Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Seven persons i.e. P, Q, R, S, T, U, V of different ages i.e. 6, 15, 19, 23, 30, 45, 60 years are sitting in a circular table facing towards center.
Note- No two consecutive letters are in alphabetical order. Person’s age must not be a factor or a multiple of sum of the ages of their immediate neighbors.
R sits immediate right of the person whose age is 15. One person sits between T and R (either left or right). One person sits between P and the person whose age is 6 (either left or right). Age of T is twice the age of the person who sits 2nd to the right of T. Difference between the age of the immediate neighbors of V is more than 14. Age of U must not be multiple of 10. Sum of the ages of immediate neighbors of R is 34. Q is younger than P.
Question:
What is the age of Q?
15
60
23
6
None of these
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Seven persons i.e. P, Q, R, S, T, U, V of different ages i.e. 6, 15, 19, 23, 30, 45, 60 years are sitting in a circular table facing towards center.
Note- No two consecutive letters are in alphabetical order. Person’s age must not be a factor or a multiple of sum of the ages of their immediate neighbors.
R sits immediate right of the person whose age is 15. One person sits between T and R (either left or right). One person sits between P and the person whose age is 6 (either left or right). Age of T is twice the age of the person who sits 2nd to the right of T. Difference between the age of the immediate neighbors of V is more than 14. Age of U must not be multiple of 10. Sum of the ages of immediate neighbors of R is 34. Q is younger than P.
Question:
Who among the following sits 2nd to the left of the person whose age is 19 years?
U
V
P
Q
None of these
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Seven persons i.e. P, Q, R, S, T, U, V of different ages i.e. 6, 15, 19, 23, 30, 45, 60 years are sitting in a circular table facing towards center.
Note- No two consecutive letters are in alphabetical order. Person’s age must not be a factor or a multiple of sum of the ages of their immediate neighbors.
R sits immediate right of the person whose age is 15. One person sits between T and R (either left or right). One person sits between P and the person whose age is 6 (either left or right). Age of T is twice the age of the person who sits 2nd to the right of T. Difference between the age of the immediate neighbors of V is more than 14. Age of U must not be multiple of 10. Sum of the ages of immediate neighbors of R is 34. Q is younger than P.
Question:
Which of the following is true?
S’s age is 60 years
R is younger than Q
U sits immediate right of P
V’s age is 19
None is true
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Seven persons i.e. P, Q, R, S, T, U, V of different ages i.e. 6, 15, 19, 23, 30, 45, 60 years are sitting in a circular table facing towards center.
Note- No two consecutive letters are in alphabetical order. Person’s age must not be a factor or a multiple of sum of the ages of their immediate neighbors.
R sits immediate right of the person whose age is 15. One person sits between T and R (either left or right). One person sits between P and the person whose age is 6 (either left or right). Age of T is twice the age of the person who sits 2nd to the right of T. Difference between the age of the immediate neighbors of V is more than 14. Age of U must not be multiple of 10. Sum of the ages of immediate neighbors of R is 34. Q is younger than P.
Question:
What is the position of V with respect to P?
Immediate left
Immediate right
2nd to the left
2nd to the right
None of these
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Seven persons i.e. P, Q, R, S, T, U, V of different ages i.e. 6, 15, 19, 23, 30, 45, 60 years are sitting in a circular table facing towards center.
Note- No two consecutive letters are in alphabetical order. Person’s age must not be a factor or a multiple of sum of the ages of their immediate neighbors.
R sits immediate right of the person whose age is 15. One person sits between T and R (either left or right). One person sits between P and the person whose age is 6 (either left or right). Age of T is twice the age of the person who sits 2nd to the right of T. Difference between the age of the immediate neighbors of V is more than 14. Age of U must not be multiple of 10. Sum of the ages of immediate neighbors of R is 34. Q is younger than P.
Question:
Who among the following is oldest person?
Q
P
U
V
None of these
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Books which have different number of pages is shown below with their codes.
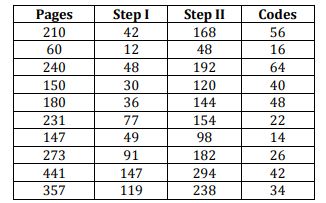
If number of pages in different books are 90, 120, 270, 300, 330, 315, 231, 567, 399, 525 then find the codes of these books as per the above-mentioned operations and placed these books in two different stores i.e. A and B. Arrange all codes in ascending order. After arranging the codes, first five codes are placed in store A and last five are placed in store B. Now, answer the given questions
Question:
Which of the following page book have highest code in store A?
315
120
399
525
567
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Books which have different number of pages is shown below with their codes.

If number of pages in different books are 90, 120, 270, 300, 330, 315, 231, 567, 399, 525 then find the codes of these books as per the above-mentioned operations and placed these books in two different stores i.e. A and B. Arrange all codes in ascending order. After arranging the codes, first five codes are placed in store A and last five are placed in store B. Now, answer the given questions
Question:
Which of the following pages book is not in store B?
270
300
330
525
315
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Books which have different number of pages is shown below with their codes.

If number of pages in different books are 90, 120, 270, 300, 330, 315, 231, 567, 399, 525 then find the codes of these books as per the above-mentioned operations and placed these books in two different stores i.e. A and B. Arrange all codes in ascending order. After arranging the codes, first five codes are placed in store A and last five are placed in store B. Now, answer the given questions
Question:
What is the difference in the codes of 2nd lowest code in store A and 2nd highest code in store B?
66
56
64
58
None of these
tudy the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
P@Q means P is neither smaller nor equal to Q
P$Q means P is not smaller than Q
P%Q means P is not greater than Q
P*Q means P is neither smaller nor greater than Q
P#Q means P is neither greater nor equal to Q
Question:
Statements: A$B%F#D, Y@M*F
Conclusion
I: B#M
II: A%Y
III: Y@B
Only I follow
Only II follows
Only III follows
I and III follows
I and II follows
tudy the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
P@Q means P is neither smaller nor equal to Q
P$Q means P is not smaller than Q
P%Q means P is not greater than Q
P*Q means P is neither smaller nor greater than Q
P#Q means P is neither greater nor equal to Q
Question:
Statements: M*J%G$B#X@L, S%U$N@M
Conclusion
I: S#L
II: J#U
III: G@N
Only I follow
Only II follows
Only III follows
I and III follows
I and II follows
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
P@Q means P is married to Q
P#Q means P is parent of Q
P&Q means P is sibling of Q and both are of same gender
P$Q means P is sibling of Q and both are of different gender
P+ means P is male
P* means P is female
Question:
If J@F*#T$R, V@R+#B&A, F#Q#D is true and D is only niece of T then, how is Q related to B?
Uncle
Aunt
Sister
Brother
Can’t be determined
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
P@Q means P is married to Q
P#Q means P is parent of Q
P&Q means P is sibling of Q and both are of same gender
P$Q means P is sibling of Q and both are of different gender
P+ means P is male
P* means P is female
Question:
If J@F*#T$R, V@R+#B&A, F#Q#D, Q+@W#N is true and D is only niece of T then, how is J related to N?
Grandfather
Grand mother
Grand son
Granddaughter
Can’t be determined
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
P@Q means P is married to Q
P#Q means P is parent of Q
P&Q means P is sibling of Q and both are of same gender
P$Q means P is sibling of Q and both are of different gender
P+ means P is male
P* means P is female
Question:
If J@F*#T$R, V@R+#B&A, F#Q#D, Q+@W#N is true and D is only niece of T then, how many male members are in the family?
Three
Four
Five
Seven
Six
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Thirteen boxes of different colors are placed one above another in alphabetical order either from bottom or from top. Each box contains different number of toffees which is multiple of 13. Maximum toffees in a box is 169.
There are equal number of boxes are placed above as well as below J. Two boxes are placed between box J and the Pink colored box. Five Boxes are placed between Pink and Yellow colored box. Box which have 13 toffees is placed just below Yellow colored box. Black colored box is placed just above Red colored box and just below the box which have 169 toffees. There are as many boxes are placed above Red colored box as below the box which have 13 toffees. White colored box is placed just above the box which have 65 toffees and just below the box which have 104 toffees. There are as many boxes are placed between the boxes which have 13 and 52 toffees as between the boxes which have 52 and 104 toffees. Two boxes are placed between Blue colored box which doesn’t have 13 toffees and Green colored box which is placed just below J.
Question:
If box F have 13 toffees, then which of the following is Pink colored box?
M
Box which have 52 toffees
G
Box which have 169 toffees
Can’t be determined
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Thirteen boxes of different colors are placed one above another in alphabetical order either from bottom or from top. Each box contains different number of toffees which is multiple of 13. Maximum toffees in a box is 169.
There are equal number of boxes are placed above as well as below J. Two boxes are placed between box J and the Pink colored box. Five Boxes are placed between Pink and Yellow colored box. Box which have 13 toffees is placed just below Yellow colored box. Black colored box is placed just above Red colored box and just below the box which have 169 toffees. There are as many boxes are placed above Red colored box as below the box which have 13 toffees. White colored box is placed just above the box which have 65 toffees and just below the box which have 104 toffees. There are as many boxes are placed between the boxes which have 13 and 52 toffees as between the boxes which have 52 and 104 toffees. Two boxes are placed between Blue colored box which doesn’t have 13 toffees and Green colored box which is placed just below J.
Question:
What is the sum of the toffees of Blue and Green colored box?
273
156
117
65
Can’t be determined
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Thirteen boxes of different colors are placed one above another in alphabetical order either from bottom or from top. Each box contains different number of toffees which is multiple of 13. Maximum toffees in a box is 169.
There are equal number of boxes are placed above as well as below J. Two boxes are placed between box J and the Pink colored box. Five Boxes are placed between Pink and Yellow colored box. Box which have 13 toffees is placed just below Yellow colored box. Black colored box is placed just above Red colored box and just below the box which have 169 toffees. There are as many boxes are placed above Red colored box as below the box which have 13 toffees. White colored box is placed just above the box which have 65 toffees and just below the box which have 104 toffees. There are as many boxes are placed between the boxes which have 13 and 52 toffees as between the boxes which have 52 and 104 toffees. Two boxes are placed between Blue colored box which doesn’t have 13 toffees and Green colored box which is placed just below J.
Question:
If M is Yellow colored box and sum of toffees in box O and D is equal to the sum of toffees in box H and L then, what is difference between the toffees of box L and O?
52
78
65
91
Can’t be determined
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Thirteen boxes of different colors are placed one above another in alphabetical order either from bottom or from top. Each box contains different number of toffees which is multiple of 13. Maximum toffees in a box is 169.
There are equal number of boxes are placed above as well as below J. Two boxes are placed between box J and the Pink colored box. Five Boxes are placed between Pink and Yellow colored box. Box which have 13 toffees is placed just below Yellow colored box. Black colored box is placed just above Red colored box and just below the box which have 169 toffees. There are as many boxes are placed above Red colored box as below the box which have 13 toffees. White colored box is placed just above the box which have 65 toffees and just below the box which have 104 toffees. There are as many boxes are placed between the boxes which have 13 and 52 toffees as between the boxes which have 52 and 104 toffees. Two boxes are placed between Blue colored box which doesn’t have 13 toffees and Green colored box which is placed just below J.
Question:
Which of the following colored box have 52 toffees?
Red
Pink
Blue
Green
None of these
Statement: “The simplest and the most cost effective way to upgrade your home–Exchange your old furniture and get 25% to 33% off on the new furniture”.—An advertisement of a furniture company.
Assumptions
I. Now-a-days, there is no demand for furniture products unless some attractive scheme is offered.
II. Some customers always desire to have best quality and do not bother either for cost or for convenience.
III. Some customers want to keep their home up-todate with reasonable cost and with fewer hassles.
Only I is implicit
Only II is implicit
Only III is implicit
I and II are implicit
None of these
Statement: The situation of this area still continues to be tense and out of control. People are requested to be in their homes only.
Assumptions
I. There had been some serious incidents.
II. People will not go to the office.
III. Normally will be restored shortly.
Only I is implicit
I and II are implicit
None is implicit
I and III are implicit
All are implicit
Statement: Should the consumption of aerated drinks be banned in India?
Arguments:
I. Yes, this is the only way to reduce the risk of exposing people to some diseases.
II. No, each individual should have right to choose what he wants.
III. No, there is no confirmed evidence that such products have adverse effects on human body. IV. Yes, it is banned in many other countries also.
Only I is strong
I and II are strong
Only III is strong
I and IV are strong
All are strong
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
P@Q means P is East of Q and the distance between P and Q is either 4m or 15m
P#Q means P is West of Q and the distance between P and Q is either 7m or 18m
P&Q means P is North of Q and the distance between P and Q is either 4m or 15m
P%Q means P is South of Q and the distance between P and Q is either 7m or 18m
J&K#L%M, B&N#M, BNML
Question:
What is the direction of K with respect to B?
North-west
South-west
North-east
South-east
Can’t be determined
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
P@Q means P is East of Q and the distance between P and Q is either 4m or 15m
P#Q means P is West of Q and the distance between P and Q is either 7m or 18m
P&Q means P is North of Q and the distance between P and Q is either 4m or 15m
P%Q means P is South of Q and the distance between P and Q is either 7m or 18m
J&K#L%M, B&N#M, BNML
Question:
If X is 11m West of B then, what is the distance between X and J?
7m
4m
6m
10m
11m
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
P@Q means P is East of Q and the distance between P and Q is either 4m or 15m
P#Q means P is West of Q and the distance between P and Q is either 7m or 18m
P&Q means P is North of Q and the distance between P and Q is either 4m or 15m
P%Q means P is South of Q and the distance between P and Q is either 7m or 18m
J&K#L%M, B&N#M, BNML
Question:
Four of the following five are alike in certain way and hence form a group, find the one which does not belong to that group?
BM
BL
NL
KN
JM
Some alphabets are given below. First arrange them in alphabetical order from left to right then number them I, II, III, IV, V from left to right.
1) J, P, D, B, S
2) C, M, A, Q, X
3) W, I, T, N, O
Arrange all separately in each number. Which of the following is in alphabetical order?
(a) Only I and III
Only II and IV
Only II and III
Only III and IV
Only II, III and IV
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Eleven seats are placed in a single row in which three seats are vacant. Persons sitting in these seats are facing North. No two vacant seats are placed adjacent to each other. Persons are of different ages. Seats are numbered 1 to 11 from West to East.
Note- Two Persons sitting between P and Q doesn’t means that there are only two seats are placed between them. There may be vacant seats between them.
Three persons sit between A and B. Person who is 32 years old sits immediate left of B. D and E are immediate neighbors of A whose seat number is less than 6. B is as many years older than H as younger than D. C sits 3rd to the left of A. One person sits between G and F who is 40 years old. Sum of the age of D and G is 82. H sits immediate left of one ofthe vacant seats. Age of His half the age of the person who sits at seat number 11. Persons whose age are 26 and 28 years sit at odd numbered seats. D sits left of the person whose age is 22 years and right of the person whose age is 28 years. No vacant seat is between H and the person whose age is 22 years.
Question:
Who among the following sits at seat number 8?
No One
G
B
H
None of these
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Eleven seats are placed in a single row in which three seats are vacant. Persons sitting in these seats are facing North. No two vacant seats are placed adjacent to each other. Persons are of different ages. Seats are numbered 1 to 11 from West to East.
Note- Two Persons sitting between P and Q doesn’t means that there are only two seats are placed between them. There may be vacant seats between them.
Three persons sit between A and B. Person who is 32 years old sits immediate left of B. D and E are immediate neighbors of A whose seat number is less than 6. B is as many years older than H as younger than D. C sits 3rd to the left of A. One person sits between G and F who is 40 years old. Sum of the age of D and G is 82. H sits immediate left of one ofthe vacant seats. Age of His half the age of the person who sits at seat number 11. Persons whose age are 26 and 28 years sit at odd numbered seats. D sits left of the person whose age is 22 years and right of the person whose age is 28 years. No vacant seat is between H and the person whose age is 22 years.
Question:
How many persons are sitting between the persons whose age are 22 and 35 years?
Four
Two
Three
Five
None of these
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Eleven seats are placed in a single row in which three seats are vacant. Persons sitting in these seats are facing North. No two vacant seats are placed adjacent to each other. Persons are of different ages. Seats are numbered 1 to 11 from West to East.
Note- Two Persons sitting between P and Q doesn’t means that there are only two seats are placed between them. There may be vacant seats between them.
Three persons sit between A and B. Person who is 32 years old sits immediate left of B. D and E are immediate neighbors of A whose seat number is less than 6. B is as many years older than H as younger than D. C sits 3rd to the left of A. One person sits between G and F who is 40 years old. Sum of the age of D and G is 82. H sits immediate left of one ofthe vacant seats. Age of His half the age of the person who sits at seat number 11. Persons whose age are 26 and 28 years sit at odd numbered seats. D sits left of the person whose age is 22 years and right of the person whose age is 28 years. No vacant seat is between H and the person whose age is 22 years.
Question:
In which of the following seat the person whose age is 26 years are sitting?
Seat number 3
Seat number 1
Seat number 5
Seat number 7
None of these
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Eleven seats are placed in a single row in which three seats are vacant. Persons sitting in these seats are facing North. No two vacant seats are placed adjacent to each other. Persons are of different ages. Seats are numbered 1 to 11 from West to East.
Note- Two Persons sitting between P and Q doesn’t means that there are only two seats are placed between them. There may be vacant seats between them.
Three persons sit between A and B. Person who is 32 years old sits immediate left of B. D and E are immediate neighbors of A whose seat number is less than 6. B is as many years older than H as younger than D. C sits 3rd to the left of A. One person sits between G and F who is 40 years old. Sum of the age of D and G is 82. H sits immediate left of one ofthe vacant seats. Age of His half the age of the person who sits at seat number 11. Persons whose age are 26 and 28 years sit at odd numbered seats. D sits left of the person whose age is 22 years and right of the person whose age is 28 years. No vacant seat is between H and the person whose age is 22 years.
Question:
Which of the following is true regarding C?
C doesn’t sit at seat number 1
One of the vacant seats is not adjacent to C
C’s age is 22 years
Two persons are sitting between A and C
None is true
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Eleven seats are placed in a single row in which three seats are vacant. Persons sitting in these seats are facing North. No two vacant seats are placed adjacent to each other. Persons are of different ages. Seats are numbered 1 to 11 from West to East.
Note- Two Persons sitting between P and Q doesn’t means that there are only two seats are placed between them. There may be vacant seats between them.
Three persons sit between A and B. Person who is 32 years old sits immediate left of B. D and E are immediate neighbors of A whose seat number is less than 6. B is as many years older than H as younger than D. C sits 3rd to the left of A. One person sits between G and F who is 40 years old. Sum of the age of D and G is 82. H sits immediate left of one ofthe vacant seats. Age of His half the age of the person who sits at seat number 11. Persons whose age are 26 and 28 years sit at odd numbered seats. D sits left of the person whose age is 22 years and right of the person whose age is 28 years. No vacant seat is between H and the person whose age is 22 years.
Question:
What is the age of the person who sits 2nd to the left of the person whose age is 26 years?
28 years
22 years
40 years
50 years
None of these
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Eight persons are working in three different cities i.e.Delhi, Pune, Hyderabad. At least two persons are working in a city. There are four married couples of two generations. Number of males and females are equal in each city.
Note- Married couples are not working in same city. They have different designations i.e. GM, AGM, CEO, Manager, Assistant Manager, PO, Clerk, Sub staff (these are in decreasing order of seniority means GM is senior most and Sub staff is junior most person).
Only three persons are senior than the only son of B. B doesn’t work in Pune. E is sister in law of G who is junior most person. H is son in law of D, who is immediate senior of A. F is spouse of C and both are not working in Delhi. There are as many posts above father in law of A as below sibling of A. Only C and H are working in Hyderabad. Only PO and Sub staff are working in Delhi. Spouse of E is not working in Delhi. G is daughter in law of B who is spouse of D. F is senior than H and junior than C. 30. How many persons are junior than
Question:
How many persons are junior than H?
Three
Four
Two
Five
None of these
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Eight persons are working in three different cities i.e.Delhi, Pune, Hyderabad. At least two persons are working in a city. There are four married couples of two generations. Number of males and females are equal in each city.
Note- Married couples are not working in same city. They have different designations i.e. GM, AGM, CEO, Manager, Assistant Manager, PO, Clerk, Sub staff (these are in decreasing order of seniority means GM is senior most and Sub staff is junior most person).
Only three persons are senior than the only son of B. B doesn’t work in Pune. E is sister in law of G who is junior most person. H is son in law of D, who is immediate senior of A. F is spouse of C and both are not working in Delhi. There are as many posts above father in law of A as below sibling of A. Only C and H are working in Hyderabad. Only PO and Sub staff are working in Delhi. Spouse of E is not working in Delhi. G is daughter in law of B who is spouse of D. F is senior than H and junior than C. 30. How many persons are junior than
Question:
Which of the following combination is true?
B-PO-Delhi
C-CEO-Hyderabad
H-Clerk-Hyderabad
F-AGM-Delhi
None is true
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Eight persons are working in three different cities i.e.Delhi, Pune, Hyderabad. At least two persons are working in a city. There are four married couples of two generations. Number of males and females are equal in each city.
Note- Married couples are not working in same city. They have different designations i.e. GM, AGM, CEO, Manager, Assistant Manager, PO, Clerk, Sub staff (these are in decreasing order of seniority means GM is senior most and Sub staff is junior most person).
Only three persons are senior than the only son of B. B doesn’t work in Pune. E is sister in law of G who is junior most person. H is son in law of D, who is immediate senior of A. F is spouse of C and both are not working in Delhi. There are as many posts above father in law of A as below sibling of A. Only C and H are working in Hyderabad. Only PO and Sub staff are working in Delhi. Spouse of E is not working in Delhi. G is daughter in law of B who is spouse of D. F is senior than H and junior than C. 30. How many persons are junior than
Question:
Who among the following is Assistant Manager?
B
D
C
F
None of these
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Eight persons are working in three different cities i.e.Delhi, Pune, Hyderabad. At least two persons are working in a city. There are four married couples of two generations. Number of males and females are equal in each city.
Note- Married couples are not working in same city. They have different designations i.e. GM, AGM, CEO, Manager, Assistant Manager, PO, Clerk, Sub staff (these are in decreasing order of seniority means GM is senior most and Sub staff is junior most person).
Only three persons are senior than the only son of B. B doesn’t work in Pune. E is sister in law of G who is junior most person. H is son in law of D, who is immediate senior of A. F is spouse of C and both are not working in Delhi. There are as many posts above father in law of A as below sibling of A. Only C and H are working in Hyderabad. Only PO and Sub staff are working in Delhi. Spouse of E is not working in Delhi. G is daughter in law of B who is spouse of D. F is senior than H and junior than C. 30. How many persons are junior than
Question:
Which of the following is the designation of father of G?
GM
AGM
Sub Staff
Manager
None of these
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Eight persons are working in three different cities i.e.Delhi, Pune, Hyderabad. At least two persons are working in a city. There are four married couples of two generations. Number of males and females are equal in each city.
Note- Married couples are not working in same city. They have different designations i.e. GM, AGM, CEO, Manager, Assistant Manager, PO, Clerk, Sub staff (these are in decreasing order of seniority means GM is senior most and Sub staff is junior most person).
Only three persons are senior than the only son of B. B doesn’t work in Pune. E is sister in law of G who is junior most person. H is son in law of D, who is immediate senior of A. F is spouse of C and both are not working in Delhi. There are as many posts above father in law of A as below sibling of A. Only C and H are working in Hyderabad. Only PO and Sub staff are working in Delhi. Spouse of E is not working in Delhi. G is daughter in law of B who is spouse of D. F is senior than H and junior than C. 30. How many persons are junior than
Question:
Who is immediate junior as well as immediate senior of the persons who are working in Delhi?
G
F
E
D
None of these
. Statement- The Blue Whale Challenge is reportedly a suicide game in which the player is given certain tasks to complete over a period of 50 days and the final task leads him or her to commit suicide. Taking a serious view of the Blue Whale Challenge game, the Madras High Court directed the Central and Tamil Nadu governments to explore possibilities of banning it.
(I) The Bengal government is planning to introduce a separate chapter on “Responsible use of Internet,” in school syllabus in view of regular reports of school children in the state becoming victims of deadly online game.
(II) The judges suggested to the state DGP and Home Secretary that severe warning be issued to those who shared the ‘dangerous’ online game with others.
(III) The court stressed on the need for creating awareness among students against playing such “dangerous” online games in educational institutions. The bench also said monitoring should be intensified to prevent further spread of the game through sharing.
(IV) State government will conduct workshops in different schools throughout the state to counsel students on the danger of playing games like Blue Whale either online or through mobile applications.
Which of the following will be the preventive course of action for reducing the impact of suicide game menace?
Only (III) and (IV)
Only (II) and (III)
Only (I) and (II)
All of the above
None of these
Statement- Brushing off the recent two-month discord with China over Dokalam standoff, India displayed robust participation at the BRICS meeting in the Chinese port city of Xiamen. In their first substantive meeting post the 73-day Dokalam faceoff, Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Chinese President Xi Jinping held "constructive" talks during which it was reaffirmed that maintaining peace and tranquillity in the border areas was a pre-requisite for the development of India-China relations. Which of the following can be inferred from the given statement?
(I) Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Chinese President Xi Jinping held their first substantive bilateral meeting at the BRICS meeting after the Dokalam standoff, which had put ties between the two countries under strain.
(II) Putting behind the Dokalam standoff, India and China today agreed on a "forward-looking" approach in their ties and make more efforts to ensure that such incidents do not recur.
(III) Counter terrorism issues were taken up during the course of BRICS, which were discussed in this meeting between Modi - Xi Jinping.
Only I and II
Only II and III
Only I and III
All of the above
None of the above
Statement- After the ministerial performance report and a series of meetings with BJP Chief Amit Shah, PM Modi on 5th July made major strategic changes to his Cabinet – 19 new minsters were inducted into the Government, while 5 were sacked. Government sources conceded that with 2019 Lok Sabha polls drawing near, the concern within the government was to ensure last-mile delivery of projects which was also a reason of this expansion. Which of the following can be hypothesized from the given statement?
(I) The Modi government has received criticism from the Opposition for its failures to meet its promises, particularly on job growth.
(II) This Cabinet reshuffles and expansions can generally be categorised as tactical or strategic.
(III) The makeover of the union cabinet shows the BJP has a clear eye on the coming 2019 Lok Sabha showdown
Only (I) and (III)
Only (II) and (I)
Only (III) and (II)
Only (II)
None of these
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
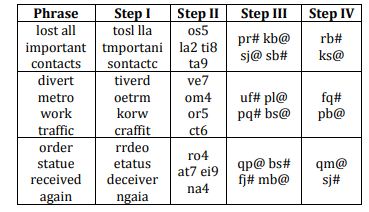
As per the rules followed in the above steps, find out in each of the following questions the appropriate step for the given phrase.
Phrase- recover that device issue
Question:
What is the step IV of this phrase?
qf# gj@
qj# bu@
qf# bj@
bj# qf@
None of these
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:

As per the rules followed in the above steps, find out in each of the following questions the appropriate step for the given phrase.
Phrase- recover that device issue
Question:
What is the 2nd element from left in step III?
qq#
gb#
qg@
qb#
None of these
Direction : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:

As per the rules followed in the above steps, find out in each of the following questions the appropriate step for the given phrase.
Phrase- recover that device issue
Question:
What is the sum of the numbers in 2nd and 4th element from left in step II?
8
7
9
6
None of these
Directions : Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below it.
Eight persons R@, R#, R$, R&, R%, R*, R© and R? are sitting around a hollow circular table such that R&, R$, R# and R? sit on the inner side of the table and the rest are sitting on the outer side of the circular table and they all are facing away from the center. The persons sitting on the inner side of the circular table are sitting just behind the persons sitting on the outer side of the circular table and all are graduated from different universities i.e. HTS, UGI, LPU, HNB, KPJ, UPI, NIT and FPT. All the information is not necessarily in the same order.
The one who is graduated from KPJ sits just behind the one who sits second to the left of the one who is graduated from UPI. R? sits just behind the R*. R% who is graduated from UGI sits opposite to the one who sits at the immediate left of R©. R& is not graduated from FPT. The one who is graduated from HTS sits at the immediate left of the one who is graduated from LPU. The one who is graduated from KPJ sits just behind the R©. R? sits at the immediate right of R&. The persons who are graduated from FPT and HNB are sitting on the same table and sit opposite to each other. R& sits just behind the one who is graduated from UGI. R$ is not graduated from FPT.
Question:
Who among the following is graduated from HTS?
R@
R?
R&
R#
None of these
Directions : Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below it.
Eight persons R@, R#, R$, R&, R%, R*, R© and R? are sitting around a hollow circular table such that R&, R$, R# and R? sit on the inner side of the table and the rest are sitting on the outer side of the circular table and they all are facing away from the center. The persons sitting on the inner side of the circular table are sitting just behind the persons sitting on the outer side of the circular table and all are graduated from different universities i.e. HTS, UGI, LPU, HNB, KPJ, UPI, NIT and FPT. All the information is not necessarily in the same order.
The one who is graduated from KPJ sits just behind the one who sits second to the left of the one who is graduated from UPI. R? sits just behind the R*. R% who is graduated from UGI sits opposite to the one who sits at the immediate left of R©. R& is not graduated from FPT. The one who is graduated from HTS sits at the immediate left of the one who is graduated from LPU. The one who is graduated from KPJ sits just behind the R©. R? sits at the immediate right of R&. The persons who are graduated from FPT and HNB are sitting on the same table and sit opposite to each other. R& sits just behind the one who is graduated from UGI. R$ is not graduated from FPT.
Question:
Which among the following statement is not true?
R? is graduated from NIT
R$ sits just behind the one who is graduated from LPU
R# is graduated from FPT
R% sits at the outer circular table
All are true
Directions : Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below it.
Eight persons R@, R#, R$, R&, R%, R*, R© and R? are sitting around a hollow circular table such that R&, R$, R# and R? sit on the inner side of the table and the rest are sitting on the outer side of the circular table and they all are facing away from the center. The persons sitting on the inner side of the circular table are sitting just behind the persons sitting on the outer side of the circular table and all are graduated from different universities i.e. HTS, UGI, LPU, HNB, KPJ, UPI, NIT and FPT. All the information is not necessarily in the same order.
The one who is graduated from KPJ sits just behind the one who sits second to the left of the one who is graduated from UPI. R? sits just behind the R*. R% who is graduated from UGI sits opposite to the one who sits at the immediate left of R©. R& is not graduated from FPT. The one who is graduated from HTS sits at the immediate left of the one who is graduated from LPU. The one who is graduated from KPJ sits just behind the R©. R? sits at the immediate right of R&. The persons who are graduated from FPT and HNB are sitting on the same table and sit opposite to each other. R& sits just behind the one who is graduated from UGI. R$ is not graduated from FPT.
Question:
How many persons are sitting between R* and R% when counted from right of R*?
One
Two
None
None of these
Can’t be determined
Directions : Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below it.
Eight persons R@, R#, R$, R&, R%, R*, R© and R? are sitting around a hollow circular table such that R&, R$, R# and R? sit on the inner side of the table and the rest are sitting on the outer side of the circular table and they all are facing away from the center. The persons sitting on the inner side of the circular table are sitting just behind the persons sitting on the outer side of the circular table and all are graduated from different universities i.e. HTS, UGI, LPU, HNB, KPJ, UPI, NIT and FPT. All the information is not necessarily in the same order.
The one who is graduated from KPJ sits just behind the one who sits second to the left of the one who is graduated from UPI. R? sits just behind the R*. R% who is graduated from UGI sits opposite to the one who sits at the immediate left of R©. R& is not graduated from FPT. The one who is graduated from HTS sits at the immediate left of the one who is graduated from LPU. The one who is graduated from KPJ sits just behind the R©. R? sits at the immediate right of R&. The persons who are graduated from FPT and HNB are sitting on the same table and sit opposite to each other. R& sits just behind the one who is graduated from UGI. R$ is not graduated from FPT.
Question:
Four of the following five are alike in a certain way and hence form a group, which of the following does not belong to the group?
R%
R©
R*
R?
R@
Directions : Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below it.
Eight persons R@, R#, R$, R&, R%, R*, R© and R? are sitting around a hollow circular table such that R&, R$, R# and R? sit on the inner side of the table and the rest are sitting on the outer side of the circular table and they all are facing away from the center. The persons sitting on the inner side of the circular table are sitting just behind the persons sitting on the outer side of the circular table and all are graduated from different universities i.e. HTS, UGI, LPU, HNB, KPJ, UPI, NIT and FPT. All the information is not necessarily in the same order.
The one who is graduated from KPJ sits just behind the one who sits second to the left of the one who is graduated from UPI. R? sits just behind the R*. R% who is graduated from UGI sits opposite to the one who sits at the immediate left of R©. R& is not graduated from FPT. The one who is graduated from HTS sits at the immediate left of the one who is graduated from LPU. The one who is graduated from KPJ sits just behind the R©. R? sits at the immediate right of R&. The persons who are graduated from FPT and HNB are sitting on the same table and sit opposite to each other. R& sits just behind the one who is graduated from UGI. R$ is not graduated from FPT.
Question:
Who among the following is sitting third to the right of the one who is sitting just behind the R©?
The one who is graduated from KPJ
R&
The one who is sitting at the immediate left of R$
R?
None of these
Directions : Given data is regarding three automatic toys on two types of movements: Neck movements (NM) and Hand rotation (HR). It starts recording from 9 AM onwards on 12 June. Each toy has different battery percentage and battery capacity.
Toy A: Battery Capacity = 1500 units, Battery Percent = 80%
At every 4th NM and 3rd HR together, 1 unit of battery is consumed. Toy A gets completely discharged at 11 AM.
Toy B: Battery Capacity = 2000 units, Battery percent = 75%
NM = 30/min, HR/min = 50% of NM/min of toy A. At every 3rd NM and 2nd HR together, 1 unit of battery is consumed. Toy C: Battery Capacity = 120% of battery capacity of toy B, Battery Percent = 60%
B, Battery Percent = 60% NM/min = NM/min of toy A + 5, HR = 30/min. at every 3rd NM and 2nd HR together. 1 unit of battery is consumed.
Question:
If toy B & A had been charged completely (100%), then what would be the difference between time taken by both the toys to get discharged completely?
50 min
90 min
0 min
15 min
10 min
Directions : Given data is regarding three automatic toys on two types of movements: Neck movements (NM) and Hand rotation (HR). It starts recording from 9 AM onwards on 12 June. Each toy has different battery percentage and battery capacity.
Toy A: Battery Capacity = 1500 units, Battery Percent = 80%
At every 4th NM and 3rd HR together, 1 unit of battery is consumed. Toy A gets completely discharged at 11 AM.
Toy B: Battery Capacity = 2000 units, Battery percent = 75%
NM = 30/min, HR/min = 50% of NM/min of toy A. At every 3rd NM and 2nd HR together, 1 unit of battery is consumed. Toy C: Battery Capacity = 120% of battery capacity of toy B, Battery Percent = 60%
B, Battery Percent = 60% NM/min = NM/min of toy A + 5, HR = 30/min. at every 3rd NM and 2nd HR together. 1 unit of battery is consumed.
Question:
What is the difference between total NM andHR of toy C when the battery of toy C gets completely discharged? (consider available battery percent)
1620
1440
1920
1200
1280
Directions : Given data is regarding three automatic toys on two types of movements: Neck movements (NM) and Hand rotation (HR). It starts recording from 9 AM onwards on 12 June. Each toy has different battery percentage and battery capacity.
Toy A: Battery Capacity = 1500 units, Battery Percent = 80%
At every 4th NM and 3rd HR together, 1 unit of battery is consumed. Toy A gets completely discharged at 11 AM.
Toy B: Battery Capacity = 2000 units, Battery percent = 75%
NM = 30/min, HR/min = 50% of NM/min of toy A. At every 3rd NM and 2nd HR together, 1 unit of battery is consumed. Toy C: Battery Capacity = 120% of battery capacity of toy B, Battery Percent = 60%
B, Battery Percent = 60% NM/min = NM/min of toy A + 5, HR = 30/min. at every 3rd NM and 2nd HR together. 1 unit of battery is consumed.
Question:
If power consumed per NM of toy B is 0.1 unit, then what is power consumed per HR of toy B on that day?
0.45 unit
0.35 unit
0.15 unit
0.2 unit
0.8 unit
Directions : Given data is regarding three automatic toys on two types of movements: Neck movements (NM) and Hand rotation (HR). It starts recording from 9 AM onwards on 12 June. Each toy has different battery percentage and battery capacity.
Toy A: Battery Capacity = 1500 units, Battery Percent = 80%
At every 4th NM and 3rd HR together, 1 unit of battery is consumed. Toy A gets completely discharged at 11 AM.
Toy B: Battery Capacity = 2000 units, Battery percent = 75%
NM = 30/min, HR/min = 50% of NM/min of toy A. At every 3rd NM and 2nd HR together, 1 unit of battery is consumed. Toy C: Battery Capacity = 120% of battery capacity of toy B, Battery Percent = 60%
B, Battery Percent = 60% NM/min = NM/min of toy A + 5, HR = 30/min. at every 3rd NM and 2nd HR together. 1 unit of battery is consumed.
Question:
Total number of NM/min of all the three toys together is what percent more than total number of HR/min of all the three toys together?
63.5%
52.25%
46.5%
48.25%
43.75%
Directions : Given data is regarding three automatic toys on two types of movements: Neck movements (NM) and Hand rotation (HR). It starts recording from 9 AM onwards on 12 June. Each toy has different battery percentage and battery capacity.
Toy A: Battery Capacity = 1500 units, Battery Percent = 80%
At every 4th NM and 3rd HR together, 1 unit of battery is consumed. Toy A gets completely discharged at 11 AM.
Toy B: Battery Capacity = 2000 units, Battery percent = 75%
NM = 30/min, HR/min = 50% of NM/min of toy A. At every 3rd NM and 2nd HR together, 1 unit of battery is consumed. Toy C: Battery Capacity = 120% of battery capacity of toy B, Battery Percent = 60%
B, Battery Percent = 60% NM/min = NM/min of toy A + 5, HR = 30/min. at every 3rd NM and 2nd HR together. 1 unit of battery is consumed.
Question:
battery of toy C will drain completely?
11:30 AM
11:45 AM
11:35 AM
11:40 AM
11:50 AM
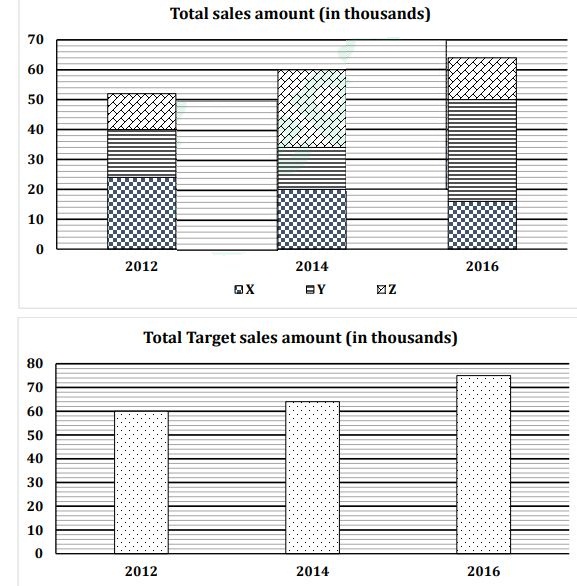
Directions : first bar graph shows total sales amount of three different companies in three different years and second bar graph shows the combined target sales amount of these 3 companies in these 3 years.
Question:
If sales amount of company X and Y in 2012 increases by 20% and 25% respectively and sales amount of company Z remains constant, then find the difference between total target sales amount of all these companies in 2012 and sales amount of these 3 companies together as per the above condition?(in Rs.)
800
8000
8800
6000
3000
Directions : first bar graph shows total sales amount of three different companies in three different years and second bar graph shows the combined target sales amount of these 3 companies in these 3 years.

Question:
If the ratio of sales amount of company Y in 2016 to that of in 2018 is 17:15, then find the average of sale amount of company Y in 2014, 2016 and 2018?(in Rs.)
24000
25500
27000
26000
26500
Directions : first bar graph shows total sales amount of three different companies in three different years and second bar graph shows the combined target sales amount of these 3 companies in these 3 years.

Question:
If the total target sales amount of all companies together in 2018 is 20% more than that of in 2016 and sales amount of company X and company Y in 2018 increases by 50% and 20% respectively than that of in 2016, then find by what percent sales amount of company Z be increased from 2016 to 2018 just to meet the total target sales amount of all companies together in 2018?
70%
80%
75%
50%
90%
Directions : first bar graph shows total sales amount of three different companies in three different years and second bar graph shows the combined target sales amount of these 3 companies in these 3 years.

Question:
Sales amount of company Y in 2014 is what percent of total target sales amount of all companies together in 2016?





Directions : first bar graph shows total sales amount of three different companies in three different years and second bar graph shows the combined target sales amount of these 3 companies in these 3 years.

Question:
Total sales amount of X in 2012, 2014 and 2016 together is how much more/less than the total sales amount of Z in the same years?(in Rs.)
11000
9000
7000
10000
8000
Directions : Given Pie Chart shows the number of total voters registered from 4 different villages and all registered voters from these four villages cast their votes.
Total Voters = Valid Voters + Invalid Voters
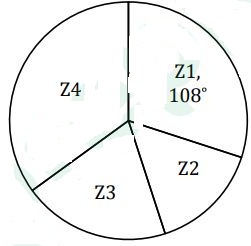
(i) Total number of valid voters in village Z3 is one-third more than the difference of that of from village Z1 & Z2.
(ii) Difference of valid voters from village Z4 and Z2 is 480. Ratio of total voters from village Z2 and that of Z4 is 3 : 7 respectively.
(iii) Total voters in village Z3 are more than that of Z2. Total invalid voters from all the villages together are 20% of total registered voters from all the villages.
Question:
. What is the central angle corresponding to total voters in village Z2?
72°
54°
60°
75°
66°
Directions : Given Pie Chart shows the number of total voters registered from 4 different villages and all registered voters from these four villages cast their votes.
Total Voters = Valid Voters + Invalid Voters

(i) Total number of valid voters in village Z3 is one-third more than the difference of that of from village Z1 & Z2.
(ii) Difference of valid voters from village Z4 and Z2 is 480. Ratio of total voters from village Z2 and that of Z4 is 3 : 7 respectively.
(iii) Total voters in village Z3 are more than that of Z2. Total invalid voters from all the villages together are 20% of total registered voters from all the villages.
Question:
If there are 10800 registered voters in village Z2 of which 98% votes were valid. What can be the difference between valid & invalid votes from village Z4? (use information of the above questions).
960
None of these
4992
Both (b) &(e)
3072
Directions : Given Pie Chart shows the number of total voters registered from 4 different villages and all registered voters from these four villages cast their votes.
Total Voters = Valid Voters + Invalid Voters

(i) Total number of valid voters in village Z3 is one-third more than the difference of that of from village Z1 & Z2.
(ii) Difference of valid voters from village Z4 and Z2 is 480. Ratio of total voters from village Z2 and that of Z4 is 3 : 7 respectively.
(iii) Total voters in village Z3 are more than that of Z2. Total invalid voters from all the villages together are 20% of total registered voters from all the villages.
Question:
What is the central angle corresponding to valid votes from village Z3? (use information of the above questions).
75°
82°
108°
60°
95°
Directions : Given Pie Chart shows the number of total voters registered from 4 different villages and all registered voters from these four villages cast their votes.
Total Voters = Valid Voters + Invalid Voters

(i) Total number of valid voters in village Z3 is one-third more than the difference of that of from village Z1 & Z2.
(ii) Difference of valid voters from village Z4 and Z2 is 480. Ratio of total voters from village Z2 and that of Z4 is 3 : 7 respectively.
(iii) Total voters in village Z3 are more than that of Z2. Total invalid voters from all the villages together are 20% of total registered voters from all the villages.
Question:
If there were total 4000 invalid voters from village Z2 & Z1 in the ratio of 9 : 11 respectively and 20% of the votes from village Z2 were found invalid then, find the difference between registered voters of Z3 and Z4? (use information of the above questions).
10000
9000
11000
9500
10500
Directions : Given Pie Chart shows the number of total voters registered from 4 different villages and all registered voters from these four villages cast their votes.
Total Voters = Valid Voters + Invalid Voters

(i) Total number of valid voters in village Z3 is one-third more than the difference of that of from village Z1 & Z2.
(ii) Difference of valid voters from village Z4 and Z2 is 480. Ratio of total voters from village Z2 and that of Z4 is 3 : 7 respectively.
(iii) Total voters in village Z3 are more than that of Z2. Total invalid voters from all the villages together are 20% of total registered voters from all the villages.
Question:
If valid voters from Z4 are more than that of from Z2 and valid voters from Z2 are 3600. Total valid voters from Z1 & Z4 are 10800. How many valid voters are from Z3?
5300
3120
4160
None of these
4080
Directions : Given graph shows the number of orders received and cancelled on particular days of a week (From Monday to Saturday) while the table shows the number of orders which were not delivered. Read the data carefully and answer the questions.
(NOTE: Refer Y-Axis values as number of orders while X-Axis values as Days i.e. 20 = Monday, 40 = Tuesday and so on) (Orders continued/booked are those which are not cancelled)
Some data is missing in the given graph.
Orders Booked = Orders Received – Orders Cancelled
Orders Delivered = Orders Booked – Orders not delivered
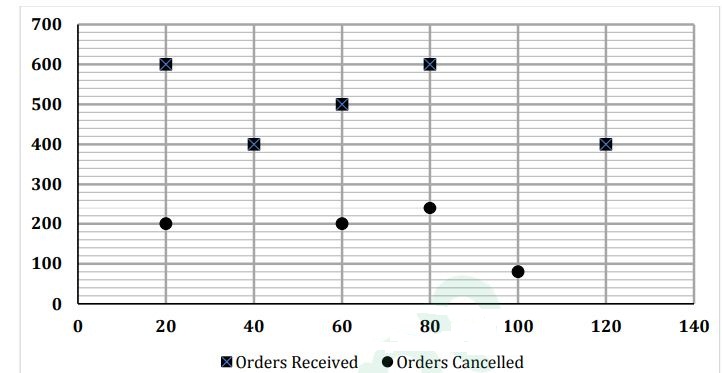
Number of orders not delivered
Monday 120
Tuesday 80
Wednesday 160
Thursday 300
Friday 200
Saturday 120
Question:
what is the difference between number of orders delivered on Monday & Wednesday together and number of orders booked on Wednesday & Thursday together?
300
280
320
240
260
Directions : Given graph shows the number of orders received and cancelled on particular days of a week (From Monday to Saturday) while the table shows the number of orders which were not delivered. Read the data carefully and answer the questions.
(NOTE: Refer Y-Axis values as number of orders while X-Axis values as Days i.e. 20 = Monday, 40 = Tuesday and so on) (Orders continued/booked are those which are not cancelled)
Some data is missing in the given graph.
Orders Booked = Orders Received – Orders Cancelled
Orders Delivered = Orders Booked – Orders not delivered

Number of orders not delivered
Monday 120
Tuesday 80
Wednesday 160
Thursday 300
Friday 200
Saturday 120
Question:
if orders booked on Tuesday are 50 more than that of Saturday while the sum of orders cancelled on these days is 30 more than orders not delivered on same days then by what percent orders cancelled on Tuesday are more/less than orders cancelled on Friday?
37.5%
12.5%
11.11%
18.75%
31.25%
Directions : Given graph shows the number of orders received and cancelled on particular days of a week (From Monday to Saturday) while the table shows the number of orders which were not delivered. Read the data carefully and answer the questions.
(NOTE: Refer Y-Axis values as number of orders while X-Axis values as Days i.e. 20 = Monday, 40 = Tuesday and so on) (Orders continued/booked are those which are not cancelled)
Some data is missing in the given graph.
Orders Booked = Orders Received – Orders Cancelled
Orders Delivered = Orders Booked – Orders not delivered

Number of orders not delivered
Monday 120
Tuesday 80
Wednesday 160
Thursday 300
Friday 200
Saturday 120
Question:
If total orders received on last 3 days are 150 more than total orders received on first 3 days and orders delivered on Friday are more than that on Saturday then what can be the difference between orders cancelled on Saturday and orders delivered on Thursday? (Z > 60)
A. 28 B. 49 C. 23 D. 40 E. 17 F. 37
A, C, E
A, C, F
B, D, F
all of these
A, C, D, E, F
Directions : Given graph shows the number of orders received and cancelled on particular days of a week (From Monday to Saturday) while the table shows the number of orders which were not delivered. Read the data carefully and answer the questions.
(NOTE: Refer Y-Axis values as number of orders while X-Axis values as Days i.e. 20 = Monday, 40 = Tuesday and so on) (Orders continued/booked are those which are not cancelled)
Some data is missing in the given graph.
Orders Booked = Orders Received – Orders Cancelled
Orders Delivered = Orders Booked – Orders not delivered

Number of orders not delivered
Monday 120
Tuesday 80
Wednesday 160
Thursday 300
Friday 200
Saturday 120
Question:
if orders delivered on Tuesday are 33 1 3 % less than orders booked on Thursday while average of orders delivered on Friday & Saturday is 195 and orders booked on Friday are more than orders delivered on Saturday then which of the following is definitely true?
orders cancelled on Tuesday are more than that on Friday.
difference between orders cancelled on Tuesday & Saturday is 322.
orders delivered on Friday are always more than orders received on Wednesday.
difference between orders delivered on Monday & Friday can be 160.
more number of orders were cancelled on Friday than number of orders not delivered on Friday
Directions : Given graph shows the number of orders received and cancelled on particular days of a week (From Monday to Saturday) while the table shows the number of orders which were not delivered. Read the data carefully and answer the questions.
(NOTE: Refer Y-Axis values as number of orders while X-Axis values as Days i.e. 20 = Monday, 40 = Tuesday and so on) (Orders continued/booked are those which are not cancelled)
Some data is missing in the given graph.
Orders Booked = Orders Received – Orders Cancelled
Orders Delivered = Orders Booked – Orders not delivered

Number of orders not delivered
Monday 120
Tuesday 80
Wednesday 160
Thursday 300
Friday 200
Saturday 120
Question:
if ratio of orders received on Thursday & Friday together to orders delivered on Monday, Wednesday & Saturday together is 65 : 34 and orders cancelled on Tuesday are 10% less than that on Wednesday and orders cancelled on Saturday is same as difference between orders not delivered on Friday and orders cancelled on Tuesday then how many total orders were booked in these 6 days together?
2850
2450
2280
None of these
2170
Directions Read the data carefully and answer the questions. Some data are missing which you have to calculate as per information provided in the questions
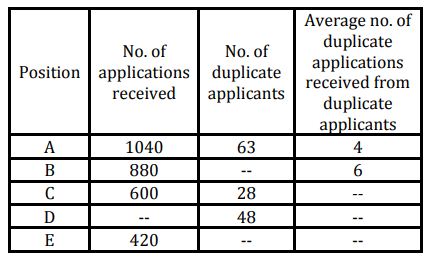
NOTE:- A duplicate applicant is an applicant who has submitted additional (duplicate) application after submitting their original application. All application forms (original + duplicate) received from duplicate applicant were rejected. Remaining all application were accepted. None of the applicants applied for more than one post.
Question:
For position A, if respective ratio between no. of accepted application from males & that of rejected applications from males is 5 : 3 & respective ratio of no. of accepted applications from females and that of rejected applications from females is 5 : 1 then find rejected applications from males.
230
315
425
255
300
Directions Read the data carefully and answer the questions. Some data are missing which you have to calculate as per information provided in the questions

NOTE:- A duplicate applicant is an applicant who has submitted additional (duplicate) application after submitting their original application. All application forms (original + duplicate) received from duplicate applicant were rejected. Remaining all application were accepted. None of the applicants applied for more than one post.
Question:
For position E, no. of accepted applications from males, from females & no. of rejected applications (total) are X, X + Y, X + 2Y respectively. Which of the following is true? (average no. of duplicate applications received from duplicate applicant is nonzero integer) A. no. of accepted applications from males for E can be 139. B. no. of accepted applications from males for E can be 141. C. no. of accepted applications from males for E can be 131.
C
A & B
A & C
B
A
Directions Read the data carefully and answer the questions. Some data are missing which you have to calculate as per information provided in the questions

NOTE:- A duplicate applicant is an applicant who has submitted additional (duplicate) application after submitting their original application. All application forms (original + duplicate) received from duplicate applicant were rejected. Remaining all application were accepted. None of the applicants applied for more than one post.
Question:
If average no. of accepted applications for position A & B is 659. What is the value of rejected applications for position B?
287
246
254
275
263
Directions Read the data carefully and answer the questions. Some data are missing which you have to calculate as per information provided in the questions

NOTE:- A duplicate applicant is an applicant who has submitted additional (duplicate) application after submitting their original application. All application forms (original + duplicate) received from duplicate applicant were rejected. Remaining all application were accepted. None of the applicants applied for more than one post.
Question:
For position D, if respective ratio of accepted & rejected applications is 4 : 1. Which of the following can be true? (average number of duplicate applications received for D is a non – zero integer)
A. no. of applications received for D (all original + all duplicate) can be 240.
B. no. of applications accepted for D can be 768.
C. least no. of applications (all original + all duplicate) were received for D is a possibility.
only B & C
none of the option
only C
only A & C
only B
Directions Read the data carefully and answer the questions. Some data are missing which you have to calculate as per information provided in the questions

NOTE:- A duplicate applicant is an applicant who has submitted additional (duplicate) application after submitting their original application. All application forms (original + duplicate) received from duplicate applicant were rejected. Remaining all application were accepted. None of the applicants applied for more than one post.
Question:
for position C, no. of accepted applications from males is between 150 &200 while that of females is between 130 & 180. Which of the following can be a possible value (s) of average no. of duplicate applications submitted by duplicate applicants for position C?
A. 11 B. 5 C. 9 D. 13 E. 7
B, C & E
C & E
A & D
B & E
A, C & D
Directions : Given below is no. of male & female students in classes A, B & C. some data are missing which you have to calculate as per instructions provided.
A B C
Boys 50 -- --
Girls -- 80 60
NOTE:
(i) probability of selecting a boy from class A is 5 12 .
(ii) probability of selecting a boy from all the boys of all classes is 14 19 such that the boy selected is either from class B or class C.
(iii) probability of selecting a boy from class B is equal to probability of selecting a boy from class C.
Question:
how many boys are in class C?
60
50
70
80
90
Directions : Given below is no. of male & female students in classes A, B & C. some data are missing which you have to calculate as per instructions provided.
A B C
Boys 50 -- --
Girls -- 80 60
NOTE:
(i) probability of selecting a boy from class A is 5 12 .
(ii) probability of selecting a boy from all the boys of all classes is 14 19 such that the boy selected is either from class B or class C.
(iii) probability of selecting a boy from class B is equal to probability of selecting a boy from class C.
Question:
By what percent total students in class B are more than that of in class A?


25%

None of these
Given below is the series in which one number is wrong. Consider this wrong number as the value of A in the second series and find the value of D based on the pattern of first series
1, 3, 6, 21, 88, 445, 2676
(A), (B), (C), (D)
685
136
33
10
30
Directions : Read the following information carefully and answer the questions. x women can complete a piece of work in 2y days. 1.5x men can complete the same work in y days while 2x children can complete the same work in 3y days. 8 women, 8 children and 8 men together can complete same work i n 22 1/2 days. 9 men can complete the same work in (y + 20) days.
Question:
What is the value of y.
14
18
20
16
24
Directions : Read the following information carefully and answer the questions. x women can complete a piece of work in 2y days. 1.5x men can complete the same work in y days while 2x children can complete the same work in 3y days. 8 women, 8 children and 8 men together can complete same work i n 22 1/2 days. 9 men can complete the same work in (y + 20) days.
Question:
If 36 women started the work and after 4 days 30 women are replaced by 8 men then, find the total time in which work will be completed.


12 days
12.5 days

Directions : Read the following information carefully and answer the questions. x women can complete a piece of work in 2y days. 1.5x men can complete the same work in y days while 2x children can complete the same work in 3y days. 8 women, 8 children and 8 men together can complete same work i n 22 1/2 days. 9 men can complete the same work in (y + 20) days.
Question:
Find the value of x.
12
14
10
15
11
Directions : Read the following information carefully and answer the questions. x women can complete a piece of work in 2y days. 1.5x men can complete the same work in y days while 2x children can complete the same work in 3y days. 8 women, 8 children and 8 men together can complete same work i n 22 1/2 days. 9 men can complete the same work in (y + 20) days.
Question:
When 8 women, 8 children and 8 men work together and completed the work, then what percentage of total work is completed by children.
16%
10%
15%
8.33%
12.5%
Directions : Read the following information carefully and answer the questions. x women can complete a piece of work in 2y days. 1.5x men can complete the same work in y days while 2x children can complete the same work in 3y days. 8 women, 8 children and 8 men together can complete same work i n 22 1/2 days. 9 men can complete the same work in (y + 20) days.
Question:
(x – 6) women worked for (y – 6) days and (x – 6) men worked for (y – 10) days then in what time remaining work will be completed by (x – 6) children.


145 days
154 days
158 days
Directions : Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
There are some students (male + female) in Class A and Class B in CCA School. In class A, females are 30% of total students of class A. In class B, number of male and female students are equal and male students in class B are thrice the number of female students of Class A.
Question:
If male students passed in Class A and Class B are in ratio 1:3 respectively and failed male students of class A and Class B are equal, then total male students who got passed from both classes together are what percent of total students of both the classes?





Directions : Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
There are some students (male + female) in Class A and Class B in CCA School. In class A, females are 30% of total students of class A. In class B, number of male and female students are equal and male students in class B are thrice the number of female students of Class A.
Question:
If 10% of male students and 20% of female students from Class A left the school and male and female students in class B increased by 25% and 30% respectively, then total male students of Class A and B together are approximately what percent of total students of Class A and B together?
55.45%
45.45%
55.15%
45.15%
50%
Directions : Read the following passage and answer the following questions based on the given passage.
The inflation devil is back and at the wrong time. The 7.35% rise in consumer price inflation in December is a shocker even to those who were prepared for an elevated level of inflation in the backdrop of the rise in prices of food commodities in general, and the astronomical rise in the price of onions, in particular. The disturbing December print has set off fears over whether India is entering a period of slow growth accompanied by high inflation, in other words, stagflation. Such fears have to be weighed against a few facts. First, the headline inflation number is driven mainly by food inflation at 14.12% — it was 10.01% in November and -2.65% in December 2018. While onion was the prime villain pushing up price inflation in vegetables to a huge 60.50% compared to December 2018, prices of other food items such as meat and fish (up 9.57%), milk (up 4.22%), eggs (up 8.79%) and some pulses were also on the upswing. These are a largely seasonal rise in prices and are driven mainly by supply-side factors and the prices will reverse once the supply shortfall is addressed. Second, core inflation, which is the one that should be of concern, has only inched up marginally from 3.5% in November to 3.7% in December. That said, it would be worrisome indeed if core inflation were to shoot up or if food inflation does not cool down in the next couple of months.
The sharp jump in the CPI has queered the pitch for the Reserve Bank of India’s monetary policy review in February. The central bank stood pat on rates in the December policy precisely due to fears of inflation and had even revised upwards its inflation projection for the second half of the fiscal to 4.7-5.1%. The December print is way above the monetary policy committee’s (MPC) mandated limit of 6% (4% plus 2%) which means that a rate cut is pretty much off the table for now. Yet, with growth sagging, there is pressure on the central bank to cut rates at least one more time to stimulate growth. It would be interesting to watch the deliberations of the MPC in February. While the market may be prepared to accept a standstill policy for now, any change in the RBI’s stance from accommodative to neutral may not go down well. A lot would also depend on the fiscal arithmetic that would emerge from the budget to be presented on February 1. Meanwhile, the government should engage all levers to address the supply-side issues that are behind the rise in food inflation. A calming down of food prices will help the bank do what the government and markets want — lower rates.
Question:
Which of the following can be inferred in context of the phrase “queered the pitch”, as highlighted in the above passage?
With the inflation figures are rising, it has become difficult to address the challenges now faced in setting policy rates to sustain the growth of the Indian economy.
The MPC is expected to announce the consecutive rate cut to boost economic activity amid benign inflation.
both (a) and (d)
Owing to the steady rise of CPI inflation, RBI will have to face the challenge in its upcoming meeting, to decide to whether to cut the policy rates or keep them unchanged.
None of these
Directions : Read the following passage and answer the following questions based on the given passage.
The inflation devil is back and at the wrong time. The 7.35% rise in consumer price inflation in December is a shocker even to those who were prepared for an elevated level of inflation in the backdrop of the rise in prices of food commodities in general, and the astronomical rise in the price of onions, in particular. The disturbing December print has set off fears over whether India is entering a period of slow growth accompanied by high inflation, in other words, stagflation. Such fears have to be weighed against a few facts. First, the headline inflation number is driven mainly by food inflation at 14.12% — it was 10.01% in November and -2.65% in December 2018. While onion was the prime villain pushing up price inflation in vegetables to a huge 60.50% compared to December 2018, prices of other food items such as meat and fish (up 9.57%), milk (up 4.22%), eggs (up 8.79%) and some pulses were also on the upswing. These are a largely seasonal rise in prices and are driven mainly by supply-side factors and the prices will reverse once the supply shortfall is addressed. Second, core inflation, which is the one that should be of concern, has only inched up marginally from 3.5% in November to 3.7% in December. That said, it would be worrisome indeed if core inflation were to shoot up or if food inflation does not cool down in the next couple of months.
The sharp jump in the CPI has queered the pitch for the Reserve Bank of India’s monetary policy review in February. The central bank stood pat on rates in the December policy precisely due to fears of inflation and had even revised upwards its inflation projection for the second half of the fiscal to 4.7-5.1%. The December print is way above the monetary policy committee’s (MPC) mandated limit of 6% (4% plus 2%) which means that a rate cut is pretty much off the table for now. Yet, with growth sagging, there is pressure on the central bank to cut rates at least one more time to stimulate growth. It would be interesting to watch the deliberations of the MPC in February. While the market may be prepared to accept a standstill policy for now, any change in the RBI’s stance from accommodative to neutral may not go down well. A lot would also depend on the fiscal arithmetic that would emerge from the budget to be presented on February 1. Meanwhile, the government should engage all levers to address the supply-side issues that are behind the rise in food inflation. A calming down of food prices will help the bank do what the government and markets want — lower rates.
Question:
Which of the following situations can be related with STAGFLATION, as mentioned in above passage?
General decline in the prices of goods and services in an economy, which in turn increase the purchasing power of money.
Rising food prices caused by increased demand for agricultural commodities.
An economy experiencing falling productivity along with workers becoming more inefficient; leading to increased costs and reduced output.
None of these
All of the given situations are correct
Directions : Read the following passage and answer the following questions based on the given passage.
The inflation devil is back and at the wrong time. The 7.35% rise in consumer price inflation in December is a shocker even to those who were prepared for an elevated level of inflation in the backdrop of the rise in prices of food commodities in general, and the astronomical rise in the price of onions, in particular. The disturbing December print has set off fears over whether India is entering a period of slow growth accompanied by high inflation, in other words, stagflation. Such fears have to be weighed against a few facts. First, the headline inflation number is driven mainly by food inflation at 14.12% — it was 10.01% in November and -2.65% in December 2018. While onion was the prime villain pushing up price inflation in vegetables to a huge 60.50% compared to December 2018, prices of other food items such as meat and fish (up 9.57%), milk (up 4.22%), eggs (up 8.79%) and some pulses were also on the upswing. These are a largely seasonal rise in prices and are driven mainly by supply-side factors and the prices will reverse once the supply shortfall is addressed. Second, core inflation, which is the one that should be of concern, has only inched up marginally from 3.5% in November to 3.7% in December. That said, it would be worrisome indeed if core inflation were to shoot up or if food inflation does not cool down in the next couple of months.
The sharp jump in the CPI has queered the pitch for the Reserve Bank of India’s monetary policy review in February. The central bank stood pat on rates in the December policy precisely due to fears of inflation and had even revised upwards its inflation projection for the second half of the fiscal to 4.7-5.1%. The December print is way above the monetary policy committee’s (MPC) mandated limit of 6% (4% plus 2%) which means that a rate cut is pretty much off the table for now. Yet, with growth sagging, there is pressure on the central bank to cut rates at least one more time to stimulate growth. It would be interesting to watch the deliberations of the MPC in February. While the market may be prepared to accept a standstill policy for now, any change in the RBI’s stance from accommodative to neutral may not go down well. A lot would also depend on the fiscal arithmetic that would emerge from the budget to be presented on February 1. Meanwhile, the government should engage all levers to address the supply-side issues that are behind the rise in food inflation. A calming down of food prices will help the bank do what the government and markets want — lower rates.
Question:
Which of the following is not true in context of the information given in the above passage?
The increase in core inflation has not been as high as increase in CPI inflation
During the December monetary policy review, RBI had largely left the rates fluctuating.
Addressing the issues that led to inflation in food commodities can marginally reduce the intensity of burden created by the current situation.
both (a) and (b)
All are correct
Directions : Read the following passage and answer the following questions based on the given passage.
For years, the government of Bhutan has enshrined gross national happiness as its guiding light. Though national leaders had long eschewed traditional economic metrics like gross domestic product in favor of a more subjective understanding of development, in 2008, the country’s constitution formally established that ensuring “a good quality of life for the people of Bhutan” would be its primary aim. GNH would be the measure of the country’s progress, quantified by a complicated index based on “areas of psychological well being, cultural diversity and resilience, education, health, time use, good governance, community vitality, ecological diversity and resilience and economic living standards”—an array of factors that might all together quantify well-being and happiness. Sperling said, economists and policy makers too often set their sights on certain goals—high GDP and low unemployment—that can disregard how Americans actually feel. To re-center economics in people’s lived experiences, Sperling proposed the adoption of a different goal: dignity. Economic dignity would mean being able “to care for your family and enjoy the most meaningful moments of family life, without economic deprivation taking away those most meaningful moments,” Sperling said.
By Sperling’s criteria, he said, America is failing on all three fronts. Even as the unemployment rate in the United States is hovering near a 50-year low, the country has no universal paid-family-leave requirement to ensure that new parents have time to spend with their infant children or to heal after birth. No law grants employees bereavement leave with which to mourn loved ones and begin to piece their lives back together in their absence. The federal minimum wage falls beneath the poverty line for families of two or more. Officially, about 13 million Americans—and likely more unofficially—have to work multiple jobs to make ends meet. The U.S. also fails to provide adequate support for people who have lost their jobs, Sperling said, and adequate resources with which to find new ones. Students are taking on crippling debt to go to college. In 2017, 12.3 percent of Americans were living in poverty.
Together, Sperling observed, that adds up to millions of Americans living without what he defines as economic dignity: unable to provide a basic quality of life for themselves and the people they love, enduring unfulfilling or downright exploitative work conditions out of a desperate need for money. And with the nation’s economic mobility in sharp decline over the past few decades, many workers and their families could remain mired in that state for generations. But Americans can fight for greater economic dignity, Sperling said, arguing that many already are: By unionizing; pushing for a higher minimum wage; lobbying for better leave, child-care, and health-care policies; and demanding action against workplace sexual misconduct, they’re working to claim more of what he put forward as the base necessities for all working people. Policies to promote dignity could take a number of different forms, he said. “But that’s the right way to look at it,” Sperling said: as an array of options. “Don’t make the means the end,” he emphasized. “Happiness is the end goal. So try asking why people are unhappy”—and work from there.
Question:
What is author’s view regarding minimum wage policy as a measure of economic stability of country?
None of the given statements is correct
American citizens have achieved a higher economic stability
GNP, as used in Bhutan has been an inefficient and inaccurate way to assess economic stability
With minimum wages policy, Americans enjoy higher access of civil rights
The benefits achieved under GNP regimes are higher than those where governments have introduced minimum wage policy
Directions : Read the following passage and answer the following questions based on the given passage.
For years, the government of Bhutan has enshrined gross national happiness as its guiding light. Though national leaders had long eschewed traditional economic metrics like gross domestic product in favor of a more subjective understanding of development, in 2008, the country’s constitution formally established that ensuring “a good quality of life for the people of Bhutan” would be its primary aim. GNH would be the measure of the country’s progress, quantified by a complicated index based on “areas of psychological well being, cultural diversity and resilience, education, health, time use, good governance, community vitality, ecological diversity and resilience and economic living standards”—an array of factors that might all together quantify well-being and happiness. Sperling said, economists and policy makers too often set their sights on certain goals—high GDP and low unemployment—that can disregard how Americans actually feel. To re-center economics in people’s lived experiences, Sperling proposed the adoption of a different goal: dignity. Economic dignity would mean being able “to care for your family and enjoy the most meaningful moments of family life, without economic deprivation taking away those most meaningful moments,” Sperling said.
By Sperling’s criteria, he said, America is failing on all three fronts. Even as the unemployment rate in the United States is hovering near a 50-year low, the country has no universal paid-family-leave requirement to ensure that new parents have time to spend with their infant children or to heal after birth. No law grants employees bereavement leave with which to mourn loved ones and begin to piece their lives back together in their absence. The federal minimum wage falls beneath the poverty line for families of two or more. Officially, about 13 million Americans—and likely more unofficially—have to work multiple jobs to make ends meet. The U.S. also fails to provide adequate support for people who have lost their jobs, Sperling said, and adequate resources with which to find new ones. Students are taking on crippling debt to go to college. In 2017, 12.3 percent of Americans were living in poverty.
Together, Sperling observed, that adds up to millions of Americans living without what he defines as economic dignity: unable to provide a basic quality of life for themselves and the people they love, enduring unfulfilling or downright exploitative work conditions out of a desperate need for money. And with the nation’s economic mobility in sharp decline over the past few decades, many workers and their families could remain mired in that state for generations. But Americans can fight for greater economic dignity, Sperling said, arguing that many already are: By unionizing; pushing for a higher minimum wage; lobbying for better leave, child-care, and health-care policies; and demanding action against workplace sexual misconduct, they’re working to claim more of what he put forward as the base necessities for all working people. Policies to promote dignity could take a number of different forms, he said. “But that’s the right way to look at it,” Sperling said: as an array of options. “Don’t make the means the end,” he emphasized. “Happiness is the end goal. So try asking why people are unhappy”—and work from there.
Question:
What can be the possible inference drawn from the statement“Happiness is the end goal”, as highlighted in the above passage?
ensuring universal basic income will promote happiness within countries, which is the primary goal of every country
dignity should not be framed as a metric to fulfill happiness
author has considered happiness as the highest priority and countries must find means to achieve it for overall development
the GDP a country must be given due attention to achieve the overall happiness of the citizens
none is correct
Directions : Read the following passage and answer the following questions based on the given passage.
For years, the government of Bhutan has enshrined gross national happiness as its guiding light. Though national leaders had long eschewed traditional economic metrics like gross domestic product in favor of a more subjective understanding of development, in 2008, the country’s constitution formally established that ensuring “a good quality of life for the people of Bhutan” would be its primary aim. GNH would be the measure of the country’s progress, quantified by a complicated index based on “areas of psychological well being, cultural diversity and resilience, education, health, time use, good governance, community vitality, ecological diversity and resilience and economic living standards”—an array of factors that might all together quantify well-being and happiness. Sperling said, economists and policy makers too often set their sights on certain goals—high GDP and low unemployment—that can disregard how Americans actually feel. To re-center economics in people’s lived experiences, Sperling proposed the adoption of a different goal: dignity. Economic dignity would mean being able “to care for your family and enjoy the most meaningful moments of family life, without economic deprivation taking away those most meaningful moments,” Sperling said.
By Sperling’s criteria, he said, America is failing on all three fronts. Even as the unemployment rate in the United States is hovering near a 50-year low, the country has no universal paid-family-leave requirement to ensure that new parents have time to spend with their infant children or to heal after birth. No law grants employees bereavement leave with which to mourn loved ones and begin to piece their lives back together in their absence. The federal minimum wage falls beneath the poverty line for families of two or more. Officially, about 13 million Americans—and likely more unofficially—have to work multiple jobs to make ends meet. The U.S. also fails to provide adequate support for people who have lost their jobs, Sperling said, and adequate resources with which to find new ones. Students are taking on crippling debt to go to college. In 2017, 12.3 percent of Americans were living in poverty.
Together, Sperling observed, that adds up to millions of Americans living without what he defines as economic dignity: unable to provide a basic quality of life for themselves and the people they love, enduring unfulfilling or downright exploitative work conditions out of a desperate need for money. And with the nation’s economic mobility in sharp decline over the past few decades, many workers and their families could remain mired in that state for generations. But Americans can fight for greater economic dignity, Sperling said, arguing that many already are: By unionizing; pushing for a higher minimum wage; lobbying for better leave, child-care, and health-care policies; and demanding action against workplace sexual misconduct, they’re working to claim more of what he put forward as the base necessities for all working people. Policies to promote dignity could take a number of different forms, he said. “But that’s the right way to look at it,” Sperling said: as an array of options. “Don’t make the means the end,” he emphasized. “Happiness is the end goal. So try asking why people are unhappy”—and work from there.
Question:
What have been the measures suggested by Sperling to achieve economic dignity?
giving due attention to health and child care facilities within a country
assurance of provision of basic necessities
higher amount of minimum wages must be ascertained
both (a) and (b)
all of the above
Directions : Read the following passage and answer the following questions based on the given passage.
For years, the government of Bhutan has enshrined gross national happiness as its guiding light. Though national leaders had long eschewed traditional economic metrics like gross domestic product in favor of a more subjective understanding of development, in 2008, the country’s constitution formally established that ensuring “a good quality of life for the people of Bhutan” would be its primary aim. GNH would be the measure of the country’s progress, quantified by a complicated index based on “areas of psychological well being, cultural diversity and resilience, education, health, time use, good governance, community vitality, ecological diversity and resilience and economic living standards”—an array of factors that might all together quantify well-being and happiness. Sperling said, economists and policy makers too often set their sights on certain goals—high GDP and low unemployment—that can disregard how Americans actually feel. To re-center economics in people’s lived experiences, Sperling proposed the adoption of a different goal: dignity. Economic dignity would mean being able “to care for your family and enjoy the most meaningful moments of family life, without economic deprivation taking away those most meaningful moments,” Sperling said.
By Sperling’s criteria, he said, America is failing on all three fronts. Even as the unemployment rate in the United States is hovering near a 50-year low, the country has no universal paid-family-leave requirement to ensure that new parents have time to spend with their infant children or to heal after birth. No law grants employees bereavement leave with which to mourn loved ones and begin to piece their lives back together in their absence. The federal minimum wage falls beneath the poverty line for families of two or more. Officially, about 13 million Americans—and likely more unofficially—have to work multiple jobs to make ends meet. The U.S. also fails to provide adequate support for people who have lost their jobs, Sperling said, and adequate resources with which to find new ones. Students are taking on crippling debt to go to college. In 2017, 12.3 percent of Americans were living in poverty.
Together, Sperling observed, that adds up to millions of Americans living without what he defines as economic dignity: unable to provide a basic quality of life for themselves and the people they love, enduring unfulfilling or downright exploitative work conditions out of a desperate need for money. And with the nation’s economic mobility in sharp decline over the past few decades, many workers and their families could remain mired in that state for generations. But Americans can fight for greater economic dignity, Sperling said, arguing that many already are: By unionizing; pushing for a higher minimum wage; lobbying for better leave, child-care, and health-care policies; and demanding action against workplace sexual misconduct, they’re working to claim more of what he put forward as the base necessities for all working people. Policies to promote dignity could take a number of different forms, he said. “But that’s the right way to look at it,” Sperling said: as an array of options. “Don’t make the means the end,” he emphasized. “Happiness is the end goal. So try asking why people are unhappy”—and work from there.
Question:
The author is in line with
Economists believe that GDP and higher per capita income is necessary for economic growth
Gross National Happiness and quality of life are necessary aims for any economy
Although GNH is premised on the idea of overall psychological well-being, the significance of governance is undermined
The developed nations have been successfully providing support for the unemployed but are still lagging in GNH
All are correct
Directions: Read the following passage and answer the following questions based on the given passage.
Conversations about the role of flexible working have shifted. It’s no longer enough for companies to offer employees the option to either work from home or the office. Employees want to work from anywhere. Companies that want to attract and retain top talent, and ensure teams are highly productive, need to adapt their culture and technology to accommodate this shift in attitudes. And this is where the IT department can solidify its role as a valued contributor to the success of a company, by implementing technologies that enable secure and remote collaboration.
According to a recently commissioned Polycom survey, 24,000 respondents across 12 countries indicate that nearly two-thirds of today’s global workforce take advantage of the anywhere working model. This is a significant shift since May of 2012 when only 14% of mployees benefited from remote working.
The survey results also provide insights into some of the oncerns among companies in moving forward with the nywhere working model. Two significant concerns are a lack of trust and the perception that employees are not working as hard when they are not in the office. Also, among the 45-60-year-old age group, 59% worry that working anywhere will cause them to work longer hours. The fear of being always connected to work and overworking is a significant deterrent for this age group.
A good first step for companies to overcome the trust and perception concern is to ensure workers are measured by output and not by the hours they have worked, commonly referred to as ‘presenteeism.’
Countries like Brazil __________ here with 80% of employees adopting the anywhere working model, and 64% respondents use video to communicate several times a day. When respondents were asked how their companies could improve trust and perceptions with the anywhere working model, the most popular recommendations were to: Equip workers with technology that is easy to use and which connects them to their colleagues; Ensure the same policies are applied to everyone in the business, regardless of seniority or their situation; and Provide guidelines on how to manage working from anywhere.
91% of those surveyed agreed that technology is a key factor in improving relationships and fostering better teamwork. This suggests that investing in the right technologies, in particular video collaboration, to get the most out of individuals and teams can help solve the lack of trust and perception concerns. And this is where the IT department can become a difference maker as they can enact technologies, such as video conferencing, to ensure colleagues can seamlessly collaborate wherever they are.
Question:
Which of the following can be considered true in context of the information available in the given passage?
most of the employers feel that the employees do not provide optimum output when working away from their office locations
emphasis has been laid on the growing preference for remote working
provision of user friendly technological ways of communication helps employers build better relations with employees preferring anywhere working model
the It department of any country has a large role to play when it comes to efficient functioning of changing models of working preference
all are correct
Directions: Read the following passage and answer the following questions based on the given passage.
Conversations about the role of flexible working have shifted. It’s no longer enough for companies to offer employees the option to either work from home or the office. Employees want to work from anywhere. Companies that want to attract and retain top talent, and ensure teams are highly productive, need to adapt their culture and technology to accommodate this shift in attitudes. And this is where the IT department can solidify its role as a valued contributor to the success of a company, by implementing technologies that enable secure and remote collaboration.
According to a recently commissioned Polycom survey, 24,000 respondents across 12 countries indicate that nearly two-thirds of today’s global workforce take advantage of the anywhere working model. This is a significant shift since May of 2012 when only 14% of mployees benefited from remote working.
The survey results also provide insights into some of the oncerns among companies in moving forward with the nywhere working model. Two significant concerns are a lack of trust and the perception that employees are not working as hard when they are not in the office. Also, among the 45-60-year-old age group, 59% worry that working anywhere will cause them to work longer hours. The fear of being always connected to work and overworking is a significant deterrent for this age group.
A good first step for companies to overcome the trust and perception concern is to ensure workers are measured by output and not by the hours they have worked, commonly referred to as ‘presenteeism.’
Countries like Brazil __________ here with 80% of employees adopting the anywhere working model, and 64% respondents use video to communicate several times a day. When respondents were asked how their companies could improve trust and perceptions with the anywhere working model, the most popular recommendations were to: Equip workers with technology that is easy to use and which connects them to their colleagues; Ensure the same policies are applied to everyone in the business, regardless of seniority or their situation; and Provide guidelines on how to manage working from anywhere.
91% of those surveyed agreed that technology is a key factor in improving relationships and fostering better teamwork. This suggests that investing in the right technologies, in particular video collaboration, to get the most out of individuals and teams can help solve the lack of trust and perception concerns. And this is where the IT department can become a difference maker as they can enact technologies, such as video conferencing, to ensure colleagues can seamlessly collaborate wherever they are.
Question:
Which of the following statement can be inferred by author’s view of not giving too much importance to “presenteeism”?
Highly paid jobs can be highly pressurised too, demanding unhealthy amounts of overtime.
Business should be using output numbers to set an average instead of calculating the time spent working by each employee
When it comes to work, we should value the returns instead of time apportioned by employees towards their workplace.
Both (b) and (c)
none of these
Directions: Read the following passage and answer the following questions based on the given passage.
Conversations about the role of flexible working have shifted. It’s no longer enough for companies to offer employees the option to either work from home or the office. Employees want to work from anywhere. Companies that want to attract and retain top talent, and ensure teams are highly productive, need to adapt their culture and technology to accommodate this shift in attitudes. And this is where the IT department can solidify its role as a valued contributor to the success of a company, by implementing technologies that enable secure and remote collaboration.
According to a recently commissioned Polycom survey, 24,000 respondents across 12 countries indicate that nearly two-thirds of today’s global workforce take advantage of the anywhere working model. This is a significant shift since May of 2012 when only 14% of mployees benefited from remote working.
The survey results also provide insights into some of the oncerns among companies in moving forward with the nywhere working model. Two significant concerns are a lack of trust and the perception that employees are not working as hard when they are not in the office. Also, among the 45-60-year-old age group, 59% worry that working anywhere will cause them to work longer hours. The fear of being always connected to work and overworking is a significant deterrent for this age group.
A good first step for companies to overcome the trust and perception concern is to ensure workers are measured by output and not by the hours they have worked, commonly referred to as ‘presenteeism.’
Countries like Brazil __________ here with 80% of employees adopting the anywhere working model, and 64% respondents use video to communicate several times a day. When respondents were asked how their companies could improve trust and perceptions with the anywhere working model, the most popular recommendations were to: Equip workers with technology that is easy to use and which connects them to their colleagues; Ensure the same policies are applied to everyone in the business, regardless of seniority or their situation; and Provide guidelines on how to manage working from anywhere.
91% of those surveyed agreed that technology is a key factor in improving relationships and fostering better teamwork. This suggests that investing in the right technologies, in particular video collaboration, to get the most out of individuals and teams can help solve the lack of trust and perception concerns. And this is where the IT department can become a difference maker as they can enact technologies, such as video conferencing, to ensure colleagues can seamlessly collaborate wherever they are.
Question:
Which of the following phrases could fit in the given blank, to make the statement contextually and grammatically meaningful?
are all and sundry
have a cup of Joe
go back to the drawing board
lead the pack
all are correct
Directions: Read the following passage and answer the following questions based on the given passage.
Conversations about the role of flexible working have shifted. It’s no longer enough for companies to offer employees the option to either work from home or the office. Employees want to work from anywhere. Companies that want to attract and retain top talent, and ensure teams are highly productive, need to adapt their culture and technology to accommodate this shift in attitudes. And this is where the IT department can solidify its role as a valued contributor to the success of a company, by implementing technologies that enable secure and remote collaboration.
According to a recently commissioned Polycom survey, 24,000 respondents across 12 countries indicate that nearly two-thirds of today’s global workforce take advantage of the anywhere working model. This is a significant shift since May of 2012 when only 14% of mployees benefited from remote working.
The survey results also provide insights into some of the oncerns among companies in moving forward with the nywhere working model. Two significant concerns are a lack of trust and the perception that employees are not working as hard when they are not in the office. Also, among the 45-60-year-old age group, 59% worry that working anywhere will cause them to work longer hours. The fear of being always connected to work and overworking is a significant deterrent for this age group.
A good first step for companies to overcome the trust and perception concern is to ensure workers are measured by output and not by the hours they have worked, commonly referred to as ‘presenteeism.’
Countries like Brazil __________ here with 80% of employees adopting the anywhere working model, and 64% respondents use video to communicate several times a day. When respondents were asked how their companies could improve trust and perceptions with the anywhere working model, the most popular recommendations were to: Equip workers with technology that is easy to use and which connects them to their colleagues; Ensure the same policies are applied to everyone in the business, regardless of seniority or their situation; and Provide guidelines on how to manage working from anywhere.
91% of those surveyed agreed that technology is a key factor in improving relationships and fostering better teamwork. This suggests that investing in the right technologies, in particular video collaboration, to get the most out of individuals and teams can help solve the lack of trust and perception concerns. And this is where the IT department can become a difference maker as they can enact technologies, such as video conferencing, to ensure colleagues can seamlessly collaborate wherever they are.
Question:
Which of the following is opposite to COLLABORATION¸ as highlighted in the given passage?
unraveled
cognizant
confrontation
denunciation
none of these
In the given question, three statements have been given which are then divided in four parts. Following the statements are options which mention the part of statements which contains grammatical error. Mark the option mentioning the incorrect part of the statement(s).
[I] The most striking thing on the JMI wall is (A)/ the national flag, hundreds of which are (B)/ strung together in such a way that the (C)/ tricolour runs parallel with the road. (D)
[II] It is disturbing that assassination (A)/ is no longer universally (B)/condemned by all, as it was (C)/until the last decade or two. (D)
[III] While, Gurdwara Bangla Sahib (A)/ is known by all, there are (B)/ other Sikh shrines too that(C)/ tell interesting and inspiring stories. (D)
III-A
I-C; II-C
II-C; III-B
I-C; II-B; III-C
II-D; III-D
Directions : In the following questions two columns are given containing three sentences/phrases each. In first column, sentences/phrases are A, B and C and in the second column the sentences/phrases are D, E and F. A sentence/phrase from the first column may or may not connect with another sentence/phrase from the second column to make a grammatically and contextually correct sentence. Each question has five options, four of which display the sequence(s) in which the sentences/phrases can be joined to form a grammatically and contextually correct sentence. If none of the options given forms a correct sentence after combination, mark (e), i.e. “None of these” as your answer.
Question:
COLUMN I
(A) If organizations or states do not learn from one another, (B) Wide collaboration means including everyone (C) The more we talk about the importance of cybersecurity COLUMN II (D) generations of cybersecurity professionals we very much need (E) the same attacks will needlessly take down countless entities (F) repositories that are part of our operational systems
C-D & B-F
A-E
B-D
C-F & A-E
None of these
Directions : In the following questions two columns are given containing three sentences/phrases each. In first column, sentences/phrases are A, B and C and in the second column the sentences/phrases are D, E and F. A sentence/phrase from the first column may or may not connect with another sentence/phrase from the second column to make a grammatically and contextually correct sentence. Each question has five options, four of which display the sequence(s) in which the sentences/phrases can be joined to form a grammatically and contextually correct sentence. If none of the options given forms a correct sentence after combination, mark (e), i.e. “None of these” as your answer.
Question:
COLUMN I
(A) Only one museum currently has the funding to contend for (B) Speculators, thieves, and promoters long ago created (C) Ethical appeals notwithstanding, great
COLUMN II
(D) transfer will disseminate once static fortunes (E) art will increasingly devolve into big business (F) and fed a market where cultural icons could be traded like commodities
B-F & C-D
C-E & A-F
B-E & A-D
C-E & B-F
None of these
Directions : In the following questions two columns are given containing three sentences/phrases each. In first column, sentences/phrases are A, B and C and in the second column the sentences/phrases are D, E and F. A sentence/phrase from the first column may or may not connect with another sentence/phrase from the second column to make a grammatically and contextually correct sentence. Each question has five options, four of which display the sequence(s) in which the sentences/phrases can be joined to form a grammatically and contextually correct sentence. If none of the options given forms a correct sentence after combination, mark (e), i.e. “None of these” as your answer.
Question:
COLUMN I
(A) A lack of meaningful GDPR enforcement by (B) Neither companies nor CMPs seem keen on (C) The results of our empirical survey
COLUMN II
(D) shoring up that pathetic 12 percent compliance rate (E) regulators had already been fairly well established (F) stop data collection, or misled the end user
A-E & B-D
A-E & B-F
C-F & A-D
B-E & C-D
None of these
Direction : Given below are few sentences where parts of the sentence have been jumbled. Rearrange the parts sentences in the proper sequence to form a meaningful statement and then answer the questions given below.
[I] Confessions of a Shopaholic sold three (A) / million copies and was even (B) / turned into a Hollywood blockbuster (C)/ published in 2000, the novel (D)
[II] in production and disposal of unsold stock(A)/ and their just-in-time manufacturing at the expense (B)/ take fast fashion – the wear-it-once culture of highstreet brands (C)/of low labour costs leads to untold waste (D)
[III] about the impact of their choices (A)/ on the environment and on societies (B)/ even the most extravagant consumers (C)/ have become more discerning (D)
[IV] only two decades later, the obsession (A)/ core of the story, feels terribly outdated (B)/ luxury items, which was at the (C)/ with treating oneself by buying (D) [V] perhaps it is because (A)/ today’s youth has grown (B)/ up with an abundance (C)/ of (often cheap) products (D)
Question:
What will be the correct sequence of rearrangement of parts of the statement [I]?
ACBD
CADB
DABC
BACD
No rearrangement is possible
Direction : Given below are few sentences where parts of the sentence have been jumbled. Rearrange the parts sentences in the proper sequence to form a meaningful statement and then answer the questions given below.
[I] Confessions of a Shopaholic sold three (A) / million copies and was even (B) / turned into a Hollywood blockbuster (C)/ published in 2000, the novel (D)
[II] in production and disposal of unsold stock(A)/ and their just-in-time manufacturing at the expense (B)/ take fast fashion – the wear-it-once culture of highstreet brands (C)/of low labour costs leads to untold waste (D)
[III] about the impact of their choices (A)/ on the environment and on societies (B)/ even the most extravagant consumers (C)/ have become more discerning (D)
[IV] only two decades later, the obsession (A)/ core of the story, feels terribly outdated (B)/ luxury items, which was at the (C)/ with treating oneself by buying (D) [V] perhaps it is because (A)/ today’s youth has grown (B)/ up with an abundance (C)/ of (often cheap) products (D)
Question:
What will be the correct sequence of rearrangement of parts of the statement [II]?
BCDA
CBDA
ACBD
DCAB
No rearrangement is possible
Direction : Given below are few sentences where parts of the sentence have been jumbled. Rearrange the parts sentences in the proper sequence to form a meaningful statement and then answer the questions given below.
[I] Confessions of a Shopaholic sold three (A) / million copies and was even (B) / turned into a Hollywood blockbuster (C)/ published in 2000, the novel (D)
[II] in production and disposal of unsold stock(A)/ and their just-in-time manufacturing at the expense (B)/ take fast fashion – the wear-it-once culture of highstreet brands (C)/of low labour costs leads to untold waste (D)
[III] about the impact of their choices (A)/ on the environment and on societies (B)/ even the most extravagant consumers (C)/ have become more discerning (D)
[IV] only two decades later, the obsession (A)/ core of the story, feels terribly outdated (B)/ luxury items, which was at the (C)/ with treating oneself by buying (D) [V] perhaps it is because (A)/ today’s youth has grown (B)/ up with an abundance (C)/ of (often cheap) products (D)
Question:
When the statements given above are rearranged, which of the following statement will not be coherent with the theme of the passage?
III
V
II
I
All are coherent
Direction : Given below are few sentences where parts of the sentence have been jumbled. Rearrange the parts sentences in the proper sequence to form a meaningful statement and then answer the questions given below.
[I] Confessions of a Shopaholic sold three (A) / million copies and was even (B) / turned into a Hollywood blockbuster (C)/ published in 2000, the novel (D)
[II] in production and disposal of unsold stock(A)/ and their just-in-time manufacturing at the expense (B)/ take fast fashion – the wear-it-once culture of highstreet brands (C)/of low labour costs leads to untold waste (D)
[III] about the impact of their choices (A)/ on the environment and on societies (B)/ even the most extravagant consumers (C)/ have become more discerning (D)
[IV] only two decades later, the obsession (A)/ core of the story, feels terribly outdated (B)/ luxury items, which was at the (C)/ with treating oneself by buying (D) [V] perhaps it is because (A)/ today’s youth has grown (B)/ up with an abundance (C)/ of (often cheap) products (D)
Question:
What will be the correct sequence of rearrangement of parts of the statement [III]?
DABC
BDCA
CDAB
ABCD
No rearrangement is possible
Direction : Given below are few sentences where parts of the sentence have been jumbled. Rearrange the parts sentences in the proper sequence to form a meaningful statement and then answer the questions given below.
[I] Confessions of a Shopaholic sold three (A) / million copies and was even (B) / turned into a Hollywood blockbuster (C)/ published in 2000, the novel (D)
[II] in production and disposal of unsold stock(A)/ and their just-in-time manufacturing at the expense (B)/ take fast fashion – the wear-it-once culture of highstreet brands (C)/of low labour costs leads to untold waste (D)
[III] about the impact of their choices (A)/ on the environment and on societies (B)/ even the most extravagant consumers (C)/ have become more discerning (D)
[IV] only two decades later, the obsession (A)/ core of the story, feels terribly outdated (B)/ luxury items, which was at the (C)/ with treating oneself by buying (D) [V] perhaps it is because (A)/ today’s youth has grown (B)/ up with an abundance (C)/ of (often cheap) products (D)
Question:
What will be the correct sequence of rearrangement of parts of the statement [IV]?
ADCB
BACD
CDBA
DABC
No rearrangement is possible
Directions : In the sentences given below, four words have been highlighted and placed in a sentence. Identify the correct sequence of the words in the sentence. Also, one of the given words will need to be replaced. Identify the correct sequence and the correct replacement and mark that option as your answer.
Question:
Governments and (A) contagion institutions can set targets and (B) multilateral for other parties to change their (C) sustainably and use their resources both efficiently and (D) behaviour.
BDAC; C- sufficiently
DCBA; D- hyphenated
BACD; A- mandate
CADB; A- tenets
No interchange required
Directions : In the sentences given below, four words have been highlighted and placed in a sentence. Identify the correct sequence of the words in the sentence. Also, one of the given words will need to be replaced. Identify the correct sequence and the correct replacement and mark that option as your answer.
Question:
Specifically, (A) harshest in technology enable solar panels to work even in the (B) generate conditions, such as in (C) innovations hot climes, and can even (D) eternity power in damp weather.
DABC; A- harangued
BCDA; all words are correct
CBDA; B- genre
CADB; D- extremely
No interchange required
Directions : In the sentences given below, four words have been highlighted and placed in a sentence. Identify the correct sequence of the words in the sentence. Also, one of the given words will need to be replaced. Identify the correct sequence and the correct replacement and mark that option as your answer.
Question:
The “Clean Up Mekong”(A) realistic in Viet Nam is an example of how cross-sector (B) collaboration helps provide (C) solutions and actionable (D) champagne to climate change.
BADC; A- virtual
CDBA; B- condolence
DBAC; D- campaign
DCBA; B- corroboration
No interchange required
Directions : In the sentences given below, four words have been highlighted and placed in a sentence. Identify the correct sequence of the words in the sentence. Also, one of the given words will need to be replaced. Identify the correct sequence and the correct replacement and mark that option as your answer.
Question:
When (A) engaged lead, and when their entire workforces are (B) mindset, the public’s (C)livid, behaviour and (D) companies can also change.
CADB; B- miniscule
BADC; C- livelihood
DABC; C- lifestyles
CDAB; D- cognates
No interchange required
Directions : In the sentences given below, four words have been highlighted and placed in a sentence. Identify the correct sequence of the words in the sentence. Also, one of the given words will need to be replaced. Identify the correct sequence and the correct replacement and mark that option as your answer.
Question:
Partnerships between governments, the private sector, (A) civil institutions and (B) essential society will be (C) targets to ensure we meet the UN Sustainable Development Goals (D) multilateral.
BDCA; C- torment
DCAB; B- efficacy
CDAB; A- civilian
DABC; all words are correct
No interchange required
Directions : In the sentences given below, four words have been highlighted and placed in a sentence. Identify the correct sequence of the words in the sentence. Also, one of the given words will need to be replaced. Identify the correct sequence and the correct replacement and mark that option as your answer.
Question:
Companies can provide (A) technologies to make solutions more (B) accessible and affordable to all - especially MNCs (C) operating across multiple business sectors and (D) industries.
BDAC; C- occupational
DCBA; D- industrious
BACD; A- technocracy
CADB; A- compelling
No interchange required
Directions : Read the following passage and answer the following questions based on the given passage.
Mr. A. Rangaswami Iyangar B.A. B.L., Editor, “Swadesa Mitran” writes: — The unique sequence of events which have been crowded into the past fortnight in the history of India can hardly be ignored by any thinking Indian and it may be useful to take just a _____(I)_____ with a view to indicate the immediate work that looms before Indian Nationalists. That the Indian National Congress Session of the year forms one of the greatest landmarks in the political history of the country can admit of no doubt. Although the moderates have re-christened their insignificant gathering by the ____(II)___ name of the National Liberal Federation, it is evident that under the guidance of the new-born, though lukewarm, political enthusiasm of Sir. P.S. Sivaswami Iyer and the out of date political oratory of Babu Surendra Nath Banerjea, it is hardly likely to carry the country along the path of national progress with anything like the fire of the genuine national movement that animates the whole country.
Question:
Which of the phrases could fit in the blank (I), to make the statement grammatically correct and contextually meaningful?
roughly form the entities of modern-day
merely on territorial extent of its sovereignty
cursory survey of them
religious intermingling to new level of exploration
none of these
Directions : Read the following passage and answer the following questions based on the given passage.
Mr. A. Rangaswami Iyangar B.A. B.L., Editor, “Swadesa Mitran” writes: — The unique sequence of events which have been crowded into the past fortnight in the history of India can hardly be ignored by any thinking Indian and it may be useful to take just a _____(I)_____ with a view to indicate the immediate work that looms before Indian Nationalists. That the Indian National Congress Session of the year forms one of the greatest landmarks in the political history of the country can admit of no doubt. Although the moderates have re-christened their insignificant gathering by the ____(II)___ name of the National Liberal Federation, it is evident that under the guidance of the new-born, though lukewarm, political enthusiasm of Sir. P.S. Sivaswami Iyer and the out of date political oratory of Babu Surendra Nath Banerjea, it is hardly likely to carry the country along the path of national progress with anything like the fire of the genuine national movement that animates the whole country.
Question:
Which of the following words could fit in the blank (II) to make the statement grammatically correct and contextually meaningful? Also,the same word mustfit in the statements given below.
(A) I don't think anyone could read this behaviour in any other way than being _______ and patronising.
(B) In their statements, they have become expert in using ________ phrases and key buzzwords to cover up ugly banalities.
subsume
ligature
mooted
pompous
none of these
irections : Read the following passage and answer the following questions based on the given passage.
The United States plans to put a space workshop into orbit in 1972, the Space Agency announced here [Houston] yesterday. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) said the third stage of the giant Saturn 5 rocket used to send Apollo spaceships to the moon would be used to house the orbiting laboratory and observatory. The project will study man’s physiological and psychological responses in the space environment and provide more detailed information on his capabilities for extended manned flight. The workshop is to be fitted out on the ground and will be launched into a 220 nautical mile circular earth orbit. It will be occupied by a crew of three astronauts who will follow in a smaller rocket about a day later. At first, the astronaut-scientists will spend about 26 days in the orbiting workshop, but later visits lasting up to 56 days are planned. The laboratory will be built into a modified S-IVB third stage of the Saturn 5 rocket. The SIVB is used as the Saturn 1B’s second stage.
Question:
Which of the following statements is not true in context of the information given in the passage?
The astronaut scientists will be spending fortnight in the workshop in the orbit.
Saturn 5 rocket had been used prior to its current requirement for housing laboratory and observatory
The plan proposed by NASA will conduct an in depth study of physiological and psychological reaction of humans within space environment.
both (a) and (b)
all are correct
irections : Read the following passage and answer the following questions based on the given passage.
The United States plans to put a space workshop into orbit in 1972, the Space Agency announced here [Houston] yesterday. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) said the third stage of the giant Saturn 5 rocket used to send Apollo spaceships to the moon would be used to house the orbiting laboratory and observatory. The project will study man’s physiological and psychological responses in the space environment and provide more detailed information on his capabilities for extended manned flight. The workshop is to be fitted out on the ground and will be launched into a 220 nautical mile circular earth orbit. It will be occupied by a crew of three astronauts who will follow in a smaller rocket about a day later. At first, the astronaut-scientists will spend about 26 days in the orbiting workshop, but later visits lasting up to 56 days are planned. The laboratory will be built into a modified S-IVB third stage of the Saturn 5 rocket. The SIVB is used as the Saturn 1B’s second stage.
Question:
Which of the following is similar to MODIFIED, as highlighted in the passage given above?
immutable
incertitude
voracious
overhaul
none of these
Directions : In the following questions, a sentence is given which is divided into few parts. The sentence may or may not be grammatically or contextually correct. To make the sentence correct, interchange the positions of the phrase and mark the correct interchange as your answer. If no interchange is required, mark (e) i.e., “no interchange required” as your correct answer.
Question:
The small savings scheme, (A)/ investment avenues in India (B)/ is arguably one of the most popular(C)/ which offers guaranteed returns along with tax benefit(D)
A-C
B-D
A-D
A-D, B-C
No interchange required
Directions : In the following questions, a sentence is given which is divided into few parts. The sentence may or may not be grammatically or contextually correct. To make the sentence correct, interchange the positions of the phrase and mark the correct interchange as your answer. If no interchange is required, mark (e) i.e., “no interchange required” as your correct answer.
Question:
Such as stress in balance sheets, (A)/ deteriorating financial conditions of the group (B)/ the agencies did not alter ratings despite (C)/ lack of cash flows, inability to monetise assets (D)
A-C
B-D
A-D
A-D, B-C
No interchange required
Directions : In the following questions, a sentence is given which is divided into few parts. The sentence may or may not be grammatically or contextually correct. To make the sentence correct, interchange the positions of the phrase and mark the correct interchange as your answer. If no interchange is required, mark (e) i.e., “no interchange required” as your correct answer.
Question:
have benefited from rate reductions (A)/ restaurants and under-construction properties (B)/ from the preGST era, only a few services such as (C)/though taxes on goods have come down(D)
A-C
B-D
A-D
A-D, B-C
No interchange required
Directions : In the following questions, a sentence is given which is divided into few parts. The sentence may or may not be grammatically or contextually correct. To make the sentence correct, interchange the positions of the phrase and mark the correct interchange as your answer. If no interchange is required, mark (e) i.e., “no interchange required” as your correct answer.
Question:
The railway is incurring losses (A)/ in the passenger segment as the fare is subsidized, (B)/ while its ends up cross-subsidizing (C)/ passengers by overcharging freight.(D)
A-C
B-D
A-D
A-D, B-C
No interchange required
Directions : In the following questions, a sentence is given which is divided into few parts. The sentence may or may not be grammatically or contextually correct. To make the sentence correct, interchange the positions of the phrase and mark the correct interchange as your answer. If no interchange is required, mark (e) i.e., “no interchange required” as your correct answer.
Question:
five-day schedule and breaks (A)/ for lunch and tea, might seem an anachronism (B)/ in this universe of instant (C)/ gratification, Test cricket with its (D)
(B)-(D)
(A)- (B)
(A)-(C); (B)-(D)
(A)-(D); (B)-(C)
None of these