trade.
Directions : Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions.
These are difficult times for America's free-traders. There is anger at `globalism'. Even Americans who were in favour of the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP)-an ambitious new agreement between 12 Pacificrim-countries- have turned against it. This may be linked to the globalisation of supply chains. Production of traded goods has become `unbundled'. Firms once tended to design new gadgets and order the supplies needed to build them in a single factory or city. In the past' few decades, more efficient global shipping and improvements in communications allow firms to spread production across far-flung locations to design phone in America, source parts from several Asian economies and assemble it in China. The share of parts and components in trade rose from 22% to 28% between 1980 and 2000. In 2005, trade-in 'intermediate inputs' accounted for an estimated 56% of trade in goods and 73% in services across rich countries. This dispersion of production chains contributed to a dramatic acceleration in global trade growth. It also changed the way many workers view trade. As production has spread around the world, countries have specialised in different segments of the supply chain. While those, such as China, with lots of low-cost labour, focused on manufacturing and assembly, more advanced economies followed a different path. Cities like New York and San Francisco enjoyed an initial advantage in the most lucrative bits of the Modern supply chain: research and development, engineering and finance. As a result, growth in supply-chain trade has been a boon for the powerful and profitable firms with headquarters in those cities, and for the highly skilled, well compensated workers they employ. America's lot in this new world is, on the whole, a happy one. Many countries envy its fortunate position as a hub for innovative cities. Most studies of the potential effects of TPP conclude that the deal would raise American output by a small but meaningful amount: just under a percentage point of GDP, perhaps over the next 15 years. But the obstacles confronting new trade deals are formidable. More generous redistribution, perhaps through an expanded programme of tradeadjustment assistance, could help neutralise some opposition. But discomfort with TPP is mostly rooted in a mistrust of the elite. Voters who are sceptical of the value of TPP will be unlikely to change their stripes without some demonstration that pacts of its kind benefit the many rather than just the few.
Question:
According to the passage, which of the following is/are (an) effects of ‘unbundling’?
A. Unfair and exploitative working conditions in developing countries.
B. Drop in quality standards of manufactured goods.
C. Unemployment for some sections of the workforce in developed countries.
Only A and B
Only B and C
Only C
All A, B and C
Only A and C
Directions : In the following number series only one number is wrong.
Find out the wrong number
Question:
18.3, 20.6, 16, 22.9, 13.7, 2.2, 11.4
2.2
16
22.9
20.6
13.7
Directions : In the following number series only one number is wrong.
Find out the wrong number
Question:
2, 4, 11, 37, 151, 771, 4633
151
4
37
771
11
Directions : In the following number series only one number is wrong.
Find out the wrong number
Question:
188, 154, 140, 132, 128, 126, 125
154
132
128
140
126
Directions : In the following number series only one number is wrong.
Find out the wrong number
Question:
6, 4, 5, 11, 39, 179, 1127
4
39
179
5
11
Directions : In the following number series only one number is wrong.
Find out the wrong number
Question:
9, 5, 6, 10.5, 23, 61, 18
61
23
10.5
6
5
To complete a project, 18 women take 4 more days than the number of days taken by 12 men. If eight men complete the project in 9 days, how much work will be left when 15 women and 12 men together work for 3 days?
2/3
3/4
3/2
1/4
1/2
The respective ratio between the time taken by a boat to travel the same distance downstream in stream A and stream B is 8:7. The speed of the boat is 12 km/h and the speed of stream A is half the speed of stream B. What is the speed of stream B? (in km/h)
5
2
3
4
6
Directions : Each of the following questions is followed by three statements I, II and III. Find out whether the data given in each statement is sufficient to answer the questions.
Question:
Arun and Bhadra are brothers. In how many years from now will Bhadra’s age be 50 years?
I. The ratio of the current ages of Arun and Bhadra is 5:7 respectively.
II. Bhadra was born 10 years before Arun.
III. 5 years hence, Arun’s age would be three-fourth of Bhadra’s age at that time.
Any two of the three
Only II and either I or III
All I, II and III
Only II and III
Only I and III
Directions : Each of the following questions is followed by three statements I, II and III. Find out whether the data given in each statement is sufficient to answer the questions.
Question:
A right-angled triangle is inscribed in a given circle. What is the area of the given circle (in cm2 )?
I. The base and height of the triangle (in cm) are both the roots of the equation x2 - 23x + 120 = 0
II. The sum of the base and height of the triangle is 23 cm.
III. The height of the right-angled triangle is greater than the base of the same.
III and either I or II
All of them
Only II and III
Only I
Either I or II
Directions : Each of the following questions is followed by three statements I, II and III. Find out whether the data given in each statement is sufficient to answer the questions.
Question:
What is the ratio between the marked price of two identical items, P and Q, which had been purchased at the same price?
I. Item P was sold at a profit of 20%, while item Q was sold at a loss of 10%.
II. Item P was sold at a discount of 4%. The percentage by which Item Q’s cost price been marked up is 2.5 times the profit % earned on selling item P.
III. The overall profit earned on selling items P and Q was 5%.
Only I and II.
All I, II and III.
Any two of the three.
Only II and III.
The information provided in all three statements are not sufficient.
Directions : Each of the following questions is followed by three statements I, II and III. Find out whether the data given in each statement is sufficient to answer the questions.
Question:
Three workers A, B and C complete a given piece of work within different time spans while working individually. What is the ratio of efficiencies of C and B respectively?
I. A takes 100% more time than C to complete the given piece of work.
II. B completes the given piece of work within 8 days.
III. B takes 2 days less than A to complete the given piece of work.
Information in all three statements are not sufficient
All of the three
Only II and III
II and either only I or only III
Only I and III
Directions : Each of the following questions is followed by three statements I, II and III. Find out whether the data given in each statement is sufficient to answer the questions.
Question:
What is the three-digit number having each digit different from the other?
I. Each of the digits of the given number is a multiple of 3.
II. The digit in the unit’s place is 50% less than that in the hundred’s place.
Both I and II
The information in all three statements is not sufficient
Only II
Only I
Either I or II
Directions : Study the following table and answer the given questions
Question:
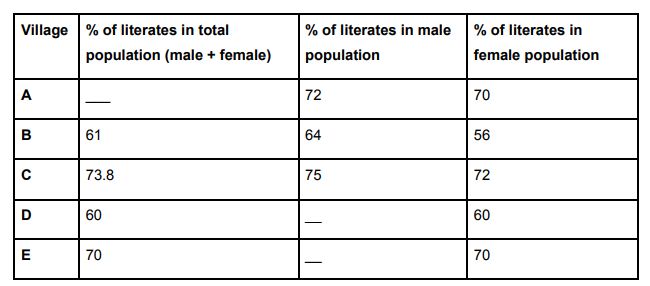
Only 40% and 20% of females were graduates in villages A and C respectively. If the female population of villages A and C were equal, what is the respective ratio of the number of non-graduate females (including illiterate females) in villages A and C?
81:107
90:107
90:121
40:49
45:49
Directions : Study the following table and answer the given questions

Question:
If in village E, 40% of male literates and 40% of female literates were graduates, what percent of the total population were graduates?
32%
28%
35%
40%
30%
Directions : Study the following table and answer the given questions

Question:
In village B, the number of females was what percent less than the number of males?
20%
30%
32%
40%
45%
Directions : Study the following table and answer the given questions

Question:
The total number of literates (male and female) in Village D was 4320. If the number of illiterate females was 320 more than the number of illiterate males, what was the male population of the village?
3200
3000
2800
3600
3500
Directions : Study the following table and answer the given questions

Question:
In village C, the number of females increased by 20% from 2011 to 2015. If the number of literate females was equal in 2011 and 2015, what percent of the female population of village C was literate?
66%
54%
60%
72%
56%
Directions: In the given questions, read the statement and compare the two given quantities on its basis
Question:
1 > a > 0 > b
I. value of [(??+??) 2 − ??2 − ??²] / [(??+??) 2 - ( ??−??)²]
II. value of 1 / 2(????3 + ????)
Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
Quantity I > Quantity II
Quantity I < Quantity II
Quantity I = Quantity II
Quantity ≤ Quantity I
Directions: In the given questions, read the statement and compare the two given quantities on its basis
Question:
There are three positive numbers - a, b and c. The average of a and b is less than the average of b and c by 1.
I. Value of c
II. Value of a
1. Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
Quantity I > Quantity II
Quantity I < Quantity II
Quantity I = Quantity II
Quantity ≤ Quantity II
Directions: In the given questions, read the statement and compare the two given quantities on its basis
Question:
Three equal circles are drawn on a triangle ABC, with points A, B and C as the centres. The radius of each of the circle is equal to half of the side of the triangle ABC
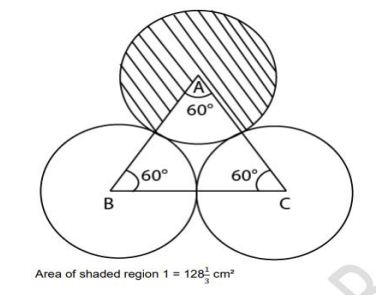
I. The area of the shaded region 2 (in cm²)
II. 30 cm²
Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
Quantity I > Quantity II
Quantity I <Quantity II
Quantity I = Quantity II
Quantity ≤ Quantity II
Directions: In the given questions, read the statement and compare the two given quantities on its basis
Question:
Rutuja bought two articles - article A at Rs. X and article B at Rs. X + 50. She sold article A at 20% profit and article B at 10% loss and earned Rs.35 as profit on the whole deal.
I. Profit earned by Rutuja on selling article A (in Rs.).
II. Loss incurred (in Rs.) when an article which costs Rs.480 is sold at 20% loss.
Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
Quantity I & Quantity II
Quantity I & Quantity II
Quantity I = Quantity II
Quantity ≤ Quantity II
Directions: In the given questions, read the statement and compare the two given quantities on its basis
Question:
Ram invested Rs. P in scheme A and Rs. 2P in scheme B, for two years each. Scheme A offers simple interest p.a. Scheme B offers compound interest (compounded annually) at the rate of 10% p.a. The ratio between the interest earned from scheme A and that earned from scheme B was 8 : 21.
I. Rate of interest offered by scheme A.
II. Rate of interest offered by scheme C (simple interest p.a.), when Rs. 1,600 is invested for 3 years earns an interest of Rs.384.
Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
Quantity I > Quantity II
Quantity I < Quantity II
Quantity I = Quantity II
Quantity ≤ Quantity II
Directions : Refer to the pie charts and answer the given questions. Data regarding the number of foreign students (male + female) from different countries - A, B, C, D and E, studying in higher education level in the country XYZ in the year 2014. Total number of foreign students (male + female) = 9000
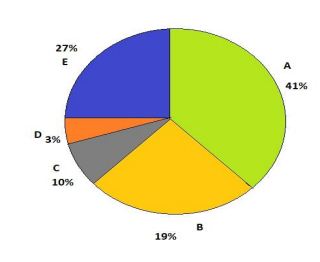
Foreign female students = 3500
Question:
What is the respective ratio between the total number of male students from countries B and C together and the total number of students (male + female) from the same countries together?
4:7
5:14
4:9
5:6
5:9
Directions : Refer to the pie charts and answer the given questions. Data regarding the number of foreign students (male + female) from different countries - A, B, C, D and E, studying in higher education level in the country XYZ in the year 2014. Total number of foreign students (male + female) = 9000

Foreign female students = 3500
Question:
What is the average number of male students from countries C, D and E?
910
915
900
945
901
Directions : Refer to the pie charts and answer the given questions. Data regarding the number of foreign students (male + female) from different countries - A, B, C, D and E, studying in higher education level in the country XYZ in the year 2014. Total number of foreign students (male + female) = 9000

Foreign female students = 3500
Question:
The total number of female students from countries A and B together is what percent of male students from country A?
60%
59.5%
65.25%
70.5%
50%
Directions : Refer to the pie charts and answer the given questions. Data regarding the number of foreign students (male + female) from different countries - A, B, C, D and E, studying in higher education level in the country XYZ in the year 2014. Total number of foreign students (male + female) = 9000

Foreign female students = 3500
Question:
Female students from country D is what percent more than those from country B?
45%
50%
40%
60%
30%
Directions : Refer to the pie charts and answer the given questions. Data regarding the number of foreign students (male + female) from different countries - A, B, C, D and E, studying in higher education level in the country XYZ in the year 2014. Total number of foreign students (male + female) = 9000

Foreign female students = 3500
Question:
Male students from country E in the year 2015 were 20% more than those from the same country in the previous year. If the male students from country E constituted 60% of the total students (male + female), in the year 2015, how many foreign students from country E in the same year were females?
1400
1480
1280
1140
1260
A shopkeeper purchased 15 kg of variety A rice at X per kg and 10 kg of variety B rice at ‘X+ 5’ per kg. The shopkeeper sold the whole quantity of variety A rice at 10% profit and that of variety B rice at 20% profit. The total selling price of variety A rice was Rs. 30 more than that of variety B rice. Had the two varieties been mixed and sold at an overall profit of 20%, what would have been the selling price (per kg)?
26.40
23.20
24.20
25.00
28.30
Abhay rolled a pair of die together. What is the probability that one die showed a multiple of 2 and the second die showed neither a multiple of 3 nor 2?
1/3
1/9
1/6
2/3
2/6
A, B and C started a business with investments of 1,600, 2,100 and 1,500 respectively. After 8 months from the start of the business, B and C invested additional amounts in the ratio of 3 : 5 respectively. If the ratio between total annual profit and C’s share in the annual profit was 3: 1, what was the additional amount invested by B after 8 months?
1,200
600
900
300
700
In the past, consumers would rarely walk into an ice cream store and order low-fat ice cream. But that isn't the case today. An increasing health consciousness combined with a much bigger selection of tasty low-fat foods in all categories has made low-fat ice cream a very profitable item for ice cream store owners. Which of the following best support the statement?
low-fat ice cream produces more revenue than other low-fat foods.
ice cream store owners would be better off carrying only low-fat ice cream.
ice cream store owners no longer think that low-fat ice cream is an unpopular item.
low-fat ice cream is more popular than other kinds of ice cream.
consumers are fickle and it is impossible to please them.
All the major rivers in the state have been flowing way over the danger level for the past few weeks. Which of the following is/are the possible effect(s) of the above cause?
A. Many villages situated near the river banks are submerged forcing residents to flee.
B. Government has decided to provide alternate shelter to all the affected villagers residing near the river banks.
C. The entire state has been put on high flood alert
Only A
Only A and B
Only B and C
All A, B and C
None of these
Directions : In these questions, the relationship between different elements is shown in the statements. These statements are followed by two conclusions. Read them carefully and mark the appropriate answer.
Question:
Statements: C ≥ V ≤ R = N ≥ T > Q, Y ≥ N < A
Conclusion I: Q > V
Conclusion II: Q < Y
Only conclusion I follows
Only conclusion II follows
Both conclusion I and II follow
Neither conclusion I nor II follows
Either conclusion I or II follows
Directions : In these questions, the relationship between different elements is shown in the statements. These statements are followed by two conclusions. Read them carefully and mark the appropriate answer.
Question:
Statements: C ≥ V ≤ R = N ≥ T > Q, Y ≥ N < A
Conclusion I: Q ≥ Y
Conclusion II: A > Q
Only conclusion I follows
Only conclusion II follows
Both conclusion I and II follow
Either conclusion I or II follows
Neither conclusion I nor II follows
Directions : In these questions, the relationship between different elements is shown in the statements. These statements are followed by two conclusions. Read them carefully and mark the appropriate answer.
Question:
Statements: P ≥ R < U ≤ M < V ; T ≤ U ; L < M
Conclusion I: T < L
Conclusion II: V >L
Only conclusion I follows
Only conclusion II follows
Either conclusion I or conclusion II follow
Neither conclusion I nor conclusion II follow
Both conclusion I and conclusion II follow
Directions : In these questions, the relationship between different elements is shown in the statements. These statements are followed by two conclusions. Read them carefully and mark the appropriate answer.
Question:
Statements: P ≥ R < U ≤ M < V; T ≤ U; L < M
Conclusion I: V > T
Conclusion II: T ≤ P
Only conclusion I follow
Only conclusion II follows
Both conclusion I and II follow
Neither conclusion I nor II follows
Either conclusion I or conclusion II follow
Study the given information carefully and answer the given question. Following are the observations of an experiment on 'sleep and memory' conducted on 18 healthy young adults (ages 18 to 25) and 18 healthy older adults (ages 61 to 81).
A. The recall after 8 hours of sleep in younger adults was 65% more than that in the older adults.
B. Night-sleep had a higher negative impact on all of the participants as compared to that of day sleep of equal duration.
C. If a given set of words is memorised immediately before going to sleep, its recall after waking up was found to be better in younger adults than in older adults.
Which of the following can be concluded from the given findings of the research?
I. As per the experiment, there is some correlation between sleep and memory.
II. The part of the brain involved in memory is more active during the day as compared to that during the night.
III. A sleep of more than 8 hours can improve memory in older adults. IV. Memorising something immediately after waking up from an 8-hour long sleep will yield better results than memorising before sleep.
Only IV
All the given statements can be concluded from the given findings of the research.
Both I and III
Both II and IV
Only II
In this question are given two statements I and II. These statements may be either independent causes or may be effects of independent causes or a common cause. One of those statements may be the effect of the other statement. Read both the statements and. decide which of the given answer choice correctly depicts the relationship between these two statements.
Statement I: Company ABC, a leading automobile company in country G has decided to merge all its subsidiary companies into the parent company last week.
Statement II: Company XYZ, a subsidiary of automobile company ABC, has opened five new branches in country F in the previous financial year.
Both the statements I and II are effects of some common cause. -
Both the statements I and II are independent causes.
Statement II is the cause, and statement I is its effect.
Statement I is the cause and statement II is its effect.
Both the statements I and II are the effects of independent causes.
If all the letters in the word ‘REGULATION' are arranged in English alphabetical order from left to right and then all the vowels are changed to the next alphabet in the English alphabetical series and all the consonants are changed to the previous alphabet in English alphabetical series, how will the word be written?
BFFJKOQQSV
ZFFJKONSSV
ZDHHMONSUT
BFHUKMPORV
BFFJKMPQSV
In Country A, it is mandatory for all government organizations to provide transportation facilities (home pick-up and drop) to employees if 75% or number of total employees working in the organization reside more than 15 km away from the office. The same, however, does not apply to XY enterprises as only 1500 of their employees travel more than 15 km to work.
Which of the following can be inferred from the given statement?
A. The total number of employees in XY enterprises is definitely more than 2000.
B. Only 25% of employees of XY enterprises travel less than 15km to office.
C. If 25 new recruits who travel more than 15 km join XY enterprises, the XY enterprises will definitely have to provide transportation facilities.
D. XY enterprises is definitely not a government enterprise
Only A
Only C
Both B and D
Only D
A, B and C
Directions : Study the given information carefully to answer the given questions.
Seven people — J, K, L, M, N, O and P have an interview on seven different days of the same week, starting from Monday and ending on Sunday, but not necessarily in the same order. Each one of them also likes different subjects namely - Statistics, Zoology, Sociology, English, Mathematics, Psychology and Economics, but not necessarily in the same order. Only four people have an interview between N and the one who likes Zoology. Neither N nor the one who likes Zoology has an interview on Sunday. P has an interview immediately after the one who likes Zoology. Only two people have their interviews between P and J. The one who likes Psychology has an interview on one of the days before J but not on Wednesday. Neither N nor P likes Psychology. Only two people have their interviews between the one who likes Psychology and the one who likes Statistics. The one who likes Economics has an interview immediately before the one who likes Statistics. The number of people having interview between P and the one who likes Economics is the same as that of the number of people between J and the one who likes English. N does not like English. Only one person has an interview between the one who likes English and K. The one who likes Sociology has an interview immediately after O. L has an interview on one of the days after M.
Question:
Four of the following five are alike in a certain way based on the given arrangement and hence form a group.
Which of the following does not belong to the group?
K-English
Wednesday-K
Mathematics-Wednesday
Sociology-Statistics
Friday-L
Directions : Study the given information carefully to answer the given questions.
Seven people — J, K, L, M, N, O and P have an interview on seven different days of the same week, starting from Monday and ending on Sunday, but not necessarily in the same order. Each one of them also likes different subjects namely - Statistics, Zoology, Sociology, English, Mathematics, Psychology and Economics, but not necessarily in the same order. Only four people have an interview between N and the one who likes Zoology. Neither N nor the one who likes Zoology has an interview on Sunday. P has an interview immediately after the one who likes Zoology. Only two people have their interviews between P and J. The one who likes Psychology has an interview on one of the days before J but not on Wednesday. Neither N nor P likes Psychology. Only two people have their interviews between the one who likes Psychology and the one who likes Statistics. The one who likes Economics has an interview immediately before the one who likes Statistics. The number of people having interview between P and the one who likes Economics is the same as that of the number of people between J and the one who likes English. N does not like English. Only one person has an interview between the one who likes English and K. The one who likes Sociology has an interview immediately after O. L has an interview on one of the days after M.
Question:
How many people have their interviews between L and M?
Two
Three
None
One
More than three
Directions : Study the given information carefully to answer the given questions.
Seven people — J, K, L, M, N, O and P have an interview on seven different days of the same week, starting from Monday and ending on Sunday, but not necessarily in the same order. Each one of them also likes different subjects namely - Statistics, Zoology, Sociology, English, Mathematics, Psychology and Economics, but not necessarily in the same order. Only four people have an interview between N and the one who likes Zoology. Neither N nor the one who likes Zoology has an interview on Sunday. P has an interview immediately after the one who likes Zoology. Only two people have their interviews between P and J. The one who likes Psychology has an interview on one of the days before J but not on Wednesday. Neither N nor P likes Psychology. Only two people have their interviews between the one who likes Psychology and the one who likes Statistics. The one who likes Economics has an interview immediately before the one who likes Statistics. The number of people having interview between P and the one who likes Economics is the same as that of the number of people between J and the one who likes English. N does not like English. Only one person has an interview between the one who likes English and K. The one who likes Sociology has an interview immediately after O. L has an interview on one of the days after M.
Question:
Which of the following statements is TRUE as per the given arrangement?
None of the given statements is true
Only one person has an interview between K and J.
O likes Psychology.
M has an interview on Friday.
The one who likes Zoology has an interview on one of the day before M.
Directions : Study the given information carefully to answer the given questions.
Seven people — J, K, L, M, N, O and P have an interview on seven different days of the same week, starting from Monday and ending on Sunday, but not necessarily in the same order. Each one of them also likes different subjects namely - Statistics, Zoology, Sociology, English, Mathematics, Psychology and Economics, but not necessarily in the same order. Only four people have an interview between N and the one who likes Zoology. Neither N nor the one who likes Zoology has an interview on Sunday. P has an interview immediately after the one who likes Zoology. Only two people have their interviews between P and J. The one who likes Psychology has an interview on one of the days before J but not on Wednesday. Neither N nor P likes Psychology. Only two people have their interviews between the one who likes Psychology and the one who likes Statistics. The one who likes Economics has an interview immediately before the one who likes Statistics. The number of people having interview between P and the one who likes Economics is the same as that of the number of people between J and the one who likes English. N does not like English. Only one person has an interview between the one who likes English and K. The one who likes Sociology has an interview immediately after O. L has an interview on one of the days after M.
Question:
Who has an interview immediately after K?
M
The one who likes Zoology
The one who likes Statistics
J
P
Directions : Study the given information carefully to answer the given questions.
Seven people — J, K, L, M, N, O and P have an interview on seven different days of the same week, starting from Monday and ending on Sunday, but not necessarily in the same order. Each one of them also likes different subjects namely - Statistics, Zoology, Sociology, English, Mathematics, Psychology and Economics, but not necessarily in the same order. Only four people have an interview between N and the one who likes Zoology. Neither N nor the one who likes Zoology has an interview on Sunday. P has an interview immediately after the one who likes Zoology. Only two people have their interviews between P and J. The one who likes Psychology has an interview on one of the days before J but not on Wednesday. Neither N nor P likes Psychology. Only two people have their interviews between the one who likes Psychology and the one who likes Statistics. The one who likes Economics has an interview immediately before the one who likes Statistics. The number of people having interview between P and the one who likes Economics is the same as that of the number of people between J and the one who likes English. N does not like English. Only one person has an interview between the one who likes English and K. The one who likes Sociology has an interview immediately after O. L has an interview on one of the days after M.
Question:
How many people have their interview before the one who likes Mathematics?
One
More than three
None
Two
Three
Directions : Study the following information and answer the given questions.
Seven people, namely, J, K, L, M, N, O and P like seven different movies namely, Twilight, Gladiator, Wanted, Dread, Hero, Jumanji and Signs but not necessarily in the same order. Each person also works in the same office but in a different department (on the basis of experience) namely Administration, Production, Marketing, HR, Finance, R&D; and Client relations (CR), not necessarily in the same order. (Please Note: Each person has been allocated to a department as per increasing order of experience with the one in Administration being the least experienced whilst the one in Client Relations (CR) being the most experienced). Only two persons have less experience than K. P works in R&D.; The one who likes Wanted has more experience than K but less than one who likes Jumanji. P neither likes Wanted nor Jumanji. The one who likes Wanted does not work in Finance. J, who is more experienced than K, likes twilight. The person who works in Production is less experienced than the person who likes Hero. K does not like Hero. The person who works in HR is more experienced than both L and N. N is not the least experienced person. The one who likes Signs has more experience than N. M is more experienced than J. L does not like Dread.
Question:
Four of the following five are alike in a certain way based on the given arrangement and so form a group. Which is the one that does not belong to that group?
MO
NK
PK
NJ
LO
Directions : Study the following information and answer the given questions.
Seven people, namely, J, K, L, M, N, O and P like seven different movies namely, Twilight, Gladiator, Wanted, Dread, Hero, Jumanji and Signs but not necessarily in the same order. Each person also works in the same office but in a different department (on the basis of experience) namely Administration, Production, Marketing, HR, Finance, R&D; and Client relations (CR), not necessarily in the same order. (Please Note: Each person has been allocated to a department as per increasing order of experience with the one in Administration being the least experienced whilst the one in Client Relations (CR) being the most experienced). Only two persons have less experience than K. P works in R&D.; The one who likes Wanted has more experience than K but less than one who likes Jumanji. P neither likes Wanted nor Jumanji. The one who likes Wanted does not work in Finance. J, who is more experienced than K, likes twilight. The person who works in Production is less experienced than the person who likes Hero. K does not like Hero. The person who works in HR is more experienced than both L and N. N is not the least experienced person. The one who likes Signs has more experience than N. M is more experienced than J. L does not like Dread.
Question:
Which combination represents the department in which 0 works and the movie he likes?
CR-Signs
CR-Gladiator
HR-Gladiator
Marketing-Wanted
HR-Wanted
Directions : Study the following information and answer the given questions.
Seven people, namely, J, K, L, M, N, O and P like seven different movies namely, Twilight, Gladiator, Wanted, Dread, Hero, Jumanji and Signs but not necessarily in the same order. Each person also works in the same office but in a different department (on the basis of experience) namely Administration, Production, Marketing, HR, Finance, R&D; and Client relations (CR), not necessarily in the same order. (Please Note: Each person has been allocated to a department as per increasing order of experience with the one in Administration being the least experienced whilst the one in Client Relations (CR) being the most experienced). Only two persons have less experience than K. P works in R&D.; The one who likes Wanted has more experience than K but less than one who likes Jumanji. P neither likes Wanted nor Jumanji. The one who likes Wanted does not work in Finance. J, who is more experienced than K, likes twilight. The person who works in Production is less experienced than the person who likes Hero. K does not like Hero. The person who works in HR is more experienced than both L and N. N is not the least experienced person. The one who likes Signs has more experience than N. M is more experienced than J. L does not like Dread.
Question:
Which of the following movies does M like?
Jumanji
Hero
Gladiator
Signs
Dread
Directions : Study the following information and answer the given questions.
Seven people, namely, J, K, L, M, N, O and P like seven different movies namely, Twilight, Gladiator, Wanted, Dread, Hero, Jumanji and Signs but not necessarily in the same order. Each person also works in the same office but in a different department (on the basis of experience) namely Administration, Production, Marketing, HR, Finance, R&D; and Client relations (CR), not necessarily in the same order. (Please Note: Each person has been allocated to a department as per increasing order of experience with the one in Administration being the least experienced whilst the one in Client Relations (CR) being the most experienced). Only two persons have less experience than K. P works in R&D.; The one who likes Wanted has more experience than K but less than one who likes Jumanji. P neither likes Wanted nor Jumanji. The one who likes Wanted does not work in Finance. J, who is more experienced than K, likes twilight. The person who works in Production is less experienced than the person who likes Hero. K does not like Hero. The person who works in HR is more experienced than both L and N. N is not the least experienced person. The one who likes Signs has more experience than N. M is more experienced than J. L does not like Dread.
Question:
As per the given arrangement, HR is related to Signs and CR is related to Hero in a certain way. To which of the following is Production related to in the same way?
Dread
Jumanji
Wanted
Gladiator
Twilight
Directions : Study the following information and answer the given questions.
Seven people, namely, J, K, L, M, N, O and P like seven different movies namely, Twilight, Gladiator, Wanted, Dread, Hero, Jumanji and Signs but not necessarily in the same order. Each person also works in the same office but in a different department (on the basis of experience) namely Administration, Production, Marketing, HR, Finance, R&D; and Client relations (CR), not necessarily in the same order. (Please Note: Each person has been allocated to a department as per increasing order of experience with the one in Administration being the least experienced whilst the one in Client Relations (CR) being the most experienced). Only two persons have less experience than K. P works in R&D.; The one who likes Wanted has more experience than K but less than one who likes Jumanji. P neither likes Wanted nor Jumanji. The one who likes Wanted does not work in Finance. J, who is more experienced than K, likes twilight. The person who works in Production is less experienced than the person who likes Hero. K does not like Hero. The person who works in HR is more experienced than both L and N. N is not the least experienced person. The one who likes Signs has more experience than N. M is more experienced than J. L does not like Dread.
Question:
Which of the following pairs represent the respective people who have more experience than J and less experience than K?
M, N
P, O
O, J
L, N
P, M
Read the given information and answer the question.
‘Despite spending huge amount of money, we have not yet been able to find life on other planets. I am personally of the opinion that such research should stop with immediate effect as it is a waste of time and money as no good will ever come out of it Instead it would be better to use this money to research other elements in space' Statement by a Scientist from Space Institute of Country X. Which of the following does not weaken the statement of the scientist of space institute of country X?
Although life on other planets has not been discovered yet, such research has widened our knowledge and understanding of other planets and has led to growth and development in science.
According to space scientists, if such efforts are continued, the probability of finding life in at least one other planet is much higher as compared to not finding life at all.
Various other research projects taken up by the said institute in the past have also failed despite spending huge amount of time as well as money on them.
With the amount of time and money that has already been invested in this research, shutting it now would lead to a greater loss than continuing the search.
None of the above
This question consists of information and two statements numbered I and II given below it. You have to decide which of the given statements weaken(s) or strengthen(s) the information and decide the appropriate answer. In order to discourage crowd built-up at railway station X, the platform ticket (charged to all such priced at Rs. 10 should be increased to Rs. 20.
I. The price of a ticket from X to the nearest railway station is Rs. 12.
II. On average, every railway station generates Rs. 24 lacs revenue by charging Rs. 10 for platform ticket while X generates Rs.28 lacs.
Both statements I and II weaken the information.
Statement I weakens the information while Statement II is a neutral statement.
Statement I strengthens the information while statement II weakens the information.
Statement I weakens the information while Statement II strengthens the information.
Both statements I and II strengthen the information
Which of the following expressions will be definitely false if the given expression
‘G > H = I ≥ V ≤ Y ≤ Z ≤T’ is definitely true?
I < G
T ≥ V
T ≤ Y
Z ≥ V
None of these
Directions : A word and number arrangement machine when given an input line of words and numbers rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.(All the numbers are two-digit numbers.)
Input: 42 prey burn 78 21 melt gulp 96 83 head
Step I: ban 23 42 prey 78 melt gulp 96 83 head
Step II: gap 44 ban 23 prey 78 melt 96 83 head
Step III: had 80 gap 44 ban 23 prey melt 96 83
Step IV: mat 85 had 80 gap 44 ban 23 prey 96
Step V: pay 98 mat 85 had 80 gap 44 ban 23
Step V is the last step of the above arrangement as the intended output of arrangement is obtained.
As per the rules followed in the given steps, find the appropriate steps for the given input.
Input : 61 rust 33 colt 86 four torn 28 49 leap
Question:
Which of the following is the fourth to the left of the eighth element from the left end of step II?
cat
far
35
rust
30
Directions : A word and number arrangement machine when given an input line of words and numbers rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.(All the numbers are two-digit numbers.)
Input: 42 prey burn 78 21 melt gulp 96 83 head
Step I: ban 23 42 prey 78 melt gulp 96 83 head
Step II: gap 44 ban 23 prey 78 melt 96 83 head
Step III: had 80 gap 44 ban 23 prey melt 96 83
Step IV: mat 85 had 80 gap 44 ban 23 prey 96
Step V: pay 98 mat 85 had 80 gap 44 ban 23
Step V is the last step of the above arrangement as the intended output of arrangement is obtained.
As per the rules followed in the given steps, find the appropriate steps for the given input.
Input : 61 rust 33 colt 86 four torn 28 49 leap
Question:
Which of the following represents the element that is fifth to the right of 'cat' in step III?
torn
63
lap
far
86
Directions : A word and number arrangement machine when given an input line of words and numbers rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.(All the numbers are two-digit numbers.)
Input: 42 prey burn 78 21 melt gulp 96 83 head
Step I: ban 23 42 prey 78 melt gulp 96 83 head
Step II: gap 44 ban 23 prey 78 melt 96 83 head
Step III: had 80 gap 44 ban 23 prey melt 96 83
Step IV: mat 85 had 80 gap 44 ban 23 prey 96
Step V: pay 98 mat 85 had 80 gap 44 ban 23
Step V is the last step of the above arrangement as the intended output of arrangement is obtained.
As per the rules followed in the given steps, find the appropriate steps for the given input.
Input : 61 rust 33 colt 86 four torn 28 49 leap
Question:
In step III, how many elements are there between '86' and the third element from the left end ?
More than three
One
Three
None
Two
Directions : A word and number arrangement machine when given an input line of words and numbers rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.(All the numbers are two-digit numbers.)
Input: 42 prey burn 78 21 melt gulp 96 83 head
Step I: ban 23 42 prey 78 melt gulp 96 83 head
Step II: gap 44 ban 23 prey 78 melt 96 83 head
Step III: had 80 gap 44 ban 23 prey melt 96 83
Step IV: mat 85 had 80 gap 44 ban 23 prey 96
Step V: pay 98 mat 85 had 80 gap 44 ban 23
Step V is the last step of the above arrangement as the intended output of arrangement is obtained.
As per the rules followed in the given steps, find the appropriate steps for the given input.
Input : 61 rust 33 colt 86 four torn 28 49 leap
Question:
What is the difference between the third element from the right end in step V and the fifth element from the left end in step II?
31
55
26
5
10
Directions : A word and number arrangement machine when given an input line of words and numbers rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.(All the numbers are two-digit numbers.)
Input: 42 prey burn 78 21 melt gulp 96 83 head
Step I: ban 23 42 prey 78 melt gulp 96 83 head
Step II: gap 44 ban 23 prey 78 melt 96 83 head
Step III: had 80 gap 44 ban 23 prey melt 96 83
Step IV: mat 85 had 80 gap 44 ban 23 prey 96
Step V: pay 98 mat 85 had 80 gap 44 ban 23
Step V is the last step of the above arrangement as the intended output of arrangement is obtained.
As per the rules followed in the given steps, find the appropriate steps for the given input.
Input : 61 rust 33 colt 86 four torn 28 49 leap
Question:
'torn' is related to 'rust' in step I in the same way as `lap' is related to 'tan' in step V. Following the same pattern to which element is '86' related to in step IV?
cat
51
35
far
30
This question consists of a statement followed by two courses of action numbered I and II given below it. A course of action is an administrative decision to be everything in the statement to be true and then decide which of the suggested courses of action logically follow(s) from the given statement.
Most of the people looking for buying/renting properties these days complain of being taken to the same property by more than 6-7 brokers. So even after contracting multiple agents, they end up having usually the same options.
Courses of action:
I. All the owners should strictly give responsibility for their properties to only one.
II. The brokers should be instructed to mandatorily disclose the list of all the properties they will be showing the customers on a particular day before taking them to the actual site.
Both I and II follow
Only II follows
Only I follows
Neither I nor II follows
Either I or II follows
Directions : Study the following information to answer the given questions. In a certain code language, ‘economy and work related’ is written as ‘oj my bx st’ ‘work and employment today’ is written as ‘pk bx oj dy’ ‘employment for growth only’ is written as ‘el pk fd zn’ ‘growth is related today’ is written as ‘el dy gm my’ (All codes are two-letter codes only)
Question:
If the code for ‘related people only’ is 'xd my fd' then what may be the code for ‘people for decision’ in the given code language?
to xd my
zn xd fd
zn xd dy
zn kz xd
kz fd xd
Directions : Study the following information to answer the given questions. In a certain code language, ‘economy and work related’ is written as ‘oj my bx st’ ‘work and employment today’ is written as ‘pk bx oj dy’ ‘employment for growth only’ is written as ‘el pk fd zn’ ‘growth is related today’ is written as ‘el dy gm my’ (All codes are two-letter codes only)
Question:
What does the code ‘pk’ stand for in the given code language?
growth
employment
only
economy
today
Directions : Study the following information to answer the given questions. In a certain code language, ‘economy and work related’ is written as ‘oj my bx st’ ‘work and employment today’ is written as ‘pk bx oj dy’ ‘employment for growth only’ is written as ‘el pk fd zn’ ‘growth is related today’ is written as ‘el dy gm my’ (All codes are two-letter codes only)
Question:
What may be the code for ‘economy is boosting’ in the given code language?
gm rc st
zn gm st
ye st el
cp st rc
st bx gm
Directions : Study the following information to answer the given questions. In a certain code language, ‘economy and work related’ is written as ‘oj my bx st’ ‘work and employment today’ is written as ‘pk bx oj dy’ ‘employment for growth only’ is written as ‘el pk fd zn’ ‘growth is related today’ is written as ‘el dy gm my’ (All codes are two-letter codes only)
Question:
Which of the following additional statements is required to definitely find the code of ‘and’ in the given code language?
‘work and prosper now’ is written as ‘bx yp jn oj’
‘work today also important’ is written as ‘Iv en oj dy’
No additional statement is required to find the code
‘and more work today’ is written as ‘zn oj dy bx’
‘related only for employment’ is written as ‘my zn fd pk’
Directions : Study the following information to answer the given questions. In a certain code language, ‘economy and work related’ is written as ‘oj my bx st’ ‘work and employment today’ is written as ‘pk bx oj dy’ ‘employment for growth only’ is written as ‘el pk fd zn’ ‘growth is related today’ is written as ‘el dy gm my’ (All codes are two-letter codes only)
Question:
What is the code for ‘growth today’ in the given code language?
fd el
dy fd
pk dy
dy el
an fd
irections : Study the following information carefully to answer the given question.
Ten persons from different companies viz Samsung, Bata, Microsoft, Google, Apple, HCL, ITC, Reliance, Airtel and Vodafone are sitting in two parallel rows containing five people each, in such a way that there is an equal distance between adjacent persons. In row 1- B, C, D, E and F are seated and all of them are facing south. In row-2 R, S, T, U and V are seated and all of them are facing north. Therefore, in the given seating arrangement, each member seated in a row faces another member of the other row. (All the information given above does not the order of seating as in give the final arrangement.)
• Three people sit between R and the person from Apple. The person from Reliance is an immediate neighbour of the one who faces the person from Apple. V sits to the immediate left of the one who faces the person from Reliance.
• Only one person sits between V and T. The person from Bata sits second to the right of the one who faces T. F sits second to the left of the person from Google. The person from Google does not sit at an extreme end of the line.
• Only two people sit between F and D. The person from Samsung faces an immediate neighbour of D. U is an immediate neighbour of the person from Microsoft. V is not from Microsoft. B sits second to the left of C.
• The person from ITC is an immediate neighbour of the person from Vodafone. Neither V nor F is from ITC. The person from ITC faces the person from HCL.
Question:
F is related to ITC in the same way as T is related to HCL, based on the given arrangement. Who amongst the following is D related to following the same pattern?
Microsoft
Samsung
Apple
Bata
Reliance
irections : Study the following information carefully to answer the given question.
Ten persons from different companies viz Samsung, Bata, Microsoft, Google, Apple, HCL, ITC, Reliance, Airtel and Vodafone are sitting in two parallel rows containing five people each, in such a way that there is an equal distance between adjacent persons. In row 1- B, C, D, E and F are seated and all of them are facing south. In row-2 R, S, T, U and V are seated and all of them are facing north. Therefore, in the given seating arrangement, each member seated in a row faces another member of the other row. (All the information given above does not the order of seating as in give the final arrangement.)
• Three people sit between R and the person from Apple. The person from Reliance is an immediate neighbour of the one who faces the person from Apple. V sits to the immediate left of the one who faces the person from Reliance.
• Only one person sits between V and T. The person from Bata sits second to the right of the one who faces T. F sits second to the left of the person from Google. The person from Google does not sit at an extreme end of the line.
• Only two people sit between F and D. The person from Samsung faces an immediate neighbour of D. U is an immediate neighbour of the person from Microsoft. V is not from Microsoft. B sits second to the left of C.
• The person from ITC is an immediate neighbour of the person from Vodafone. Neither V nor F is from ITC. The person from ITC faces the person from HCL.
Question:
Which of the following is true regarding E?
E is from ITC.
E is an immediate neighbour of the person from Samsung.
E sits at the extreme end of the line.
The person from Airtel faces E.
None of the given options is true
irections : Study the following information carefully to answer the given question.
Ten persons from different companies viz Samsung, Bata, Microsoft, Google, Apple, HCL, ITC, Reliance, Airtel and Vodafone are sitting in two parallel rows containing five people each, in such a way that there is an equal distance between adjacent persons. In row 1- B, C, D, E and F are seated and all of them are facing south. In row-2 R, S, T, U and V are seated and all of them are facing north. Therefore, in the given seating arrangement, each member seated in a row faces another member of the other row. (All the information given above does not the order of seating as in give the final arrangement.)
• Three people sit between R and the person from Apple. The person from Reliance is an immediate neighbour of the one who faces the person from Apple. V sits to the immediate left of the one who faces the person from Reliance.
• Only one person sits between V and T. The person from Bata sits second to the right of the one who faces T. F sits second to the left of the person from Google. The person from Google does not sit at an extreme end of the line.
• Only two people sit between F and D. The person from Samsung faces an immediate neighbour of D. U is an immediate neighbour of the person from Microsoft. V is not from Microsoft. B sits second to the left of C.
• The person from ITC is an immediate neighbour of the person from Vodafone. Neither V nor F is from ITC. The person from ITC faces the person from HCL.
Question:
Who amongst the following sit at the extreme end of the rows ?
The person from Apple and F.
V, E
The person from Samsung and C.
The person from HCL and Bata
R and the person from Reliance.
irections : Study the following information carefully to answer the given question.
Ten persons from different companies viz Samsung, Bata, Microsoft, Google, Apple, HCL, ITC, Reliance, Airtel and Vodafone are sitting in two parallel rows containing five people each, in such a way that there is an equal distance between adjacent persons. In row 1- B, C, D, E and F are seated and all of them are facing south. In row-2 R, S, T, U and V are seated and all of them are facing north. Therefore, in the given seating arrangement, each member seated in a row faces another member of the other row. (All the information given above does not the order of seating as in give the final arrangement.)
• Three people sit between R and the person from Apple. The person from Reliance is an immediate neighbour of the one who faces the person from Apple. V sits to the immediate left of the one who faces the person from Reliance.
• Only one person sits between V and T. The person from Bata sits second to the right of the one who faces T. F sits second to the left of the person from Google. The person from Google does not sit at an extreme end of the line.
• Only two people sit between F and D. The person from Samsung faces an immediate neighbour of D. U is an immediate neighbour of the person from Microsoft. V is not from Microsoft. B sits second to the left of C.
• The person from ITC is an immediate neighbour of the person from Vodafone. Neither V nor F is from ITC. The person from ITC faces the person from HCL.
Question:
Four of the following five are alike in a certain way based on the given arrangement and so form a group. Which is the one that does not belong to that group?
R
V
C
F
B
irections : Study the following information carefully to answer the given question.
Ten persons from different companies viz Samsung, Bata, Microsoft, Google, Apple, HCL, ITC, Reliance, Airtel and Vodafone are sitting in two parallel rows containing five people each, in such a way that there is an equal distance between adjacent persons. In row 1- B, C, D, E and F are seated and all of them are facing south. In row-2 R, S, T, U and V are seated and all of them are facing north. Therefore, in the given seating arrangement, each member seated in a row faces another member of the other row. (All the information given above does not the order of seating as in give the final arrangement.)
• Three people sit between R and the person from Apple. The person from Reliance is an immediate neighbour of the one who faces the person from Apple. V sits to the immediate left of the one who faces the person from Reliance.
• Only one person sits between V and T. The person from Bata sits second to the right of the one who faces T. F sits second to the left of the person from Google. The person from Google does not sit at an extreme end of the line.
• Only two people sit between F and D. The person from Samsung faces an immediate neighbour of D. U is an immediate neighbour of the person from Microsoft. V is not from Microsoft. B sits second to the left of C.
• The person from ITC is an immediate neighbour of the person from Vodafone. Neither V nor F is from ITC. The person from ITC faces the person from HCL.
Question:
Who amongst the following faces the person from Airtel?
The person from Google
B
The person from reliance
E
The person from Bata
Which of the following symbols should replace the question mark(?) in the given expression in order to make the expressions
‘H < R’ as well as ‘D ≥ M’ definitely true? D ≥ I ≥ H = S (?) M < P ≤ R
≥
≤
<
>
=
T is the father of M and P. P is the only daughter of V. M is married to N. A and B are children of M. How is V related to B?
Grandmother
Uncle
Aunt
Sister
Grandfather
A severe cyclonic storm hit the Eastern coastline;te last month resulting in huge loss of life and property on the entire east coast and the Government had to disburse a considerable amount for relief activities through the district administration machinery. Which of the following may possibly be a follow up measure to be taken by the Government?
The Government may set up a task force to review the post relief scenario in all districts and also to confirm proper end-user receipt of the relief supplies.
The Government may set up a committee for proper disbursement of relief supplies in the future.
The Government may empower the District magistrates to make all future disbursements of relief.
The Government may send relief supplies to the affected people in future only after proper assessment of the damage caused by such calamities.
The government may need not to activate any follow-up measure.
Directions These questions consist of a question and two statements numbered I and II given below it. You have to decide whether the data provided in the statements are sufficient to answer the question. Read both the statements and mark the appropriate answer.
Question:
In a building, the ground floor is numbered one, first floor is numbered two and so on till the topmost floor is numbered five. Amongst five people- M, N, O, P and Q, each living on a different floor, but not necessarily in the same order, on which floor does Q live?
Statement I: O lives on an odd-numbered floor. M lives immediately below O. Only two people live between M and P. N lives neither immediately below M nor immediately below P.
Statement II: N lives on an even-numbered floor. Only two people live between N and O. Only one person lives between O and Q.
The data even in both statements I and II together are not sufficient to answer the question.
The data in statement I alone are sufficient to answer the question while the data in statement II alone are not sufficient to answer the question.
The data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question.
The data in both statements I and II together are necessary to answer the question.
The data in statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question while the data in statement I are not sufficient to answer the question.
Directions These questions consist of a question and two statements numbered I and II given below it. You have to decide whether the data provided in the statements are sufficient to answer the question. Read both the statements and mark the appropriate answer.
Question:
Among people A, B, C, D, E and F, each having a different height, who is the second shortest?
Statement I: Only two people are taller than A. E is taller than both B and C. F is shorter than E. F is taller than C.
Statement II: Only two people are shorter than D. A is taller than D but shorter than E. F is neither the tallest nor the shortest. B is taller than C.
The data even in both statements I and II together are not sufficient to answer the question.
The data in statement I alone are sufficient to answer the question while the data in statement II alone are not sufficient to answer the question.
The data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question.
The data in both statements I and II together are necessary to answer the question.
The data in statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question while the data in statement I are not sufficient to answer the question.
Directions These questions consist of a question and two statements numbered I and II given below it. You have to decide whether the data provided in the statements are sufficient to answer the question. Read both the statements and mark the appropriate answer.
Question:
How many people are standing between A and D (Note: All are standing in a straight line facing north)?
Statement I: K stands second from the left end of the line. Only four people stand between K and T. Y is an immediate neighbour of T. A stands second to the right of Y. As many people stand between K and D as between A and D.
Statement II: A stands second from the right end of the line. Z stands third from the left end of the line. D stands exactly in the centre of the line. As many people stand between A and T as between D and Z.
The data even in both statements I and II together are not sufficient to answer the question.
The data in statement I alone are sufficient to answer the question while the data in statement II alone are not sufficient to answer the question.
The data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question.
The data in both statements I and II together are necessary to answer the question.
The data in statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question while the data in statement I are not sufficient to answer the question.
Directions These questions consist of a question and two statements numbered I and II given below it. You have to decide whether the data provided in the statements are sufficient to answer the question. Read both the statements and mark the appropriate answer.
Question:
How far and in which direction is Point M from Point S ?
Statement I: Point E is 2m to the east of Point S. Point B is 4m to the south of Point E. Point L is 10m to the east of Point B. Point L forms a midpoint of the vertical straight line of 8m formed by joining points Q and D. Point M is 5m to the west of Point Q.
Statement II: Point M is 8m to the north of Point A. Point M forms the midpoint of the horizontal straight line formed by joining points O and F. Point F is 8m to the west of Point O. Point S is 4m to the west of Point F.
The data even in both statements I and II together are not sufficient to answer the question.
The data in statement I alone are sufficient to answer the question while the data in statement II alone are not sufficient to answer the question.
The data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question.
The data in both statements I and II together are necessary to answer the question.
The data in statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question while the data in statement I are not sufficient to answer the question
Directions These questions consist of a question and two statements numbered I and II given below it. You have to decide whether the data provided in the statements are sufficient to answer the question. Read both the statements and mark the appropriate answer.
Question:
Amongst six people-P, Q R, S, T and U standing around a circle, some facing the centre while some facing outside (i.e. opposite to the centre) but not necessarily in the same order, what is the position of T with respect to U ?
Statement I: P stands second to the right of R. R faces the centre. Q stands second to the left of P. Q is an immediate neighbour of both U and T. U and P face opposite directions (i.e. if U faces the centre then P faces outside and vice-versa.) Only two people stand between P and T.
Statement II: Only two people stand between R and U. P stands to the immediate left of U. P faces outside. R is an immediate neighbour of T.
The data even in both statements I and II together are not sufficient to answer the question.
The data in statement I alone are sufficient to answer the question while the data in statement II alone are not sufficient to answer the question.
The data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question.
The data in both statements I and II together are necessary to answer the question.
The data in statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question while the data in statement I are not sufficient to answer the question.
Directions : In these questions, two/three statements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II are given. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Question:
Statements:
Some coffee is tea.
All tea is water.
All water is milk
. Conclusion
I: All coffee being water is a possibility.
Conclusion II: All milk is tea.
If either conclusion I or II follows
If neither conclusion I nor II follows
If only conclusion II follows
If both conclusions I and II follow
If only conclusion I follows
Directions : In these questions, two/three statements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II are given. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Question:
Statements:
No sea is a sky.
Some skies are kites.
All kites are balloons.
Conclusion I: Some balloons are seas.
Conclusion II: All balloons being skies is a possibility.
If either conclusion I or II follows
If neither conclusion I nor II follows
If only conclusion II follows
If both conclusions I and II follow
If only conclusion I follows
Directions : In these questions, two/three statements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II are given. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Question:
Statements:
Some stars are planets.
Some planets are galaxies.
Some galaxies are suns.
Conclusions I: All suns being galaxies is a possibility.
Conclusion II: Some galaxies are stars.
If either conclusion I or II follows
If neither conclusion I nor II follows
If only conclusion II follows
If both conclusions I and II follow
If only conclusion I follows
Directions : In these questions, two/three statements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II are given. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Question:
Statements:
All registers are pens.
All pens are pencils.
No pencil is rubber.
Conclusions I: No register is rubber.
Conclusion II: All pencils are pens.
If either conclusion I or II follows
If neither conclusion I nor II follows
If only conclusion II follows
If both conclusions I and II follow
If only conclusion I follows
Directions : In these questions, two/three statements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II are given. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Question:
Statements:
Some radios are televisions.
Some televisions are phones.
All phones are computers.
Conclusions I: All computers being televisions is a possibility.
Conclusion II: Some radios being phones is a possibility.
If either conclusion I or II follows
If neither conclusion I nor II follows
If only conclusion II follows
If both conclusions I and II follow
If only conclusion I follows
Directions : In these questions, two/three statements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II are given. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Question:
Statements:
All cats are dogs.
All wolves are dogs.
All dogs are jackals.
Conclusions I: All wolves are jackals.
Conclusion II: Atleast some jackals are cats.
If either conclusion I or II follows
If neither conclusion I nor II follows
If only conclusion II follows
If both conclusions I and II follow
If only conclusion I follows
Directions : Study the given information carefully to answer the given questions:
Seven boxes- A, B, C, D, E, F and G are kept one above the other, but not necessarily in the same order. Each box has a different number viz. 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 and 12, but not necessarily in the same order. Only three boxes are kept between G and box number 9. Only two boxes are kept between G and B. B is kept at one of the positions below box number 9. Only one box is kept between B and box number 4. E is kept immediately below box number 12. E is kept at one of the places above box number 9. There is only one box between E and the box having number less than E. E's box number is neither 7 nor 8. Only two boxes are kept between box number 5 and F. The difference between F and the box immediately below it is less than four. C is not the topmost box. C's box number is not 4. Only two boxes are kept between C and A.
Question:
What is the number of box C?
5
9
12
8
2
Directions : Study the given information carefully to answer the given questions:
Seven boxes- A, B, C, D, E, F and G are kept one above the other, but not necessarily in the same order. Each box has a different number viz. 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 and 12, but not necessarily in the same order. Only three boxes are kept between G and box number 9. Only two boxes are kept between G and B. B is kept at one of the positions below box number 9. Only one box is kept between B and box number 4. E is kept immediately below box number 12. E is kept at one of the places above box number 9. There is only one box between E and the box having number less than E. E's box number is neither 7 nor 8. Only two boxes are kept between box number 5 and F. The difference between F and the box immediately below it is less than four. C is not the topmost box. C's box number is not 4. Only two boxes are kept between C and A.
Question:
How many boxes are kept between E and box number 4?
Three
One
Two
None
More than three
Directions : Study the given information carefully to answer the given questions:
Seven boxes- A, B, C, D, E, F and G are kept one above the other, but not necessarily in the same order. Each box has a different number viz. 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 and 12, but not necessarily in the same order. Only three boxes are kept between G and box number 9. Only two boxes are kept between G and B. B is kept at one of the positions below box number 9. Only one box is kept between B and box number 4. E is kept immediately below box number 12. E is kept at one of the places above box number 9. There is only one box between E and the box having number less than E. E's box number is neither 7 nor 8. Only two boxes are kept between box number 5 and F. The difference between F and the box immediately below it is less than four. C is not the topmost box. C's box number is not 4. Only two boxes are kept between C and A.
Question:
What is the position of D in the given stack of boxes?
Fourth from the top
Fifth from the bottom
First from the top
Second from the bottom
Third from the bottom
Directions : Study the given information carefully to answer the given questions:
Seven boxes- A, B, C, D, E, F and G are kept one above the other, but not necessarily in the same order. Each box has a different number viz. 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 and 12, but not necessarily in the same order. Only three boxes are kept between G and box number 9. Only two boxes are kept between G and B. B is kept at one of the positions below box number 9. Only one box is kept between B and box number 4. E is kept immediately below box number 12. E is kept at one of the places above box number 9. There is only one box between E and the box having number less than E. E's box number is neither 7 nor 8. Only two boxes are kept between box number 5 and F. The difference between F and the box immediately below it is less than four. C is not the topmost box. C's box number is not 4. Only two boxes are kept between C and A.
Question:
Which of the following boxes is kept immediately above A? 1. B 2. Box number 5 3. Box number 7 4. G 5. Box number 4
B
Box number 5
Box number 7
G
Box number 4
Directions : Study the given information carefully to answer the given questions:
Seven boxes- A, B, C, D, E, F and G are kept one above the other, but not necessarily in the same order. Each box has a different number viz. 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 and 12, but not necessarily in the same order. Only three boxes are kept between G and box number 9. Only two boxes are kept between G and B. B is kept at one of the positions below box number 9. Only one box is kept between B and box number 4. E is kept immediately below box number 12. E is kept at one of the places above box number 9. There is only one box between E and the box having number less than E. E's box number is neither 7 nor 8. Only two boxes are kept between box number 5 and F. The difference between F and the box immediately below it is less than four. C is not the topmost box. C's box number is not 4. Only two boxes are kept between C and A.
Question:
Four of the following five are alike in a certain way and hence form a group.
Which of the following does not belong to the group?
B-4
C-7
E-2
D-9
A-8
Directions : Study the given information carefully to answer the given questions:
Seven boxes- A, B, C, D, E, F and G are kept one above the other, but not necessarily in the same order. Each box has a different number viz. 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 and 12, but not necessarily in the same order. Only three boxes are kept between G and box number 9. Only two boxes are kept between G and B. B is kept at one of the positions below box number 9. Only one box is kept between B and box number 4. E is kept immediately below box number 12. E is kept at one of the places above box number 9. There is only one box between E and the box having number less than E. E's box number is neither 7 nor 8. Only two boxes are kept between box number 5 and F. The difference between F and the box immediately below it is less than four. C is not the topmost box. C's box number is not 4. Only two boxes are kept between C and A.
Question:
Which of the following boxes is numbered 8?
A
F
B
G
D
A major portion of cash flow that country M yields is through agricultural activities. However, in the past half a decade the revenue earned from agriculture has noticeably reduced." — A report. Which of the given statements may be a reason for the given situation?
A. Country M is employing new techniques to yield good crop and boom the productivity.
B. Country M has faced two major droughts in the last five years.
C. The revenue from other industries has increased in the past five years.
Only B
Both A and B
Only A
Only C
All A, B and C
The ‘2019 cricket World Cup’ will be hosted by ___________
South Africa and Zimbabwe
England and Wales
South Africa and West Indies
India, Sri Lanka and Bangladesh
Australia and New Zealand
Anurag Thakur is the first serving BJP “Member of Parliament’ to join the territorial army as an officer. The constituency represented by Shri Thakur in the parliament is ___________
Hamirpur, Himachal Pradesh
Bikaner, Rajasthan
Hisar, Haryana
Hazaribagh, Jharkhand
Rohtak, Haryana
With a view to providing comprehensive support for start-ups and other self-employment activities, the government has set up ‘Self Environment and Talent Utilization’ (SETU) under the ___________
Mudra Bank
National Bank of Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI
NITI Aayog
Jeddah – based Islamic Development Bank has recently announced that it will open its first Indian branch in __________
Ahmedabad
Surat
New Delhi
Hyderabad
Mumbai
The Khangchendzonga National Park (KNP) is the first ‘mixed; heritage sort from India to make it to the UNESCO World Heritage List. The KNP is situated in the Indian state of __________
Tripura
Assam
Manipur
Odisha
Sikkim
According to the 2015 revision of the UN world population projection the world population in 2100 is projected to be around ___________
10.2 billion
11.2 billion
10.7 billion
9.7 billion
9.9 billion
The Union cabinet has recently (July 2016) approved setting up of a major part at Enayam near Colachel in the Indian state of _____________
Telangana
Kerala
Tamil Nadu
Karnataka
Andhra Pradesh
The Reserve Bank of India has authorised non-banks to operate “White Label ATMs’ under the provision of __________
Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934
Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881
Negotiable Instruments (Amendment) Act, 2015- 16
Banking Regulation Act, 1949
Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007
A new museum ‘The Stables’, constructed by the Central Public Works Department in a building which was earlier used as part of the stables, was inaugurated in ___________
Teen Murti House, New Delhi
Parliament House Annexe, New Delhi
Red Fort, New Delhi
National Museum, New Delhi
Rashtrapati Bhawan, New Delhi
The ‘Ringgit’ is the present-day currency of _____________
Singapore
Thailand
Malaysia
Myanmar
Bhutan
The State Bank of India (SBI) has recently (August 2016) unveiled a new home loan scheme ‘SBI Shaurya Home Loan’, which is targeted at _____________
Government employees other than defence personnel
Rural women
Senior citizens
Corporate women executives
Defence personnel
The headquarters of the ‘United Nations World Trade Organisation’ is situated in ____________
Madrid, Spain
Geneva, Switzerland
Washington DC, USA
Paris, France
Frankfurt, Germany
The first unit of the Kudankulam Power Plant was recently (August 2016) dedicated to the nation jointly by PM Narendra Modi and Russian President Vladimir Putin. The plant is situated in the Indian state of ____________
Maharashtra
Tamil Nadu
Karnataka
Andhra Pradesh
Kerala
The ‘PMKVY’ scheme pertains to _____________
Skill training/development
Rural irrigation facilities
Solar energy initiatives
Development of roads
Urban sanitation services
The city of ‘Ottawa’ is the capital of _________________
Australia
Canada
New Zealand
Chile
Cuba
The 750-MW Rewa ultra-mega solar power project is proposed to be set up in the Indian state of _________________
Andhra Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh
‘September 28’, the death anniversary of Louis Pasteur, observed every year as the _____________
World Heart Day
World Rabies Day
World Milk Day
World Thrombosis Day
World Health Day
Kalikho Pul, who was recently (August 2016) found dead under mysterious circumstances was the former Chief Minister of the Indian state of _____________
Meghalaya
Tripura
Arunachal Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh
Assam
The National Thermal Power Corporation Limited’ (NTPC) had recently (August 2016) listed the first Indian quasi-sovereign ‘green Masala bond’ on London Stock Exchange (LSE) and had raised an amount of _____________
USD500 million
USD100 million
USD450 million
USD300 million
USD400 million
The Reserve Bank of India prepared a ‘Financial stability Report’ (FSR) on _________ basis for the apex – level Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC).
once in four years
Monthly
Quarterly
Half-yearly
Yearly
The first SAARC Young Parliamentarians Conference (YPC) was recently (August 2016) held in ____________
New Delhi, India
Thimphu, Bhutan
Islamabad, Pakistan
Kabul, Afghanistan
Kathmandu, Nepal
According to the 2011 census, the Indian state that has the dubious distinction of having the worst male-female ratio is ____________
Punjab
Jammu and Kashmir
Uttar Pradesh
Bihar
Haryana
The “IFSC Code’ is an alphanumeric code comprising 11 characters that facilitates electronic fund transfer in the country. The alphabet ‘I’ in the abbreviation ‘IFSC’ stands for ______________
Inter-bank
Indian
International
Intercontinental
Institutional
‘Kudsi Erguner’, player of the ‘ney’ (reed flute), has recently been named as the UNESCO artist for peace 2016. He is a well-known musicologist and composer from __________
Ukraine
Belarus
Russia
Azerbaijan
Turkey
The International meeting on Counter-Terrorism was recently (August 2016) held in ____________
Rawalpindi, Pakistan
Bali, Indonesia
London, England
Moscow, Russia
Paris, France
India’s first ‘International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) banking unit, set by YES bank, has started operations at GIFT city in the Indian state of __________________
Andhra Pradesh
Gujarat
Telangana
Maharashtra
Kerala
The human rights activists from India who is amongst the winners of 2016 Ramon Magsaysay Award is ____________
Rahul Verma
Shantha Sinha
Bezwada Wilson
Ajamu Baraka
Kailash Satyarthi
Which of the following has recently (August 2016) been appointed as head of a legal panel by the BCCI to help implementation of the Justice Lodha Committee reforms?
Justice HL Dattu
Justice Altamas Kabir
Justice P Sathasivam
Justice Markandey Katju
Justice SH Kapadia
The first Indian captain to score a double century in a test match outside India is _______________
Rahul Dravid
Virender Sehwag
Anil Kumble
Virat Kohli
MS Dhoni
Under the Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY), the risk coverage is Rs. 2 lakh for accidental death and full disability and Rs. 1 lakh for partial disability. The cover is however not available to ____________
Senior citizens up to the age of 70 years only
Housewives and women
Illiterate adults
Individuals below 18 years of age
Physically handicapped adults
In India ‘Commodities derivatives market’ is regulated by ______________
PFRDA
FCI
IRDAI
SEBI
RBI
Who amongst the following has recently (July 2016) been appointed as the chairperson of Lok Sabha privilege committee?
NCP MP Supriya Sela
BJP MP Meenakshi Lekhi
BJP MP Poonam Mahajan
SP MP Dimple Yadav
BJP MP Kirron Kher
The 2016 “WEF Indian Economic summit” is going to be held in ____________
Geneva, Switzerland
Vienna, Austria
Paris, France
New Delhi, India
Other than those given options
Researchers have recently spotted 101 species of spiders belonging to 65 genera from the “Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary’ situated in ________________
Goa
Assam
Kerala
Uttar Pradesh
Odisha
The ‘Bhimbetka Rock Shelters’, a world heritage site, is situated in the Indian state of ____________
Uttar Pradesh
Chhattisgarh
Jharkhand
Odisha
Madhya Pradesh
Chairman of the “Bank Board of Bureau’ (BBB), Shri Vinod Rai, has recently stepped down from the board of ______________
HSBC Bank
ICICI Bank
IDBI Bank
HDFC Bank
IDFC Bank
The first technology meet under the Hydrocarbon vision 2030 for Northeast India was recently (August 2016) held in ________________
Itanagar
Guwahati
Dispur
Imphal
New Delhi
A coup was recently (July 2016) attempted (but failed) against the state institution including the government by a fraction within a country’s armed forces in which of the following countries?
Turkey
Portugal
Jordan
Cuba
Ukraine
‘Vembanad Lake’ is the longest lake in India and the largest lake in the Indian state of ___________
Kerala
Sikkim
Odisha
Assam
Gujarat
Recently introduced by National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), the ‘NACH’ is a centralized ____________
Application processing for the bank system
None of the given as options
Electronic clearing system
Core banking system
Credit appraisal system
SMERA ratings Limited is a joint initiative of Dum and Bradstreet Information Services India Private Limited (D&B), leading public/private sector banks in India and _____________
ICICI
IFCI
SIDBI
RBI
IDBI
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has introduced from April 1, 2016, a new methodology of setting lending rate by commercial banks and will replace the existing method identify the new methodology.
PLR
MCLR
Base rate system
BPLR
None of the above
With a view to training 1.24 lac youth from Jammu & Kashmir in vocational courses under the skill development initiative ‘Himayat Programmes’, the Government of India has recently (July 2016) allocated an amount of ________ for the programme
Rs. 1401 crores
Rs. 1601 crores
Rs. 110 crores
Rs. 120 crores
Rs. 100 crores
The ‘Rabobank’ is a Dutch multinational financial banking company headquartered in ____________
Limburg
Utrecht
Gelderland
Zeeland
Flevoland
‘M – Pesa’, a mobile-based money transfer and payment service, was launched by Vodafone in the year 2007. In India, Vodafone India launched it in 2013 in association with _____________
YES Bank
SBI
HDFC Bank
Kotak Mahindra Bank
ICICI Bank
State Bank of India (SBI) has initiated the process of merging its five associate banks with itself. The merged entity would create a financial sector powerhouse with total assets estimated to be worth around ______________
Rs. 37 lakh crores
Rs. 72 lakh crores
Rs. 60 lakh crores
Rs. 48 lakh crores
Rs. 15 lakh crores
According to RBI guidelines, a non-banking entity seeking authorisation as ‘Bharat Bill Payment Operating Unit (BBPOU) under the proposed Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS) should have a minimum net worth of at least _______________
Rs. 500 lakh crores
Rs. 400 lakh crores
Rs. 300 lakh crores
Rs. 200 lakh crores
Rs. 100 lakh crores
Eminent litterateur Mahim Bora, who died recently (August 2016) at the age of 92, was a well – known literary figure and educationalist from the Indian state of _____________
West Bengal
Tripura
Assam
Meghalaya
Manipur
The operation “Raahat’ was an operation if the Indian Armed Forces to evacuate Indian citizens and other foreign nationals from __________ in 2015.
Syria
Iraq
Yemen
Sudan
Turkey
The ‘Srisail Dam’ is constructed across the Krishna river in the Indian states of _____________
Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh
Telangana and Andhra Pradesh
Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh
Telangana and Madhya Pradesh
Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh
Which web portal has been launched to reduce paperwork in the Lok Sabha, the lower house of parliament of India?
e - portal
m - portal
w - portal
n - portal
s - portal
Which of the following is not the part of the structure of the financial system in India?
Industrial Finance
Agricultural Finance
Government Finance
Personal Finance
All of these are part of it
Prior to the establishment of the Reserve Bank of India, the government banking business was conducted by which of the following organisations?
Bank of India
Central Bank of India
Imperial Bank of India
National bank of India
Bank of Baroda
Which expert committee has been constituted to explore alternatives to pellet guns as non – lethal weapons?
Rajesh Kumar Committee
Rajeev Krishna Committee
TVSN Prasad Committee
Tushar Tripathy Committee
Other than those given as an option
Which of the following is not a general credit control measure?
Bank rate
Variable reserve ratios
Open market operation
Regulation of margin requirements on advances against agricultural commodities
Other than those given as an option
Which state government has recently signed a pact with Japan to develop the food value chain in the state?
Karnataka
Maharashtra
Kerala
Andhra Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh
The process of the total valuation of the financial capital assess of a country is known as ___________________
Market capitalisation
Other than those given option
Gross Domestic Product
Net Wealth of a country
Gross Domestic Resources
The 2016 India International Footwear Fair (IIFF) has started in which of the following cities?
New Delhi
Kanpur
Jaipur
Bhopal
Mumbai
The term ‘hyper-inflation’ means ________________
a situation with a moderate rise in the price level
an inflationary situation where the external sources are the primary contributing factors
a ‘runaway’ or ‘galloping’ inflationary situation where the monetary unit becomes almost worthless
a situation where the cost of living index is rising alarmingly
other than those given as options
Which state tourism has recently (August 2016) organised a ‘Freedom Ride’?
Madhya Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh
Goa
Maharashtra
Punjab
The world’s tallest girder rail bridge will come up in which of the following states of India?
Sikkim
Manipur
Himachal Pradesh
Jammu and Kashmir
Uttar Pradesh
n the presence of Bangladesh railway minister, the Union Railway Minister Suresh Prabhu recently flagged off the Tripura Sundari Express which will run between Agartala and ____________
Kolkata
Delhi
Guwahati
Chittagong
Dhaka
‘ONICRA’ is a leading _________________
Credit and performance rating agency
Asset Reconstruction Company
White Label ATM Operator
Asset Management Company
None of these
The ‘Hopman Cup’ is associated with the game of ______________
Football
Cricket
Tennis
Hockey
Badminton
IOM’s stated mission is to promote humane and orderly migration by providing services and advice to governments and migrants. What does IOM stand for?
International Organisation for Migration
International Organisation for Maritime
Interstate Organisation for Maritime
Interstate for Organisation for Migration
Institute for Organisation for Migration
Which of the following is an autobiography of lawn tennis star Sania Mirza?
From Fear to Victory
Playing It My Way
The Test of My Life
Ace Against Odds
Straight from the Heart: An Autobiography
The ‘Sultan Azlan Shah Cup’ is related to the game of _____________
Football
Hockey
Tennis
Badminton
Cricket
Kananur Lokesh Rahul, commonly known as KL Rahul, is related to which of the following sports?
Cricket
Basketball
Tennis
Badminton
Volleyball
The sportsperson who has won overall 23 gold medals in four Olympic is ____________
Larisa Latynina
Paavo Nurmi
Mark Spitz
Usain Bolt
Michael Phelps
The headquarters of Canara bank is situated on the Indian city of _____________
Delhi
Mumbai
Kolkata
Bangalore
Chennai
Who is the author of the book Exploring Marxist Bengal?
Suman Panda
Debraj Bhattacharya
Swati Bose
Chandra Banerjee
Swami Dixit
Who has won the 2016 World Snooker Championship?
Judd Trump
Steve Davis
Mark Selby
Ding Junhui
Aditya Mehta
What is the theme of the 2016 International Museum day?
Museums collection Make Connections
Museums and Cultural Landscapes
Museums for a Sustainable Society
Museums for a Social Harmony
Museums for a Better Tomorrow
The 42nd G7 summit UN 2016 was held in which country?
Japan
Canada
France
Germany
India
Banks do not provide which of the following services?
Issuing bank drafts
Depositing money
Sale of post cards and postal stamps
Lockers for valuable items/ documents
Lending money
What is the range of the advanced version of BrahMos missile, which awes recently successfully tested by the Indian Airforce?
290 km
320 km
450 km
250 km
300 km
Which of the following cities has become India’ first city to have its own “City Animal”?
Shillong
Guwahati
Lucknow
Hyderabad
Delhi
Which campaign has been launched to make gram panchayats along the banks of Ganga Open Defecation Free?
Swachh Nirbhay
Swachh Ganga
Swachh Village
Swachh Yug
Swachh Bharat
‘Raj Vayu’ mobile app has been launched by which state government for sharing data of air quality index?
Uttar Pradesh
Jharkhand
Rajasthan
Uttarakhand
Madhya Pradesh
Which country has been elected for the first time to chair the UN’s legal affairs committee?
Ukraine
Israel
Uruguay
Senega
Sweden